Abstract.
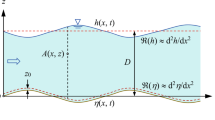
We investigate the process of ripple formation in a viscous fluid when a sand bed is submitted to a laminar shear flow. We propose a new description for the sand transport which takes into account the fact that the transport rate does not adapt instantaneously to a change of the fluid velocity due to grain inertia. It introduces a new length, called here after equilibrium length leq, corresponding to the distance needed for a immobile grain to equilibrate its velocity with that of the fluid. The transport rate is therefore found to depend not only on the fluid shear stress and bed slope (as usually assumed) but also on grain inertia. Within the framework of this model we analyzed the mechanisms of the sand bed instability. It is found that the instability results from the competition between the destabilizing effect of fluid inertia and the stabilizing ones of grain inertia and bed slope. We derive analytical scaling laws for the most amplified wavelength, its growth rate and phase velocity. We found in particular that at small particle Reynolds number Rep, the most amplified wavelength scales as the viscous length lν defined as \(\sqrt{\nu/\gamma}\) (where γ is the shear rate and ν the fluid viscosity) and at large Rep it scales as the equilibrium length leq. Our results are compared with available experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Fredsoe, R. Deigaard, Mechanics of Coastal Sediment Transport (World Scientific, 1992)
J.F. Kennedy, J. Fluid Mech. 16, 521 (1963)
J.F. Kennedy, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1, 147 (1969)
M.H. Gradowczyk, J. Fluid Mech. 33, 93 (1968)
S.E. Coleman, J.D. Fenton, J. Fluid Mech. 418, 101 (2000)
K.J. Richards, J. Fluid Mech. 99, 597 (1980)
B.M. Sumer, M. Bakioglu, J. Fluid Mech. 144, 117 (1984)
J. Nikuradse, V.D.I.-Forschungheft, no. 361 (1933)
J.D. Smith, S.R. McLean, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 1735 (1977)
S.E. Coleman, B.W. Melville, J. Hydr. Engng. ASCE 122, 301 (1996)
M.S. Yalin, J. Hydr. Engng. ASCE 111, 1148 (1985)
F. Charru, H. Mouilleron-Arnould, J. Fluid Mech. 452, 303 (2002)
T. Loiseleux, D. Doppler, P. Gondret, J.-M. Rabaud, in Second Intertational Workshop on Marine Sandwave and River Dynamics, edited by J.M.H. Hulscher, T. Garlan, D. Idier (University of Twente, Enschede 2004), pp. 200
G. Sauermann, K. Kroy, H.J. Herrmann, Phys. Rev. E 64, 031305 (2001)
B. Andreotti, P. Claudin, S. Douady, Eur. Phys. J. B 28, 341 (2002)
P. Hersen, Eur. Phys. J. B. 37, 507 (2004)
J.-P. Bouchaud, M.E. Cates, R. Prakash, S.F. Edwards, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1982 (1995)
A. Valance, unpublished (2004)
F. White, Viscous Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill (New-York, 1974)
P. Mantz, Sedimentology 25, 83 (1977)
R.A. Bagnold, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 249, 235 (1956)
F. Charru, E.J. Hinch, J. Fluid Mech. 414, 195 (2000)
A. Betat, V. Frette, I. Rehberg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 88 (1999)
A. Betat, C.A. Kruelle, V. Frette, I. Rehberg, Eur. Phys. J. E 8, 465 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valance, A., Langlois, V. Ripple formation over a sand bed submitted to a laminar shear flow . Eur. Phys. J. B 43, 283–294 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00050-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00050-6