Summary
The effect of sulpiride on dopamine-induced changes in renal function in man has been investigated. Dopamine dose-response studies were performed in 7 healthy volunteers before and after sulpiride 200 mg i. v. The same investigations were performed in 15 healthy volunteers after pretreatment with the selective alpha-1-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin (n=7) and the non-selective alpha-adrenoceptor-blocker phentolamine (n=8).
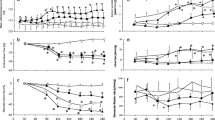
Infusion of dopamine 0.25 to 8 μg·kg−1·min−1 resulted in a dose-dependent increase in effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and a fall in filtration fraction (FF) in 7 normal volunteers. Sulpiride had no effect on base-line ERPF or GFR and did not influence the dopamine-induced renal vasodilatation in those volunteers. It did cause a fall in the fractional sodium excretion (FENa+%) from 1.7 to 1.38, and shifted the dose-response curve of the natriuretic response to a subsequent infusion of dopamine. Sulpiride enhanced the fall in diastolic blood pressure during infusion of dopamine.
In 7 other volunteers pretreated with prazosin, sulpiride did not influence base-line ERPF, GFR or FF or their response to dopamine, but the sodium excretion fell markedly (FENa+% changed from 1.13 to 0.63). Administration of sulpiride to 8 volunteers after phentolamine pretreatment 20 mg·h−1 i.v. in the first hour followed by 10 mg·h−1 i.v. resulted in a fall in sodium excretion (FENa+% from 1.09 to 0.53) without affecting ERPF or FF, and it did not affect the dose-response curve in the subsequent DA infusion. Both after prazosin pretreatment and during phentolamine infusion the usual natriuretic response to dopamine was completely absent, while phentolamine alone did not influence base-line values of sodium excretion or of ERPF, GFR and FF.
Overall, in normal men sulpiride did not antagonise the dopamine-induced renal vasodilatation. This was not due to a presumed additional alpha-antagonist activity of sulpiride. Its effect on base-line sodium excretion and dopamine-induced natriuresis did not appear to be dependent on renal haemodynamics and may be the consequence of inhibition of a direct proximal tubular effect of dopamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg LI (1972) Cardiovascular and renal actions of dopamine: potential clinical applications. Pharmacol Rev 24: 1–29
Wee PM ter, Smit AJ, Rosman JB, Sluiter WJ, Donker AJM (1986) The effect of intravenous infusion of a low dose dopamine on renal function in normal individuals and in patients with renal disease. Am J Nephrol 6: 42–46
Smit AJ, Meijer S, Wesseling H, Reitsma WD, Donker AJM (1989) Impaired renal hemodynamic but conserved natriuretic response to dopamine in patients with renal disease. Nephron 52: 338–346
Aperia A, Bertorello A, Seri I (1987) Dopamine causes inhibition of Na+-K+-AtPase activity in rat proximal convoluted tubule segments. Am J Physiol 252: F39-F45
Goldberg LI, Musgrave GE, Kohli JD (1979) Antagonism of dopamine-induced renal vasodilation in the dog by bulbocapnine and sulpiride. In: Spano PF, Trabucchi M, Corsini GU, Gessa GL (eds) Sulpiride and Other Benzamides. Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology. Raven Press, New York
Agnoli GC, Borgatyti R, Cacciari M, Garutti C, Ikonomu E, Lenzi P (1989) Antagonistic effects of sulpiride — racemic and enantiomers — on renal response to low-dose dopamine infusion in normal women. Nephron 51: 491–498
Donker AJM, Hem GK van er, Sluiter WJ, Beekhuis H (1977) A radioisotope method for simultaneous determination of the glomerular filtration rate and the effective renal plasma flow. Neth J Med 20: 97–103
Bass AS, Robie NW (1984) Stereoselectivity of S- and R-sulpiride for pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the canine kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 229: 67–71
Schmidt M, Imbs JL, Giesen EM, Schwartz J (1983) Blockade of dopamine receptors in the renal vasculature by isomers of flupenthixol and sulpiride. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 5: 86–89
Salminen JK, Lehtonen V, Allonen H, Kunto J (1980) Sulpiride in depression: plasma levels and effects. Curr Ther Res 27: 109–115
Kohli JD, Cripe LD (1979) Sulpiride: a weak antagonist of norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Eur J Pharmacol 56: 283–286
Horn N, Marcou M, Munday KA, Woodruff GN (1981) Effects of dopamine receptor agonists in the guinea-pig renal vasculature and their antagonism by sulpiride. Br J Pharmacol 72: 507P-508P
Lee MR (1982) Dopamine and the kidney. Clin Sci 62: 439–448
McDonald RH, Goldberg LI, McNay JL, Tuttle EP (1964) Effect of dopamine in man, augmentation of sodium excretion, glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow. J Clin Invest 43: 1116–1124
Chapman BJ, Horn NM, Munday KA, Robertson MJ (1980) The actions of dopamine and sulpiride on regional blood flows in the rat kidney. J Physiol 298: 437–452
Carey RM, Thorner MO, Ortt EM (1979) Effects of metoclopramide and bromocriptine on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in man. J Clin Invest 63: 727–735
Bello-Reuss E, Higashi Y, Kaneda Y (1982) Dopamine decreases fluid reabsorption in straight portions of rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 242: F634-F640
Aperia AC (1988) Dopamine inhibition of NaKATPase activity in proximal convoluted tubule cells. Prog Clin Bio Res 273: 427–434
Goldberg LI, Kohli JD (1983) Peripheral dopamine receptors: a classification based on potency series and specific antagonism. Trends Pharmacol Sci 5: 64–66
Felder RA, Jose PA (1988) Dopamine 1 receptors in rat kidneys identified with 125I-Sch 23982. Am J Physiol 255: F970-F976
Barrett RJ, Wright KF, Taylor DR, Proakis AG (1987) Involvement of dopamine receptor subtypes in dopaminergic modulation of aldosterone secretion in rats. Life Sci 40: 1499–1506
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smit, A.J., Meijer, S., Wesseling, H. et al. Dissociation of renal vasodilator and natriuretic effects of dopamine during sulpiride infusion in normal man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39, 221–226 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315100
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315100