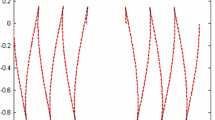
Abstract
In this investigation, a comparison is made of two methods for developing perturbation theories for non-canonical dynamical systems. The methods compared are the generalized Lie-Hori method and the method of averaging. In the comparison presented here, the equivalence of the methods up to the second order in the small parameter is shown. However, the approach used can be extended to demonstrate the equivalence for higher orders. To illustrate the equivalence Duffing's equation, the van der Pol equation and the oscillator with quadratic damping problem are solved using each method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagoliubov, N. and Mitropolsky, Y.: 1961,Asymptotic Method in the Theory of Nonlinear Oscillations, Gordon and Breach, New York.
Cefola, P., Green, A., McClain, W., Early, L., Proulx, R., and Taylor, S.: 1980,Semianalytical Satellite Theory Application to Orbit Determination, AIAA Paper No. 80-1677.
Choi, J. S. and Tapley, B. D.: 1972, ‘An Extended Canonical Perturbation Method’Celest. Mech.,7, 77.
Hori, G. I.: 1966, ‘Theory of General Perturbations with Unspecified Canonical Variables’,Astron. Soc. Japan 18, 4.
Hori, G. I.: 1971, ‘Theory of General Perturbations for Non-Canonical Systems’,Astron. Soc. Japan 23, 567.
Jefferys, W. H.: 1970,TRIGMAN — A system for Algebraic Manipulation of Poisson Series, Computation Center, The University of Texas at Austin, Texas.
Kamel, A. A.: 1971, ‘Lie Transforms and the Hamiltonization of Non-Hamiltonian Systems’,Celest. Mech. 4, 397.
Kyner, W. T.: 1965, ‘A Mathematical Theory of the Orbits about an Oblate Planet’,Siam J. 13, 136.
Lorell, J., Anderson, D., and Lass, H.: 1964,Application, of the Method of Averages to Celestial Mechanics, TR 32–482, Jet Propulsion Lab., Pasadena, California.
Mersman, W. A.: 1971, ‘Explicit Recursive Algorithms for the Construction of Equivalent Canonical Transformations’,Celest. Mech. 3, 384.
Morrison, J. A.: 1966, in R. L. Duncombe and V. G. szebehely (eds.),Methods in Astrodynamics and Celestial Mechanics, Academic Press, p. 117.
Morrison, J. A.: 1972, ‘A Novel Method for Averaging Equations of Motion’,J. Astronaut. Sci. 20, 113.
Powers, W. F. and Tapley, B. D.: 1969, ‘Canonical Applications to Optimal Trajectory Analysis’,AIAA J. 7, 394.
Shniad, H.: 1970, ‘The Equivalence of Von Zeipel Mappings and Lie Transforms’,Celest. Mech.,2, 114.
Verhulst: 1976, ‘On the Theory of Averaging’,Long Time Predictions in Dynamics, p. 119–140.
Watanabe, N.: 1974, ‘Equivalence of the Method of Averaging and the Lie Transform’,Sci. Rep. Tohoku Univ. First Ser., Vol. 57, pp. 11–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, A.H., Tapley, B.D. Equivalence of the generalized Lie-Hori method and the method of averaging. Celestial Mechanics 33, 1–20 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01231091
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01231091