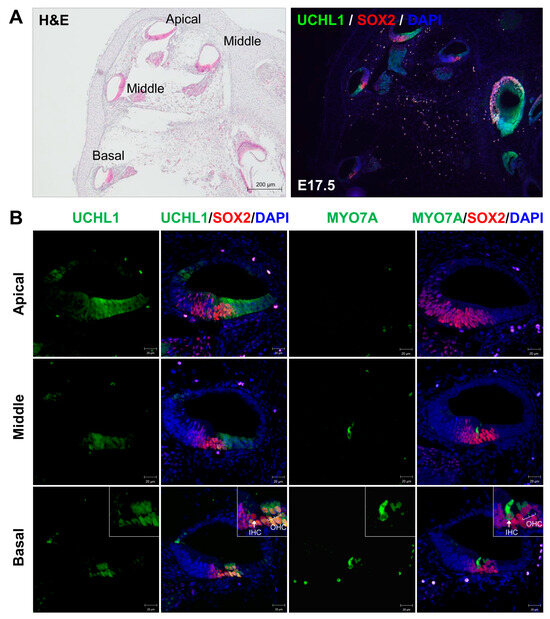
Goose erysipelas is a serious problem in waterfowl breeding in Poland. However, knowledge of the characteristics of
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains causing this disease is limited. In this study, the antimicrobial susceptibility and serotypes of four
E. rhusiopathiae strains from domestic geese were determined,
[...] Read more.
Goose erysipelas is a serious problem in waterfowl breeding in Poland. However, knowledge of the characteristics of
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains causing this disease is limited. In this study, the antimicrobial susceptibility and serotypes of four
E. rhusiopathiae strains from domestic geese were determined, and their whole-genome sequences (WGSs) were analyzed to detect resistance genes, integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs), and prophage DNA. Sequence type and the presence of resistance genes and transposons were compared with 363 publicly available
E. rhusiopathiae strains, as well as 13 strains of other
Erysipelothrix species. Four strains tested represented serotypes 2 and 5 and the MLST groups ST 4, 32, 242, and 243. Their assembled circular genomes ranged from 1.8 to 1.9 kb with a GC content of 36–37%; a small plasmid was detected in strain 1023. Strains 1023 and 267 were multidrug-resistant. The resistance genes detected in the genome of strain 1023 were
erm47,
tetM, and
lsaE-lnuB-ant(6)-Ia-s
pw cluster, while strain 267 contained the
tetM and
ermB genes. Mutations in the
gyrA gene were detected in both strains. The
tetM gene was embedded in a Tn
916-like transposon, which in strain 1023, together with the other resistance genes, was located on a large integrative and conjugative-like element of 130 kb designated as ICEEr1023. A minor integrative element of 74 kb was identified in strain 1012 (ICEEr1012). This work contributes to knowledge about the characteristics of
E. rhusiopathiae bacteria and, for the first time, reveals the occurrence of
erm47 and
ermB resistance genes in strains of this species. Phage infection appears to be responsible for the introduction of the
ermB gene into the genome of strain 267, while ICEs most likely play a key role in the spread of the other resistance genes identified in
E. rhusiopathiae.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT