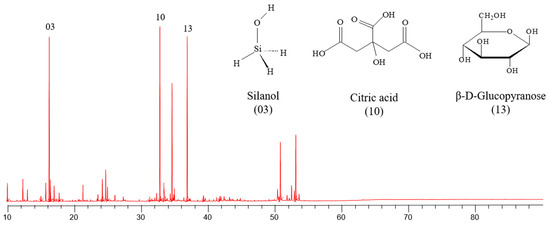
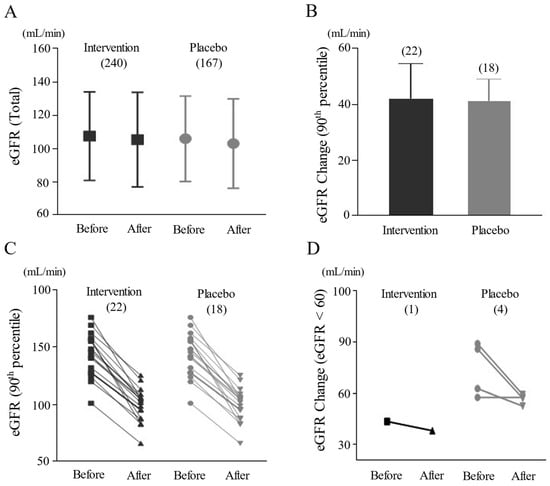
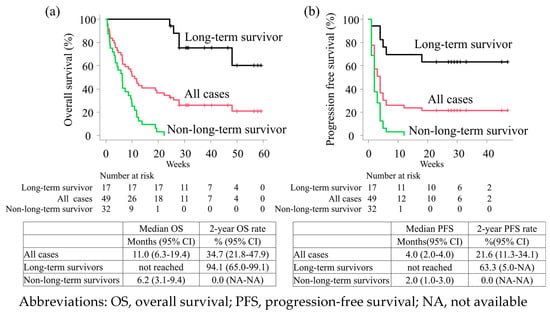
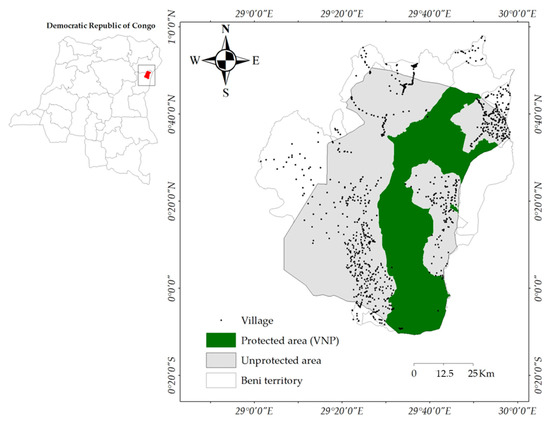
The development of novel natural product-derived nano-pesticide systems with loading capacity and sustained releasing performance of bioactive compounds is considered an effective and promising plant protection strategy. In this work, 25
L-carvone-based thiazolinone–hydrazone compounds
4a~
4y were synthesized by the multi-step
[...] Read more.
The development of novel natural product-derived nano-pesticide systems with loading capacity and sustained releasing performance of bioactive compounds is considered an effective and promising plant protection strategy. In this work, 25
L-carvone-based thiazolinone–hydrazone compounds
4a~
4y were synthesized by the multi-step modification of
L-carvone and structurally confirmed. Compound
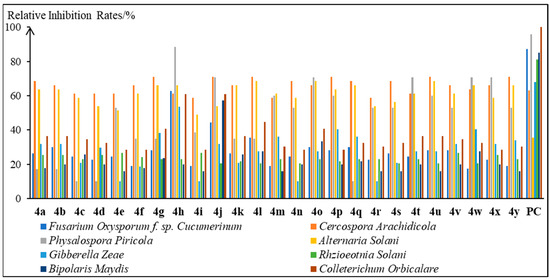
4h was found to show favorable and broad-spectrum antifungal activity through the in vitro antifungal activity evaluation of compounds
4a~
4y against eight phytopathogenic fungi. Thus, it could serve as a leading compound for new antifungal agents in agriculture. Moreover, the
L-carvone-based nanochitosan carrier
7 bearing the 1,3,4-thiadiazole-amide group was rationally designed for the loading and sustained releasing applications of compound
4h, synthesized, and characterized. It was proven that carrier
7 had good thermal stability below 200 °C, dispersed well in the aqueous phase to form numerous nanoparticles with a size of~20 nm, and exhibited an unconsolidated and multi-aperture micro-structure. Finally,
L-carvone-based thiazolinone–hydrazone/nanochitosan complexes were fabricated and investigated for their sustained releasing behaviors. Among them, complex
7/4h-2 with a well-distributed, compact, and columnar micro-structure displayed the highest encapsulation efficiency and desirable sustained releasing property for compound
4h and thus showed great potential as an antifungal nano-pesticide for further studies.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT