Abstract
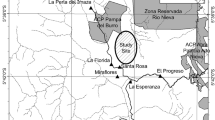
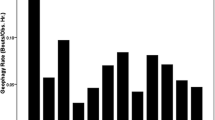
Geophagy was observed 14 times during an 11-month field study on the ecology and behavior of masked titi monkeys (Callicebus personatus melanochir). Geophagy took place in 12 cases on the surface of a leaf-cutting ant mound (Atta spec.). Analysis of chemical composition and natural features of the soils consumed by the monkeys showed elevated concentrations of several elements. In contrast, a lower concentration of carbohydrates was found in the ant mound sample compared to random non-ant mound soil samples. No difference in the concentration of clay elements, pH-value or percentage of organic matter was found between ant mound samples and randomly collected soil samples. Comparison of used versus not used samples failed to reveal significant clues about function of geophagy. However, chemical and physical properties of soils ingested support previous hypothesis that this behavior may aid in the adsorbtion of plant toxins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, J. 1974. Observational study of behavior: sampling methods.Behaviour, 49: 227–267.
Bate-Smith, E. C. 1972. Attractants and repellents in higher animals. In:Phytochemical Ecology,Harborne,J. B. (ed.), Academic Press, London, pp. 45–56.
Bicca-Marques, J. C.;Calegaro-Marques, C. 1994. A case of geophagy in the black howling monkeysAlouatta caraya.Neotrop. Prim., 2 (1): 7–8.
Chivers, D. J. 1974.The Siamang in Malaya. Contributions to Primatology, Vol. 4. S. Karger, Basel.
Clutton-Brock, T. H. 1972. Feeding and ranging behaviour of the red colobus monkey. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Univ. of Cambridge, Cambridge.
Davies, A. G.;Baillie, I. C. 1988. Soil-eating by red leaf monkeys (Presbytis rubicunda) in Sabah, Northern Borneo.Biotropica, 20 (3): 252–258.
Easley, S. P. 1982. The ecology and behaviour ofCallicebus torquatus, Cebidae, Primates. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Washington University, St. Louis.
Ganzhorn, J. U. 1987. Soil consumption of two groups of semi-free-ranging lemurs (Lemur catta andLemur fulvus).Ethology, 74: 146–154.
Gee, G. W.;Bauder, J. W. 1986. Particle-size analysis. In:Methods of Soil Analysis. Part I: Physical and Mineralogical Methods (2nd ed., No. 9 in the Series Agronomy),Klute, A. (ed.), Amer. Soc. Agronomy, Soil Science Society of Amer. Madison, Wisconsin.
Goodall, J. 1963. Feeding behavior of wild chimpanzees.Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond., 10: 39–47.
Hall, K. R. L. 1962. Numerical data, maintenance activities and locomotion in the wild chacma baboon,Papio ursinus.Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond., 139: 181–220.
Hamilton, R. A.;Galdikas, B. M. F. 1994. A preliminary study of food selection by the orangutan in relation to plant quality.Primates, 35: 255–263.
Hartmann, G.;Wedepohl, K. H. 1993. The composition of peridotite tectonites from the Ivrea Complex, northern Italy: residues from melt extraction.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 57: 1761–1782.
Heymann, E. W.;Hartmann, G. 1991. Geophagy in moustached tamarins,Saguinus mystax (Platyrrhini: Callitrichidae), at the Río Blanco, Peruvian Amazonia.Primates, 32: 533–537.
Hladik, C. M. 1977. A comparative study of the feeding strategies of two sympatric species of leaf monkeys:Presbytis senex andPresbytis entellus. In:Primate Ecology: Studies of Feeding and Ranging Behaviour in Lemurs, Monkeys and Apes,Clutton-Brock,T. H. (ed.), Academic Press, London, pp. 324–354.
Hladik, C. M.;Hladik, A. 1972. Disponibilitiés alimentaires et domaines vitaux des primates à Ceylan.Terre et Vie, 26: 149–215.
Hladik, C. M.;Gueguen, L. 1974. Géophagie et nutrition minérale chez les primates sauvages.C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris, Serie D, 279: 1393–1396.
Hohl, A. 1993. Wiederherstellung der Artenvielfalt in den Agrarzonen tropischer Regenwälder. Unpubl. Doc. thesis, Universität Hohenheim, Hohenheim.
Inoue, M. 1987. Soil-eating of Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata) at Arashiyama, Kyoto.Prim. Res., 3: 103–111. (in Japanese)
Izawa, K. 1993. Soil eating byAlouatta andAteles.Int. J. Primatol., 14: 229–242.
Johns, A. D.;Duquette, M. 1991. Detoxification and mineral supplementation as functions of geophagy.Amer. J. Clin. Nutr., 53: 448–456.
Jolly, A. 1985.The Evolution of Primate Behavior (2nd ed.). Macmillan Publ., New York.
Kinzey, W. G. 1981. The titi monkey, genusCallicebus. In:Ecology and Behavior of Neotropical Primates,Coimbra-Filho,A. F.;Mittermeier,R. A. (eds.), Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, Rio de Janeiro, pp. 241–276.
Kinzey, W. G.;Becker, M. 1983. Activity pattern of the masked titi monkey,Callicebus personatus.Primates, 24: 337–343.
Kinzey, W. G.;Rosenberger, A. L.;Heisler, P. S.;Prowse, D.;Trilling, J. 1977. A preliminary field investigation of the yellow handed titi monkey,Callicebus torquatus torquatus, in Northern Peru.Primates, 18: 159–181.
Mahaney, W. C.;Hancock, R. G. V.;Aufreiter, S.;Huffman, M. A. 1996. Geochemistry and clay mineralogy of termite mound soil and the role of geophagy in chimpanzees of the Mahale Mountains, Tanzania.Primates, 37: 121–134.
Mahaney, W. C.;Watts, D. P.;Hancock, R. G. V. 1990. Geophagia by mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) in the Virunga Mountains, Rwanda.Primates, 31: 113–120.
Melo, A. O. D. 1973.Solos do núcleo colonial de Una. Boletim Técnico No. 26. Ceplac-Cepec, Itabuna, Bahia, Brasilien.
Mopper, K.;Gindler, E. M. 1973. A new noncorrosive dye reagent for automatic sugar chromatography.Anal. Biochem., 56: 440–442.
Müller, K.-H. 1994. Capture and radio-telemetry of masked titi monkeys (Callicebus personatus melanochir, Cebidae, Primates) in tropical rain forest.Neotrop. Prim., 2 (4): 7–8.
Müller, K.-H. 1995. Langzeitstudie zur Ökologie von schwarzköpfigen Springaffen (Callicebus personatus melanochir, Cebidae, Primates) im atlantischen Küstenregenwald Ostbrasiliens. Verlag Shaker, Aachen, Germany.
Oates, J. F. 1978. Water-plant and soil consumption by guereza monkeys (Colobus guereza): a relationship with minerals and toxins in the diet?Biotropica, 10 (4): 241–253.
Poirier, F. E. 1970. The nilgiri langur (Presbytis johnii) of South India. In:Primate Behaviour: Developments in Field and Laboratory Research, Vol. 1,Rosenblum,L. A. A. (ed.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 251–383.
Robbins, C. T. 1983.Wildlife Feeding and Nutrition. Academic Press, New York.
Rylands, A. B. 1982. The behaviour and ecology of three species of marmosets and tamarins (Callitrichidae, Primates) in Brazil. Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge.
Schaller, G. B. 1965.The Mountain Gorilla: Ecology and Behavior. Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago.
Veloso, H. P. 1965.Atlas Florestal do Brasil. Rio de Janeiro, Serviço de Informação Agrícola: 82.
Wrangham, R. W.;Conklin, N. L.;Chapman, C. A.;Hunt, K. D. 1991. The significance of fibrous foods of Kibale Forest chimpanzees.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B334: 171–178.
Wright, P. C. 1985. The cost and benefits of nocturnality forAotus trivirgatus (the night monkey). Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, City University of New York, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, KH., Ahl, C. & Hartmann, G. Geophagy in masked titi monkeys (Callicebus personatus melanochir) in sBrazil. Primates 38, 69–77 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02385923
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02385923