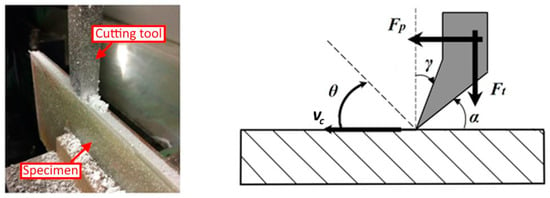
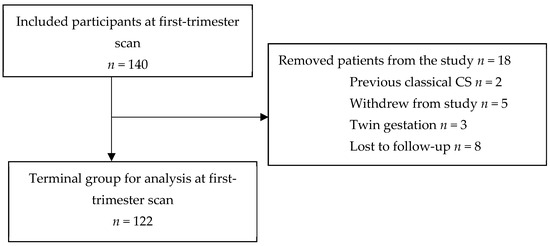
Background: The management of
erectile dysfunction (ED) shows several grey zones and new treatments are required to reduce the percentage of patients discontinuing treatment. Here, we aim to evaluate the role of a natural mixture named Icarifil
® (L-Citrulline, L-Carnitine,
Eruca vesicaria
[...] Read more.
Background: The management of
erectile dysfunction (ED) shows several grey zones and new treatments are required to reduce the percentage of patients discontinuing treatment. Here, we aim to evaluate the role of a natural mixture named Icarifil
® (L-Citrulline, L-Carnitine,
Eruca vesicaria,
Panax ginseng,
Tribulus terrestris,
Turnera diffusa, Taurine, Vitamin E, Zinc) in the management of patients with ED.
Methods: From September 2022 to March 2023, all patients attending 3 urological institutions due to ED were randomized to receive the following for 3 months: Icarifil
® 1 sachet every 24 h (Group 1) or Icarifil
® 1 sachet + tadalafil 5 mg 1 tablet every 24 h (Group 2) or tadalafil 5 mg 1 tablet daily (Group 3). All patients underwent urologic visits and dedicated questionnaires (IIEF-5, SEP-2, SEP-3) at enrollment and at the follow-up evaluation (3 months). Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs) at the follow-up evaluation were used. The primary endpoint was the difference in the questionnaires at the follow-up visit compared to the one at enrollment among the study groups.
Results: In the per-protocol analysis, 52 patients in Group 1, 55 in Group 2 and 57 in Group 3 were analyzed. At the follow-up evaluation, IIEF-5 scores improved in all the 3 groups between enrollment and the follow-up evaluation, but a statistically significant difference was reported between Group 2 (+7.4) and Group 1 (+4.1) or Group 3 (+5.1), (
p < 0.001;
p < 0.001). Moreover, 47 patients (94.0%) in Group 2 showed an improvement in the SEP questionnaires, when compared with the baseline, while 29 in Group 1 (56.9%) and 42 in Group 3 (82.3%) showed a statistically significant difference (
p = 0.004;
p = 0.003) among the groups. The PRO analysis reported better efficacy and patient satisfaction in Group 2 when compared with Group 1 or Group 3.
Conclusions: In conclusion, Icarifil
® is able to improve penile erectile function in mild–moderate ED and significantly improve the clinical efficacy of daily used tadalafil 5 mg. Icarifil
® could represent an interesting alternative treatment in patients experiencing adverse effects or with contraindications for chronic treatment with PDE5-is.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT