Summary
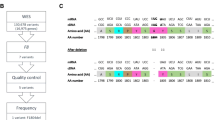
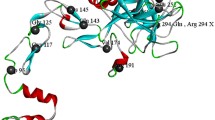
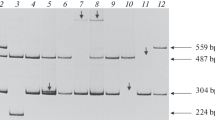
Rapid identification of gene defects allows definite carrier and prenatal diagnosis in virtually every family with haemophilia B. We report a study of the family of an isolated patient. Analysis of all the essential regions of the patient's factor IX gene (promoter, exons, transcript processing signals) revealed two mutations: one C→T transition at residue 17762 and another at residue 30890. The former created a translation stop at codon 116, and the latter caused substitution of His 257 by Tyr. The translation stop is an obvious detrimental mutation, while the His 257→Tyr substitution has uncertain functional consequences. From analysis of other family members, it was found that the first mutation had occurred at grandpaternal gametogenesis, in keeping with the negative family history, while the second was of more remote origin and did not reduce the maternal grandfather's factor IX coagulant and antigen level. This neutral mutation (His 257→Tyr) pinpoints a poorly conserved amino acid in factor IX and related serine proteases. Its coexistence with a detrimental mutation stresses the need to examine all essential regions of a gene before attempting to interpret the functional consequences of its sequence changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anson DS, Choo KH, Rees DJG, Giannelli F, Gould K, Huddleston JA, Brownlee GG (1984) The gene structure of human anti-haemophilia factor IX. EMBO J 3:1053–1060
Birktoft JJ, Blow DM (1972) Structure of crystalline alpha-chymotrypsin V. The atomic structure of tosyl-alpha-chymotrypsin at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol 68:187–240
Brownlee GG (1989) Haemophilia B: a review of patient defects, diagnosis with gene probes and prospects for gene therapy. In: Hoffman AV (ed) Recent advances in haematology, vol 5. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 251–264
Cao A, Rosatelli C, Pirastu M (1987) Diagnosis of thalassaemia by DNA analysis. In: Peters H (ed) Protides of the biological fluids, vol 35. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 15–19
Chance PF, Dyer KA, Kurachi KA, Yoshitake S, Ropers H-H, Wieacker P, Gartler SM (1983) Regional localization of the human factor IX gene by molecular hybridisation. Hum Genet 65:207–208
Chehab FF, Doherty M, Cai S, Kan YW, Cooper S, Edward R (1987) Detection of sickle cell anaemia and thalassaemias. Nature 329:293–294
Dayhoff MO, Schwartz RM, Orcut BC (1979) A model of evolutionary change in proteins. In: Dayhoff MO (ed) Atlas of protein sequence and structure, vol 5, Suppl 3. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington, DC, pp 345–352
Degen SJF, MacGillivray RTA, Davie EW (1983) Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry 22:2087–2097
Ferrari N, Rizza CA (1986) Estimation of genetic risks of carriership for possible carriers of Christmas disease (haemophilia B). Braz J Genet 9:87–99
Foster D, Davie EW (1984) Characterization of a cDNA coding for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:4766–4770
Fung MR, Hay CW, MacGillivray RTA (1985) Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3591–3595
Furie B, Bing DH, Feldmann RJ, Robinson DJ, Burnier JP, Furie BC (1982) Computer-generated models of blood coagulation factor Xa, IXa and thrombin based upon structural homology with other serine proteases. J Biol Chem 257:3875–3882
Giannelli F (1987) The identification of haemophilia B mutations. In: Peeters H (ed) Protides of the biological fluids, vol 35. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 29–32
Giannelli F (1989) Factor IX. In: Tuddenham EGD (ed) The molecular biology of coagulation. (Bailliére's clinical haematology, vol 2) Bailliére Tindall, New York London, pp 821–848
Green PM, Bentley DR, Mibashan RS, Nilsson IM, Giannelli F (1989) Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J 8:1067–1072
Hagan FS, Gray CL, O'Hara P, Grant FJ, Saari GC, Woodbury RG, Hart CE, Insley M, Kisiel W, Kurachi K, Davie EW (1986) Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2412–2416
Handford PA, Baron M, Mayhew M, Willis A, Beesley T, Brownlee GG, Campbell ID (1990) The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J 9:475–480
Leytus SP, Loeb KR, Hagen FS, Kurachi K, Davie EW (1988) A novel trypsin-like serine protease (hepsin) with a putative transmembrane domain expressed by human liver and hepatoma cells. Biochemistry 27:1067–1074
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (eds) (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Montandon AJ, Green PM, Giannelli F, Bentley DR (1989) Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3347–3358
Nilsson IM (1974) Haemorrhagic and thrombotic diseases. Wiley, London
Rees DJG, Jones IM, Handford PA, Walter SJ, Esnouf MP, Smith KJ, Brownlee GG (1988) The role of beta-hydroxy-aspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human factor IX. EMBO J 7:2053–2061
Saiki RK, Chang C-A, Levenson CH, Warren TC, Boehm CD, Kazazian HH, Erlich HA (1988a) Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia with enzymatically amplified DNA and nonradioactive allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. N Engl J Med 319:537–541
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988b) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–494
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Wallmark A, Ljung R, Nilsson IM, Holmberg L, Hedner U, Lindvall M, Sjogren HO (1985) Polymorphism of normal factor IX detected by mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3839–3843
Winship PR (1989) An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res 17:1266
Winship PR, Anson DS, Rizza CR, Brownlee GG (1984) Carrier detection in haemophilia B using two further intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8861–8872
Yoshitake S, Schach BG, Foster DC, Davie EW, Kurachi K (1985) Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry 24:3736–3750
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montandon, A.J., Green, P.M., Bentley, D.R. et al. Two factor IX mutations in the family of an isolated haemophilia B patient: direct carrier diagnosis by amplification mismatch detection (AMD). Hum Genet 85, 200–204 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193196
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193196