Abstract
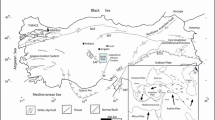
More than fifty heat flow measurements in Italy are examined. The values, corrected only for local influences (when present), are related to the main geological features with the following results: foreland areas, 55±19 mW m−2, foredeep areas, 45±21 mW m−2; folded regions and intermountain depressions, 76±29 mW m−2. In volcanic areas the heat flow rises to in excess of 600 mW m−2. From a tectonic point of view, these values are consistent with the hypothesis that the Apennine chain is intersected by two arcuate structures: the first from Liguria to Latium is very probably a continental arc, that is an are which occurs within a continent, and the second from Campania to Calabria is very similar from geophysical evidence to the classic island arcs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barberi, F., Civetta, L., Gasparini, P., Innocenti, F., Scandone, R. andVillari, L. (1974),Evolution of a section of the Africa-Europe plate boundary: paleomagnetic and volcanological evidence from Sicily, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,22, 123–132.
Beck, A. E., Jaeger, J. C. andNewstead, G. N. (1956),The measurement of the thermal conductivities of rocks by observations in boreholes, Austr. J. Phys.9, 286–296.
Birch, F. S. andHalunen, A. J. (1966),Heat flow measurements in the Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and Red Sea, J. Geophys. Res.71, 583–586.
Boccaletti, M. andGuazzone, G. (1972).Gli archi appenninici, il Mar Ligure ed il Tirreno nel quadro della tettonica dei Bacini marginali retro-arco, Mem. Soc. Geol. It.11, 201–216.
Boccaletti, M., Fazzouli, M., Loddo, M. andMongelli, F. (1977),Heat flow measurements on the Northern Apennines arc. Tectonophysics41, 101–112.
Boldizsar, T. (1963),Terrestrial heat flow in the natural steam field at Larderello, Geof. Pura Appl.56, 115–122.
Calamai, A., Cataldi, R., Locardi, E. andPraturlon, A. (1977),Distribuzione delle anomalie geotermiche nella fascia preappenninica Tosco-Laziale (Italia), ENEL, Roma, Relazione di studio e ricerca n.321, 1–50.
Cassinis, R., Finetti, I., Giese P., Morelli, C., Steinmetz, L. andVechia, O. (1969),Deep seismic refraction research on Sicily, Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.10, 140–160.
Colombi, B., Giese, P., Luongo, G., Morelli, C., Riuscetti, M., Scarascia, S., Schütte, K. G., Strowald, J. andde Visintini, G. (1973),Preliminary report on the seismic refraction profile Gargano-Salerno-Palermo-Pantelleria (1971) Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.,15, 225–252.
Erickson, J. A. (1970), ‘The measurement and interpretation of heat flow in the Mediterranean and Black Sea’, Ph. D. Thesis Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 272 pp.
Fanelli, M., Loddo, M., Mongelli, F. andSquarci, P. (1974),Terrestrial heat flow measurements near Rosignano Solvay (Tuscany), Italy, Geothermics,3, 65–73.
Finckh, P. (1976),Waermeflussmessungen in Randalpenseen, Diss. ETH Zurich, Nr. 5787.
Giorgetti, F. andIaccarino, E. (1971),Seismicity of the Italian region, Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.13, 143–154.
Haenel, R. (1974),Heat flow measurements in Northern Italy and Heat flow maps of Europe, Z. Geophys.40, 367–380.
Lavenia, A. (1967),Heat flow measurements through bottom sediments in the Southern Adriatic Sea Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.9, 323–332.
Loddo, M. (1970),Temperature in an insulated slab heated by a plane source. Application to thermal conductivity measurements of rocks, Geothermics-Special Issue2, 437–442.
Loddo, M. andMongelli, F. (1975a),Heat flow in Southern Italy and surrounding seas, Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.16, 115–122.
Loddo, M. andMongelli, F. (1975b),Gravity of sinking lithosphere in Mediterranean. Paper read at the 4th Congress of A.G.I., Rome.
Loddo, M., Mongelli, F. andRoda, C. (1973),Heat flow in Calabria, Italy, Nature Phys. Sci.244, 91–92.
Lort, J. M. (1971),The tecto tics of the Eastern Mediterranean: a geophysical review, Rev. Geophys.9, 189–216.
McKenzie, D. P. (1972),Active tectonics of the Mediterranean region, Geophys. J.R. Astron. soc.,30, 109–185.
Mongelli, F. (1968),Un metodo per la determinazione in laboratorio della conducibilità termica delle rocce, Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.10, 51–58.
Mongelli, F. (1969),Thermal conductivity measurements of some Apulian limestones by the ‘cut core’ method, Atti XVIII Convegnos annuale ‘Associazione Geof. Italiana’, Napoli, Italy, pp. 137–154.
Mongelli, F. andLoddo, M. (1974),The present state of geothermal investigations in Italy, Acta Geodaet. Geophys. et Montanist.9, 449–456.
Mongelli, F. andLoddo, M.,Regional heat flow and geothermal fields in Italy, inProceedings Second United Nations Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources, (San Francisco, 1975), vol. 1, pp. 495–498.
Mongelli, F. andMorelli, C. (1964),Studio geotermico preliminare dell' Etna, Rivista Meneraria Siciliana n. 85–87.
Mongelli, F. andRicchetti, G. (1970a),Heat flow along the Candelaro Fault-Gargano Headland (Italy), Geothermics-Special Issue2, 400–458.
Mongelli, F. andRicchetti, G. (1970b),The earth's crust and heat flow in the Fossa Bradanica, Southern Italy, Tectonophysics,10, 103–125.
Mongelli, F., Loddo, M. andCalcagnile, G. (1975),Some observations on the Apennines gravity field, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,24, 385–393.
Morelli, C., Giese, P., Cassinis, R., Colombi, B., Guerra, I., Luongo, G., Scarascia, S. andSchütte, K. G. (1975),Crustal structure of Southern Italy. A Seismic refraction prolife between Puglia-Calabria-Sicily, Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl.18, 183–210.
Peterschmitt, E. (1956),Quelques données nouvelles sur les seismes profonds de la mer Thyrrhenienne, Annali di Geofisica9, 305–334.
Ritsema, A. R. (1969),Seismic data of the Western Mediterranean and the problem of oceanization, Verhandl. K. Nederl. Geol. Mijnbouwk. Genootsch.26, 105–120.
Sugimura, A. andUyeda, S.,Island Arcs Japan and Its Environs, (Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co., Amsterdam, 1973), 247 pp.
Von Herzen, R. andMaxwell, A. E. (1959),The measurement of thermal conductivity of deep sea sediments by a needle-probe method, J. Geophys. Res.64, 1557–1563.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loddo, M., Mongelli, F. Heat flow in Italy. PAGEOPH 117, 135–149 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879741
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879741