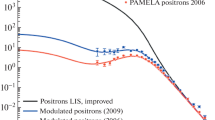
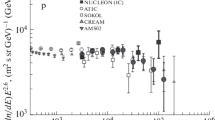
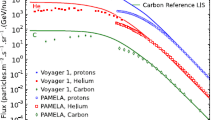
Abstract
Recent observations of the spectra of cosmic ray helium, M, LH and VH nuclei in the energy range from ≲200 MeV/nuc to>22 GeV/nuc are reported. The differential spectra of all of these groups of nuclei are found to have a maximum at 300–400 MeV/nuc at sunspot minimum. The average exponents on the integral rigidity spectra in the range 5 to 50 GV are 1.54±0.03 for He nuclei, 1.50±0.04 for M nuclei, 1.47±0.06 for LH nuclei and 1.40±0.08 for VH nuclei. The spectra of these groups of nuclei are compared and it is found that the average He/M, He/LH and He/VH ratios are 16±1, 70±3 and 200±15 respectively. These values are reasonably constant from the highest down to the lowest energies measured although some evidence for a ‘dip’ is present in the 500–1000 MeV/nuc range for both the He/LH and He/VH ratios. Solar modulation effects on these ratios are discussed and it is concluded that the ratios measured at earth are representative of those existing in interstellar space only if energy loss processes in interplanetary space are unimportant. The influence of interstellar propagation on the spectra and charge ratios at low energies arising from ionization energy loss and nuclear spallation during matter traversal is examined. It is found that propagation models that contain a large number of relatively short path lengths significantly modify the expected effects of ionization energy loss at low energies. Specifically it is suggested that the presently measured charge ratios are consistent with the passage of the average cosmic radiation through enough matter to reproduce the abundances of the so-called fragmentation nuclei, Li, Be, B and He3. Two component models are not required to explain our data. Rather we feel that a better representation of the situation results from considering a continuous spatial distribution of sources which, along with the actual interstellar propagation conditions, leads to a particular distribution of matter path lengths. It is pointed out that large differences exist in the approaches used in the literature to calculate the effects of matter traversal in interstellar space at low energies. These differences play an important role in the interpretation of the experimental results. Significant modifications of the charge ratios at low energies can also be obtained by requiring that some of the matter traversal occur in the cosmic ray sources themselves during the cosmic ray acceleration process. This may be sufficient to produce charge ratios that are essentially flat at low energies even in the presence of interstellar ionization loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubrahmanyan, V. K., Hagge, D. E., Ludwig, G. H., and McDonald, F. B.: 1966,J. Geophys. Res. 71, 1771.
Beck, F. and Yiou, F.: 1968,Astrophys. Letters,1, 75.
Bhatia, V. S., Chohan, V. S., Pabbi, S. D., and Biswas, S.: 1968,Can. J. Phys. 46, S 588.
Cleghorn, T. F.: 1967, M. S. Thesis, Univ. of Minnesota.
Comstock, G. M.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 155, 619.
Comstock, G. M., Fan, C. Y., and Simpson, J. A.: 1966,Astrophys. J. 146, 51.
Comstock, G. M., Fan, C. Y., and Simpson, J. A.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 155, 609.
Cowsik, R., Pal, Yosh, Tandon, S. M., and Verma, R. P.: 1967,Phys. Rev. 158, 1238.
Davis, L.: 1962,Proc. Moscow Ray Conf. 3, 220.
Durgaprasad, N. and Reames, D. V.: 1968,Can. J. Phys. 46, S 749.
Fan, C. Y., Gloeckler, G., and Simpson, J. A.: 1968,Can. J. Phys. 46, S 548.
Fichtel, C. E. and Reames, D. V.: 1968,Phys. Rev. 175, 1564.
Freier, P. S. and Waddington, C. J.: 1968,Phys. Rev. 175, 1641.
Ginzburg, V. L. and Syrovatskii, S. I.: 1964, The Origin of Cosmic Rays, Pergamon Press.
Gleeson, L. J. and Axford, W. I.: 1968,Astrophys. J.,154, 1011.
Gloeckler, G. and Jokipii, J. R.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 148, D41.
Hagge, D. E., Balasubrahmanyan, V. K., and McDonald, F. B.: 1968,Can. J. Phys. 46, S 539.
Ormes, J. F. and Webber, W. R.: 1968,J. Geophys. Res. 73, 4231.
Ramadurai, S.: 1967,Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 65, 219.
Reames, D. V. and Fichtel, C. E.: 1967,Phys. Rev. 162, 1291.
Shapiro, M. M. and Silberberg, R.: 1967,High Energy Nuclear Reactions in Astrophysics, Benjamin, New York.
Von Rosenvinge, T. T. and Webber, W. R.: 1968,Nuc. Inst. Methods 66, 119.
Von Rosenvinge, T. T., Webber, W. R., and Ormes, J. F.: 1969,Astrophys. Space Sci. 3, 4.
Waddington, C. J. and Freier, P. S.: 1968,Phys. Rev. 175, 1649.
Webber, W. R.: 1967, Review paper on Solar Modulation presented at 10th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Calgary, 1967 (unpublished).
Webber, W. R. and Ormes, J. F.: 1967,J. Geophys. Res. 72, 5957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Rosenvinge, T.T., Webber, W.R. & Ormes, J.F. A comparison of the energy spectra of cosmic ray helium and heavy nuclei. Astrophys Space Sci 5, 342–359 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650001
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650001