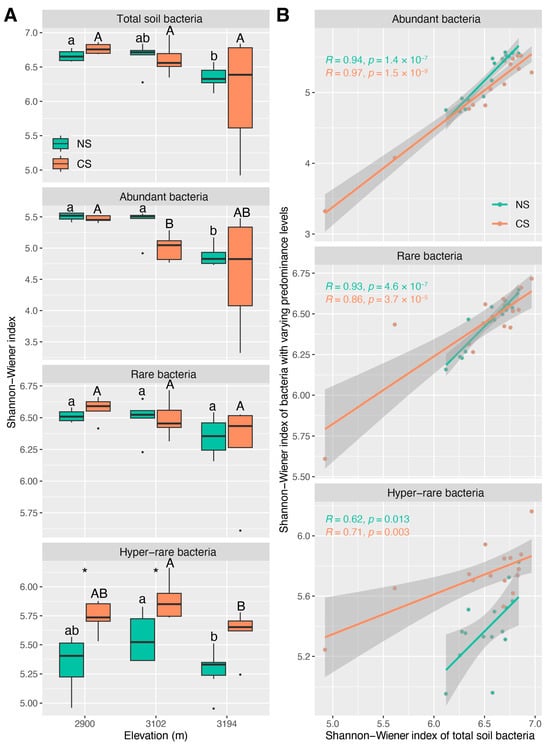
Abundant and rare bacteria exhibit unequal responses to environmental changes and disturbances, potentially resulting in differential contributions to the altitudinal characteristics of total community in natural and disturbed soils. Although the altitude patterns of soil bacteria have been widely studied, it remains unclear
[...] Read more.
Abundant and rare bacteria exhibit unequal responses to environmental changes and disturbances, potentially resulting in differential contributions to the altitudinal characteristics of total community in natural and disturbed soils. Although the altitude patterns of soil bacteria have been widely studied, it remains unclear whether these patterns are consistent among bacteria with varying predominance levels, and which subpopulation contributes more to maintaining these patterns in natural and disturbed subalpine forest soils. In this study, we collected 18 natural subalpine forest soil samples and 18 disturbed ones from three altitudes (2900 m a.s.l., 3102 m a.s.l., and 3194 m a.s.l.) along the Wenma highway in Miyaluo, Lixian, Sichuan, Southwest China. By partitioning total bacterial communities based on species predominance, we found that bacteria with higher predominance levels tended to exhibit altitude patterns (α-diversity, community structure, and functional redundancy) similar to those of total bacteria in both natural and disturbed subalpine forest soils, although they only occupied a small portion of the community. Abundant bacteria might play critical roles in maintaining the regional ecological characteristics of total community across the altitude gradient, while the rare and hyper-rare ones might contribute more to local diversity and functional redundancy. In natural soils, the altitude patterns of α-diversity inferred from total, abundant, and rare bacteria were mainly shaped by
-N, while soil conductivity mainly drove the altitude patterns of α-diversity inferred from hyper-rare bacteria. Additionally, the community structures of total, abundant, rare, and hyper-rare bacteria were mainly shaped by
-N, while the altitude patterns of functional redundancy inferred from total, abundant, and rare bacteria were mainly shaped by soil conductivity in natural soils. In disturbed subalpine forest soils, the influences of
-N for the altitude patterns of α-diversity and community structure, and those of soil conductivity for functional redundancy, were relatively weak in total, abundant, rare, and hyper-rare bacteria. This study examined the roles of bacteria with varying predominance levels in maintaining the altitude pattern of bacteria in both natural and disturbed subalpine forest soils, providing novel insights for devising strategies to conserve biodiversity and ecologically restore disturbed soils in subalpine ecosystems.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT