Abstract
Different urban air pollution problems deal with complex structure of air flows and turbulence. For such problems the Computer Fluid Dynamics (CFD) methods become widely used. However, this approach despite a number of advantages has some problems. Experience of use of CFD tools for development of models and suggestions of their applications for a local scale air pollution over a complex terrain and stable stratification are discussed in this paper, including:
• Topography and complex geometry: choose of the co-ordinate system and computer grid;
• Turbulence closure for air pollution modelling: modified k-ε model for stable stratified ABL;
• Boundary conditions for vertical profiles of velocity for stable-stratified atmosphere;
• Effects of the radiation and thermal budget of inclined surfaces to dispersion of pollutants;
• Artificial sources of air dynamics and circulation.
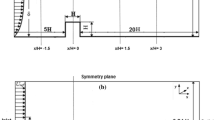
Some examples of CFD applications for air pollution modelling for a flat terrain, mountainous area, mining open cast and indoor ventilation are discussed. Modified k-ε model for stably-stratified ABL is suggested. Due to the isotropic character of the k-ε model a combination of it in vertical with the sub-grid turbulence closure in horizontal can be more suitable for ABL. An effective scheme of boundary conditions for velocity profiles, based on the developed similarity theory for stable-stratified ABL, is suggested. Alongside with the common studies of atmospheric dispersion, the CFD methods have also demonstrated a good potential for studying anthropogenic and artificial-ventilation sources of air dynamic and circulation in local-scale processes of air pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloyan, A., Baklanov, A. &; Penenko, V.: 1982, Fictitious regions in numerical simulation of quarry ventilation, Soviet Meteorology and Hydrology, 7, pp.32–37.
Baklanov, A.: 1988, Numerical modelling in mine aerology, Apatity: KSC RAS, 200 p. (in Russian) Baklanov, A.: 1995, Numerical modelling of atmosphere processes in mountain cirques and open pits, Air Pollution III, V.1: Theory and Simulation, Comp. Mech. Publ., pp.231-237.
Baklanov, A., Burman, J. &; Näslund, E.: 1996, Numerical modelling of three-dimensional flow and pollution transport over complex terrain during stable stratification, Scientific report, FOA, Umea, Sweden (FOA-R-96-00376-4.5-SE), 40 p.
Baklanov, A. &; Rigina, O.: 1994, Research of local zones atmosphere normalisation efficiency by artificial currents, Air Pollution II, V.1: Computer Simulation, Comp. Mech. Publ., 553-561.
Burman, J.: 1997, A study of the influence of topography and density on the dispersion in a gas cloud, Scientific report, FOA, Umea, Sweden (FOA-R-96-00304-4.5-SE), 27 p.
Deardorf, J.W.: 1978, Efficient prediction of ground surface temperature and moisture with inclusion of a layer of vegetation, J. Geophys. Res., 83C, 1889–1903.
Delaunay, D., Flori, J.P. &; Sacré, C.: 1996, Numerical modelling of gas dispersion from road tunnels in urban environments: Comparison with field experiment data, 4th Workshop on Harmonization within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Ostende, Belgique, 361-368.
Detering, H. W. &; Etling, D.: 1985, Application of the E-? turbulence model to the atmospheric boundary layer, Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 33, 113–133
Galperin, B. and Orszag, S.A. (Editors): 1993, Large Eddy Simulation of Complex Engineering and Geophysical Flows, Cambridge University Press.
Kalabin, G., Baklanov, A. &; Amosov, P.: 1990, Calculating the aerogas dynamics of chamber-like workings on the basis of mathematical modelling, Sov. Min. Sci., Vol. 26:1, 61-73.
Lettau, H.H.: 1962, Theoretical wind spirals in the boundary layer of a barotropic atmosphere. Beitr. Phys. Atm. 35, 195–212.
Montavon, C.: 1998, Simulation of atmospheric flows over complex terrain for wind power potential assessment, PhD thesis #1855, Lausanne, EPFL.
Murena, F., d'Allesandro, S. &; Gioia, F.: 1997, CO dispersion in urban street canyons, PHOENICS Journal, v. 10, n. 4, 407–415.
PHOENICS: 1991, The PHOENICS Reference Manual. CHAM Development team. UK.
Rodi, W.:1987, Examples of Calculation Methods for Flow and Mixing in Stratified Fluids, Journal of Geophysical Research, 92, no C5, 5305–5328.
Schatzmann, M., Rafailidias, S., Britter, R. &; Arend, M. (Editors): 1997: Database, monitoring and modelling of urban air pollution. Inventory of models and data sets. EC COST 615 Action. 109p.
Sini, J.-F., Anquentin, S. &; Mestayer, P.G.: 1996, Pollutant dispersion and thermal effects in urban street canyons. Atmos. Envir., 30:15, pp. 2659-2677.
Svensson, U.: 1986, PHOENICS in environmental flows. A review of applications at SMHI. Lecture Notes in Engineering 18, pp 87–96.
Van Ulden, A. and Holtslag, A.A.M.: 1985, Estimation of atmospheric boundary layer parameters for diffusion applications, J. Clim. Appl. Meteor., 24, pp. 1196–1207.
Zilitinkevich, S., P.-E. Johansson, D. V. Mironov &; A. Baklanov: 1998, A similarity-theory model for wind profile and resistance law in stably stratified planetary boundary layers. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn., v. 74-76, n. 1-3, pp. 209–218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baklanov, A. Application of CFD Methods for Modelling in Air Pollution Problems: Possibilities and Gaps. Environ Monit Assess 65, 181–189 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006442514766
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006442514766