Abstract
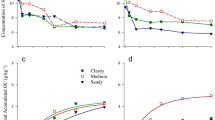
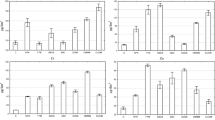
Primary sludge, secondary sludge, and wood ash from a pulp and paper mill were combined with sand to create a synthetic topsoil (C:N ratio of 18:1) to restore an abandoned gravel pit. Synthetic topsoil was applied to field microcosms at rates equivalent to 0, 2170, 4341, or 6511 kg N/ha; each was seeded with grass. Fifteen chemical constituents in leachate were measured during two field seasons. Cadmium, Ni and Zn were mobilized rapidly by soil disturbance. Chloride and SO4-S eluted rapidly from the sludge along with Na. Nitrate leached with Ca late in each field season when sludge N-mineralization and nitrification exceeded plant uptake and microbial immobilization. Ammonium elution was negligible. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was mobilized by decomposition of organic matter in the sludge, as were Mg and K. Copper eluted with DOC, probably as an organic ligand. Lead and ortho-P were below our detection limits. We concluded that a synthetic topsoil with a 30:1 C:N ratio applied at a rate of 2100-4300 kg N/ha should provide adequate plant nutrition while minimizing water quality hazards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J.: 1995, ‘The Origins of Heavy Metals in Soils’, in B. J. Alloway (ed.), Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed. Chapman and Hall, London.
Baker, D. E. and Amacher, M. C.: 1982, ‘Nickel, Copper, Zinc and Cadmium’, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Kenney (eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd ed. Amer. Soc. of Agron., and Soil Sci. Soc. Amer., Madison, WI. pp. 323–336.
Bethea, R. M., Duran, B. S. and Boullion, T H.: 1985, Statitistical Methods for Scientists and Engineers, M. Dekker, New York, p. 698.
Blake, G. R.: 1965, ‘Bulk Density’, in C. A. Black et al. (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part I. Physical and Mineralogical Properties, Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling, Amer. Soc. of Agron., Inc. Madison, WI. p. 377–378.
Bockheim, J. G., Benzel, T. C., Lu, R.-L. and Thiel, D. A.: 1988, J. Environ. Qual. 17, 729.
Bohn, H., McNeal, B. and O'Connor G.: 1979, Soil Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 329.
Bowden, W. B., Smith, C. T, McDowell, W. H.. and Catricala, C. E.: 1993, New Hampshire Agricultural Expt. Sta. Publication No. 1807, Durham, p. 75.
Brady, N. C.: 1974, The Nature and Properties of Soils, MacMillan Publishing Co., Inc., New York, p. 639.
Brockway, D. G.: 1983, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 47, 776.
Catricala, C. E.: 1993, Chemical Characteristics of Leachate from Sandy Soils Amended with Pulp and Paper Mill Residuals, M.S. thesis, University of New Hampshire, p. 128.
Cole, D. W., Henry, C. L. and Nutter, W. L. (eds.): 1986, The Forest Alternative for Treatment and Utilization of Municipal and Industrial Sludges, Univ. of Washington Press, Seattle, p. 573.
Devoe, D. R.: 1990, Influence of Sludge C:N Ratios and Loading Rates on Forest Soil Leachate Chemistry, M.S. thesis, University of New Hampshire, p. 120
Dolar, S. G., Boyle, J. R. and Kenney, D. R.: 1972, J. Environ. Qual. 4, 405.
Domergue, F.-L. and Vedy, J.-C.: 1992, Intern. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 46, 13.
Drever, J. I.: 1988, The Geochemistry of Natural Waters, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, p. 437.
Dudley, L. M., McNeal, B. L. and Baham, J. E.: 1986, J. Environ. Qual. 15, 188.
Eck, T. H.: 1986, Tappi 69, 54–59.
Elliott, H. A., Liberati, M. R. and Huang, C. P.: 1986, J. Environ. Qual. 15, 214.
Hallett, R. A.: 1991, Nitrogen Mineralization in Forest Soils After Municpal Sludge Additions, M.S. Thesis, Univ. of New Hampshire, p. 117.
Henry, C. L.: 1991, Water Sci. Tech. 24, 417.
Hertz, J. and Angehm-Bettinazzi, C.: 1990, Intern, J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 39, 91.
Hornbeck, J. W. and Kropelin, W.: 1982, J. Environ. Qual. 11, 309.
James, R. V. and Rubin, J.: 1986, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 1142.
Johnson, D. W. and Cole, D. W.: 1980, Environment International 3, 79.
Jordan Co., E. C.: 1984, Pulp and Paper Mill Sludges in Maine: A Characterization Study, Paper Industry Info. Center, Augusta, Report No. 4.84.37. p. 26.
Khaleel, R., Reddy, K. R. and Overcash, M. R.: 1981, J. Environ. Qual. 10, 133.
Khanna, S. S. and Stevenson, F. J.: 1962, Soil Sci. 93, 299.
Kenney, D. R. and Nelson, D. W.: 1982, ‘Nitrogen-Inorganic Forms’, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Kenney (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological properties, 2nd ed. Amer. Soc. of Agron., and Soil Sci. Soc. Amer., Madison, WI. pp. 643–693.
Kotrly, S. and Sucha, L.: 1985, Handbook of Chemical Equilibria in Analytical Chemistry, Halsted Press, New York, p. 414.
Kraske, C. R. and Fernandez, I. J.: 1993, J. Envirom. Qual. 22(4), 776.
Little, T. M. and Hills, F. J.: 1972, Statistical Methods in Agricultural Research, University of California at Davis, p. 242.
Maine Department of Environmental Protection: 1986, Chapter 567: Rules for Land Application of Sludge and Residuals, Augusta, p. 82.
Maine Department of Human Services: 1983, Rules Relating to Drinking Water, Augusta, p. 55.
Martin, C. W. and Pierce, R. S.: 1980, J. of Forestry 78(5), 268.
McDowell, W. H., Cole, J. J. and Driscoll, C. T.: 1987, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 44, 214.
McKeown, J. J.: 1982, ‘The Management of Paper Industry Residuals in Pennsylvania and the U.S.’, in C. A. Rock and J. A. Alexander (eds.), Long Range Alternatives for Pulp and Paper Sludge, Univ. of Maine, Orono, pp. 1–12.
McLean, E. O.: 1982, Soil pH, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Kenney, (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed. Amer. Soc. of Agron., and Soil Sci. Soc. Amer., Madison, WI. pp. 199–224.
Medalie, L., Bowden, W. B. and Smith, C. T.: 1994, J. Environ. Qual. 23, 130.
National Research Council: 1977, Drinking Water and Health, National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., p. 939.
Oliver, B. G., Thurman, E. M. and Malcolm, R. L.: 1983, Geochim. Cosmo. Acta. 47, 2031.
Reynolds, B., Emmett, B. A. and Woods, C.: 1992, J. Hyrology, 136, 155.
Rock, C. A. and Beyer, B. S.: 1982, ‘Pulp and Paper Wastewater Sludges: The Maine Perspective’, in C. A. Rock and J. A. Alexander (eds.), Long range alternatives for pulp and paper sludge, Univ. of Maine, Orono, pp. 13–20.
Rogers, D. S.: 1982, ‘Conversion of Waste Activated Sludge to Animal Feed Protein Supplement’, in C. A. Rock and J. A. Alexander (eds.), Long Range Alternatives for Pulp and Paper Sludge, Univ. of Maine, Orono, pp. 104–111.
Seaker, E. M. and Sopper, W. E.: 1988, J. Environ. Qual. 17, 591.
Sell, N. J. and McIntosh, T. H.: 1988, Tappi 71, 135.
Shimek, S., Nessman, M., Charles, T. and Ulrich, D.: 1988, Tappi 71, 101.
Sposito, G.: 1989, The Chemistry of Soils, Oxford University Press, New York, p. 277.
Sposito, G., Lund, L. J. and Chang, A. C.: 1982, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 46, 260.
Technicon: 1983, AutoAnalyzer II, Multi-test cartridge, Method No. 696-82W, Technicon Inst. Corp., Tarrytown, NY.
Technicon: 1975, Industrial Method No. 376-75W/A, Technicon Industrial Systems, Tarrytown, NY.
Thomas, G. W.: 1982, ‘Exchangeable Cations’, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Kenney (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed. Amer Soc. of Agron., and Soil Sci. Soc. Amer., Madison, WI. pp. 159–165.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: 1983, Process Design Manual for Land Application of Municipal Sludge, USEPA Center for Environmental Research Information. Cinncinnati, OH. EPA-625/1-83-016.
Vitousek, P. M., Gosz, J. R., Grier, C. C., Melillo, J. M., Reiners, W. A. and Todd, R. L.: 1979, Science 202, 469.
Waters Ion Chromatography Cookbook: 1989, Manual No. 20195. Millipore Corp., Milford, Mass.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catricala, C.E., Bowden, W.B., Smith, C.T. et al. Chemical characteristics of leachate from pulp and paper mill residuals used to reclaim a sandy soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 89, 167–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300429
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300429