Summary
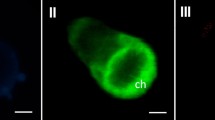
The pyrenoids of a number of siphonous green and yellow-green algae have been examined for the presence of chloroplast DNA (chloroplast nucleoids). We have found a conspicuous localization of chloroplast DNA in the pyrenoid core ofCaulerpa lentillifera andC. fergusonii (siphonous green algae), andPseudodichotomosiphon constrictus (a siphonous yellow-green alga) using fluorescence microscopy after staining with the DNA specific fluorochrome 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvert HE, Dawes CJ, Borowitzka MA (1976) Phylogenetic relationships ofCaulerpa (Chlorophyta) based on comparative chloroplast ultrastructure. J Phycol 12: 149–162
Coleman AW (1985) Diversity of plastid DNA configuration among classes of eukaryote algae. J Phycol 21: 1–16
Ehara T, Ogasawara Y, Osafune T, Hase E (1990) Behaviour of chloroplast nucleoids during the cell cycle ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyta) in synchronized culture. J Phycol 26: 317–323
Esser K (1967) Elektronenmikroskopischer Nachweis von DNS in den Pyrenoiden vonStroptotheca thamesis. Z Naturforsch 22 b: 993
Goodenough UW (1970) Chloroplast division and pyrenoid formation inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Phycol 6: 1–6
Hansmann P, Falk H, Scheer U, Sitte P (1986) Ultrastructural localization of DNA in twoCryptomonas species by use of a monoclonal DNA antibody. Eur J Cell Biol 42: 152–160
Holdsworth RH (1971) The isolation and partial characterization of the pyrenoid protein ofEremosphaera viridis. J Cell Biol 51: 499–513
Hori T (1974) Electron microscope observations on the fine structure of the chloroplasts of algae. II. The chloroplasts of Caulerpa (Chlorophyceae). Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 59: 239–245
—, Ueda R (1967) Electron microscope studies on the fine structure of plastids in siphonous green algae with special reference to their phylogenetic relationships. Sci Rep Tokyo Kyoiku Daigaku Sect B 12: 225–244
—, Kobara T, Chihara M (1979) Electron microscope observation onPseudodichotomosiphon constrictus with special reference to the systematic position of the genus. Jap J Phycol 27: 183–191
—, Inouye I (1981) The ultrastructure of mitosis inCricosphaera roscoffensis var.haptonemofera (Prymnesiophyceae). Protoplasma 106: 121–135
Kirk JTO, Tilney-Bassett RAE (1978) The plastids: their chemistry, structure, growth, and inheritance. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam
Kobara T, Chihara M (1990) On the taxonomic position of a siphonous algaPseudodichotomosiphon constrictus. J Jap Bot 65: 13–20
Kuchitsu K, Tsuzuki M, Miyachi S (1988) Characterization of the pyrenoid isolated from unicellular green algaChlamydomonas reinhardtii: particulate form of RuBisCo protein. Protoplasma 144: 17–24
Kuroiwa T, Suzuki T (1980) An improved method for the demonstration of the in situ chloroplast nuclei in higher plants. Cell Struct Funct 5: 195–197
— —, Ogawa K, Kawano S (1981) Chloroplast nucleus — general occurrence, number, size, shape and a model for amplification of chloroplast genome during chloroplast development. Plant Cell Physiol 22: 381–396
Lacoste-Royal G, Gibbs SP (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in the pyrenoid and thylakoid region of the chloroplast ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 83: 602–606
Miyamura S, Hori T (1989) Presence of DNA in the pyrenoid matrix of the siphonous green alga,Caulerpa okamurae Web. v. Bos. Plant Morphol 1: 19–22
Nakamura S, Itoh S, Kuroiwa T (1986) Behaviour of chloroplast nucleus during chloroplast development and degeneration inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol 27: 775–784
Satoh H, Okada M, Nakayama K, Miyaji K (1984) Purification and further characterization of pyrenoid proteins and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase from the green algaBryopsis maxima. Plant Cell Physiol 25: 1205–1214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamura, S., Hori, T. DNA is present in the pyrenoid core of the siphonous green algae of the genusCaulerpa and yellow-green algae of the genusPseudodichotomosiphon . Protoplasma 161, 192–196 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01322731
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01322731