Abstract
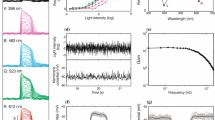
The static and dynamic characteristics of phototransduction were studied in photoreceptors of the compound eye of the fly Phormia regina (Calliphoridae) using a green light emitting diode driven by a controlled current source. The LED provides sufficiently intense light to investigate the behaviour of the receptors over about half of the dark adapted range of the response versus log intensity curve. The effects of constant adapting light intensities upon the step response and upon the frequency response and coherence functions were examined. Using both methods the effect of light adaptation upon receptor sensitivity can be closely approximated by a similar linear dependence of log sensitivity upon log adapting intensity. However, there was no reliably detectable effect of light adaptation upon the time constant of the response over the range of adapting intensities used.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LED:
-
Light Emitting Diode
References
Baumann, F.: Slow and spike potentials recorded from retinula cells of the honeybee drone in response to light. J. gen. Physiol. 52, 855–875 (1968)
Baylor, D.A., Hodgkin, A.L.: Changes in time scale and sensitivity in turtle photoreceptors. J. Physiol. 242, 729–758 (1974)
Baylor, D.A., Hodgkin, A.L., Lamb, T.D.: The electrical responses of turtle cones to flashes and steps of light. J. Physiol. 242, 685–727 (1974)
Beastall, H.R.: White noise generator. Wireless World 78, 127–128 (1972)
Bendat, J.S., Piersol, A.G.: Measurement and analysis of random data. New York Wiley 1966
Burkhardt, D.: On the vision of insects. J. comp. Physiol. 120, 33–50 (1977)
Fein, A., Charlton, S.S.: A quantitative comparison of the effects of intracellular calcium injection and light adaptation on the photoresponse of Limulus ventral photoreceptors. J. gen. Physiol. 70, 591–600 (1977)
French, A.S. Automated spectral analysis of neurophysiological data using intermediate magnetic tape storage.Comput. Prog. Biomed. 3, 45–57 (1973)
French, A.S., Järvilehto, M.: The dynamic behaviour of photoreceptor cells in the fly in response to random (white noise) stimulation at a range of temperatures. J. Physiol. 274, 311–322 (1978a)
French, A.S., Järvilehto, M.: The transmission of information by first and second order neurons in the fly visual system. J. comp. Physiol. 126, 87–96 (1978b)
Fuortes, M.G.F., Hodgkin, A.L.: Changes in time scale and sensitivity in the ommatidia of Limulus. J. Physiol. 172, 239–263 (1964)
Gemperlein, R., McCann, G.D.: A study of the response properties of retinula cells of flies using nonlinear identification theory. Biol. Cybernetics 19, 147–158 (1975)
Hausen, H.: Signal processing in the insect eye. In: Function and formation of neural systems, pp. 81–110. Stent, G.S., ed. Berlin: Dahlem Konferenzen 1977
Laughlin, S.B.: Receptor and interneuron light adaptation in the dragonfly visual system. Z. Naturforsch. 30c, 306–308 (1975)
Laughlin, S.B.: The sensitivities of dragonfly photoreceptors and the voltage gain of transduction. J. comp. Physiol. 111, 221–247 (1976a)
Laughlin, S.B.: Adaptations of the dragonfly retina for contrast detection and the elucidation of neural principles in the peripheral visual system. In: Neural principles in vision, pp. 175–193. Zettler, F., Weiler, R., ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1976b
Moring, J., Järvilehto, M.: Dark recovery of polarized light sensitive and insensitive receptor cells in the retina of the fly. J. comp. Physiol. 122, 215–226 (1977)
Smola, U.: Voltage noise in insect visual cells. In: Neural principles in vision, pp. 194–213. Zettler, F., Weiler, R., ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1976
Srebro, R., Behbehani, M.: The thermal origin of spontaneous activity in the Limulus photoreceptor. J. Physiol. 224, 349–361 (1972)
Stark, W.S., Ivanyshyn, A.M., Greenberg, R.M.: Sensitivity and photopigments of R1-6, a two-peaked photoreceptor in Drosophila, Calliphora, and Musca. J. comp. Physiol. 121, 289–305 (1977)
Zettler, F., Järvilehto, M.: Histologische Lokalisation der Ableitelektrode. Belichtungspotentiale aus retina und lamina bei Calliphora. Z. vergl. Physiologie 68, 202–210 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, A.S. The effect of light adaptation on the dynamic properties of phototransduction in the fly, Phormia regina . Biol. Cybernetics 32, 115–123 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337443
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337443