Abstract
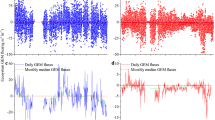
Mercury flux measurements were conducted at two lakes and three soil sites in Kejimkujik National Park, located in the eastern Canadian province of Nova Scotia. One of the lakes had high levels of both mercury and Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC). Two of the soil sites were located under the forestcanopy, while the other was in a small clearing surrounded by forest. Flux measurements were performed using the dynamic chamber method. Mercury concentrations in the air were measured with a TEKRAN mercury analyzer. Mercury fluxes over the two lakes were most strongly correlated with solar radiation, although the flux was also significantly correlated with water temperature, air temperature, and negatively correlated with relative humidity. The flux from the high DOC lake (Big Dam West) was especially high when the conditions were both sunny and windy (wind speed greater than 1.3 m s-1) and the average flux measured was 5.4 ng m-2 h-1. The mercury flux from this lake was wellparameterized in terms of a simple expression involving solar radiation and a nonlinear dependence on wind speed. The flux measured from the low DOC lake (North Cranberry) tended to be lower than from the high DOC lake. The averageflux measured was 1.1 ng m-2 h-1, but was again strongly correlated with solar radiation. The flux was low during windy conditions in the absence of sunlight, suggesting that wind enhances mercury evasion from lakes only in the presence of solar radiation. Mercury fluxes measured over the soil sites tended to be smaller than those over water (a range of –1.4–4.3 ng m-2 h-1). At one of the forest sites, mercury flux was very strongly correlated with 0.5 cm soil temperature, and this dependence was well described by an Arrhenius-typeexpression with an activation energy of 14.6 kcal-1 mole, quite close to the heat of vaporization of mercury (14.5 kcal-1 mol-1 at 20 °C). At the clearing, where there was direct exposure to the sun, the mercury flux was most strongly correlated with solar radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amyot, M., Mierle, G., Lean, D. and McQueen, D. J.: 1997, Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 61, 975.
Barkay, T., Turner, R. R., VandenBrook, A. and Liebert, C.: 1991, Microbe. Ecol. 21 151.
Beauchamp, S., Burgess, N., D'Entremont, A., Tordon, R., Schroeder, W. and Abraham J.: 1997, ‘Mercury in Air, Water and Biota in Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia, Canada’, in Proceedings of Third International Conference Science and the Management of Protected Areas, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Bloom, N. and Fitzgerald, W. F.: 1988, Anal. Chim. Acta 208, 151.
Broecker, C. H., Petermann, J. and Siems, W.: 1978, J. Marine Res. 36, 595.
Brosset, C.: 1987, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 34, 145.
Carpi, A. and Lindberg, S. E.: 1997, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2085.
Carpi, A. and Lindberg, S. E.: 1998, Atmos. Environ. 32, 873.
Environment Canada: 1996, Atlantic Region Analytical Methods Manual, Montcton, NB.
Evers, C. D., Kaplan, D. J., Meyer, W. M., Reaman, S. P., Braselaton, E. W., Major, A., Burgess, N. and Scheuhammer, M. A.: 1998, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 173.
Fitzgerald, W. F. and Gill, A. G.: 1979, Anal. Chem. 51, 1714.
Fitzgerald, W. F., Mason, R. P. and Vandal, G. M.: 1991, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 56, 745.
Fitzgerald, W. F., Engstrom, R. D., Mason, D. R. and Nater, E. A.: 1998, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 1.
Jähne, B., Münnich, O. K., Bösinger, R., Dutzi, A., Huber, W. and Libner, P.: 1987, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 1937.
Kerekes, J., Beauchamp, S., Tordon, R. and Tremblay, C.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 165.
Kirk, O. T. J: 1994, Advances in Limnology 43, 1.
Kim, K. and Lindberg, E. S.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 1059.
Kim, K., Lindberg, E. S. and Meyers, P. T.: 1995, Atmos. Environ. 29, 267.
Lindberg, S. E.: 1996, ‘Forests and the Global Biogeochemical Cycle of Mercury’, in Baeyens, W., Ebinghaus, R. and Vasiliev, O. (eds.), Regional and Global Mercury Cycles: Sources, Fluxes and Mass Balances, Kluwer Academic Publ., Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 359–380.
Lindberg, S. E., Meyers, T. P. and Munthe, J.: 1995b, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 725.
Lindberg, S. E., Kim, K. H., Meyers, T. P. and Owens, J. G.: 1995a, Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 126.
Mason, P. R., Fitzgerald, F. W. and Morel, M. M. F.: 1994, Geochi. et Cosmochi. Acta 58, 3191.
Mason, P. R., Morel, M. M. F. and Hemond, F. H.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 775.
Munthe, J. and McElroy, W. J.: 1992, Atmos. Environ. 26A, 553.
Piazena, H. and Häder, P. D.: 1997, Environmental Intelligence Unit: The Effects of Ozone Depletion on Aquatic Ecosystem, Landes R. G. Company and Academic Press, Inc.
Poissant, L. and Casimir, A.: 1998, Atmos. Environ. 32, 883.
Porcella, B. D., Ramel C. and Jernelov, A.: 1997, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 97, 205.
Schroeder, W. H., Munthe, J. and Lindqvist, O.: 1989, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 48, 337.
Schroeder, W. H., Lindqvist, O. and Munthe, J.: 1992, Sci. Total Environ. 125, 47.
Schroeder, H. W. and Munthe, J.: 1998, Atmospheric Environment 32, 809.
Slemr, F. and Langer, E.: 1992, Nature 355, 435.
Vandal, M. G. Fitzgerald, F. W., Rolfhus, R. K. and Lamborg, H. C.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 529.
Wanninkhof, R., James, R., Ledwell, R. and Broecker, S. W.: 1987, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 14567.
Xiao, Z. F., Stromberg, D. and Lindqvist, O.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 789.
Xiao, Z. F., Munthe J., Schroeder, W. H. and Lindqvist, O.: 1991, Tellus 43B, 267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boudala, F.S., Folkins, I., Beauchamp, S. et al. Mercury Flux Measurements over Air and Water in Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 122, 183–202 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005299411107
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005299411107