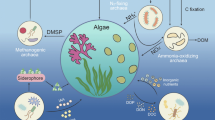
Abstract
Ectohydrolytic enzyme activity (EEA) potential of 37 bacterial isolates derived from Orbicella annularis coral and 2 coral pathogens (Vibrio shilonii and V. coralliilyticus) was measured as model to infer the role of bacteria in organic matter processing within coral reef ecosystems. Bacterial cell-specific activities of eight enzyme types were measured after incubation in organic matter enriched and unenriched filtered seawater. Max value of activities of alkaline phosphatase, oleate-lipase, stearate-lipase and proteinase were 769.3, 327.6, 82.9 and 36.7 amol cell−1 h−1, respectively. Chitinase, α-mannosidase, α-glucosidase and β-glucosidase were generally lower by comparison (max 4.7–20.7 amol cell−1 h−1). No “super” isolates (bacteria expressing high levels of all ectohydrolases) were found suggesting a “specialization” among individual bacterial strains. Cumulatively, the 39 isolates tested displayed a broad range of cell-specific enzyme activities in both organic matter conditions. Culture-independent measurement of coral mucus layer EEA in O. annularis off a Panama reef showed comparable EEA patterns and diversity as the isolates. Volume-specific EEAs of all enzymes except alkaline phosphatase were 8–48 times higher in mucus than in surrounding seawater (SSW) samples. However, cell-specific EEAs in mucus were generally lower than in the SSW partly due to more abundant cells in the mucus than in SSW. For field samples, ≥ 85% of proteinase was cell-bound, while lipase was preferentially dissolved (40–96%). In general, the production of dissolved EEAs varied among measurements depending on sample source and enzyme types, suggesting a potential role of ectoenzyme size distribution in linking the whole reef ecosystem. Our findings support that the cumulative ectoenzyme expression (“ectoenzymome”) of the coral microbiome has the potential to maintain the functional resilience of the coral holobiont and response to stress through its contribution to organic matter processing within coral reef ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaki C, Duke GE (1999) Apparent chitin digestibilities in the Eastern screech owl (Otus asio) and the American kestrel (Falco sparverius). J Exp Zool 283:387–393
Arnosti C (2008) Functional differences between Arctic seawater and sedimentary microbial communities: contrasts in microbial hydrolysis of complex substrates. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:343–351
Arnosti C, Ziervogel K, Ocampo L, Ghobrial S (2009) Enzyme activities in the water column and in shallow permeable sediments from the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 84:202–208
Azam F (1998) Microbial control of oceanic carbon flux: the plot thickens. Science 280:694–695
Bak RP, Joenje M, De Jong I, Lambrechts D, Nieuwland G (1998) Bacterial suspension feeding by coral reef benthic organisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 175:285–288
Barott KL, Rodriguez-Brito B, Janouškovec J, Marhaver KL, Smith JE, Keeling P, Rohwer FL (2011) Microbial diversity associated with four functional groups of benthic reef algae and the reef-building coral Montastraea annularis. Environ Microbiol 13:1192–1204
Bednarz VN, Grover R, Maguer J-F, Fine M, Ferrier-Pagès C (2017) The assimilation of diazotroph-derived nitrogen by scleractinian corals depends on their metabolic status. MBio 8:e02058
Benavides M, Bednarz VN, Ferrier-Pagès C (2017) Diazotrophs: overlooked key players within the coral symbiosis and tropical reef ecosystems? Front Mar Sci 4:10
Bender J, Flieger A (2010) Lipases as pathogenicity factors of bacterial pathogens of humans. In: Timmis KN (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 3241–3258
Ben-Haim Y, Thompson F, Thompson C, Cnockaert M, Hoste B, Swings J, Rosenberg E (2003) Vibrio coralliilyticus sp. nov., a temperature-dependent pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:309–315
Böer S, Arnosti C, Van Beusekom J, Boetius A (2009) Temporal variations in microbial activities and carbon turnover in subtidal sandy sediments. Biogeosciences 6:1149–1165
Bourne D, Iida Y, Uthicke S, Smith-Keune C (2008) Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J 2:350–363
Ceh J, Kilburn MR, Cliff JB, Raina JB, Keulen M, Bourne DG (2013) Nutrient cycling in early coral life stages: Pocillopora damicornis larvae provide their algal symbiont (Symbiodinium) with nitrogen acquired from bacterial associates. Ecol Evol 3:2393–2400
Chróst RJ (1990) Microbial ectoenzymes in aquatic environments. In: Overbeck J, Chróst RJ (eds) Aquat Microb Ecol. Springer, New York, pp 47–78
Cotner J, Ammerman J, Peele E, Bentzen E (1997) Phosphorus-limited bacterioplankton growth in the Sargasso Sea. Aquat Microb Ecol 13:141–149
D’Ambrosio L, Ziervogel K, MacGregor B, Teske A, Arnosti C (2014) Composition and enzymatic function of particle-associated and free-living bacteria: a coastal/offshore comparison. ISME J 8:2167–2179
D’Hondt S, Jørgensen BB, Miller DJ, Batzke A, Blake R, Cragg BA, Cypionka H, Dickens GR, Ferdelman T, Hinrichs K-U (2004) Distributions of microbial activities in deep subseafloor sediments. Science 306:2216–2221
Douglas NL, Mullen KM, Talmage SC, Harvell CD (2007) Exploring the role of chitinolytic enzymes in the sea fan coral, Gorgonia ventalina. Mar Biol 150:1137–1144
Edmunds P (2015) A quarter-century demographic analysis of the Caribbean coral, Orbicella annularis, and projections of population size over the next century. Limnol Oceanogr 60:840–855
Ezzat L, Maguer J-F, Grover R, Ferrier-Pagès C (2016) Limited phosphorus availability is the Achilles heel of tropical reef corals in a warming ocean. Sci Rep 6:1–11
Garren M, Azam F (2010) New method for counting bacteria associated with coral mucus. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6128–6133
Godinot C, Ferrier-Pagès C, Grover R (2009) Control of phosphate uptake by zooxanthellae and host cells in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnol Oceanogr 54:1627–1633
Godinot C, Ferrier-Pagès C, Sikorski S, Grover R (2013) Alkaline phosphatase activity of reef-building corals. Limnol Oceanogr 58:227–234
Guillemette R, Kaneko R, Blanton J, Tan J, Witt M, Hamilton S, Allen EE, Medina M, Hamasaki K, Koch BP, Azam F (2018) Bacterioplankton drawdown of coral mass-spawned organic matter. ISME J 12:2238–2251
Hadaidi G, Gegner HM, Ziegler M, Voolstra CR (2019) Carbohydrate composition of mucus from scleractinian corals from the central Red Sea. Coral Reefs 38:21–27
Hatcher BG (1988) Coral reef primary productivity: a beggar’s banquet. Trends Ecol Evol 3:106–111
Hedges JI (1992) Global biogeochemical cycles: progress and problems. Mar Chem 39:67–93
Hernandez-Agreda A, Leggat W, Bongaerts P, Ainsworth TD (2016) The microbial signature provides insight into the mechanistic basis of coral success across reef habitats. Mbio 7:e00560-e1516
Hernandez-Agreda A, Leggat W, Bongaerts P, Herrera C, Ainsworth TD (2018) Rethinking the coral microbiome: simplicity exists within a diverse microbial biosphere. Mbio 9:e00812-00818
Herrera-Estrella A, Chet I (1999) Chitinases in Biological Control EXS-BASEL 87:171–184
Hoarfrost A, Arnosti C (2017) Heterotrophic extracellular enzymatic activities in the atlantic ocean follow patterns across spatial and depth regimes. Front Mar Sci 4:200
Hoppe HG (1993) Use of fluorogenic model substances for extracellular enzyme activity (EEA) measurement of bacteria. In: Kemp PF, Kemp KF, Sherr BF, Cole JJ, Sherr EB (eds) Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 423–431
Hoppe H-G, Kim S-J, Gocke K (1988) Microbial decomposition in aquatic environments: combined process of extracellular enzyme activity and substrate uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:784–790
Klaus JS, Janse I, Heikoop JM, Sanford RA, Fouke BW (2007) Coral microbial communities, zooxanthellae and mucus along gradients of seawater depth and coastal pollution. Environ Microbiol 9:1291–1305
Kohn AJ (2002) World Atlas of Coral Reefs. Integr Comp Biol 42:408–408
Kushmaro A, Loya Y, Fine M, Rosenberg E (1996) Bacterial infection and coral bleaching. Nature 380:396–396
LaJeunesse TC, Parkinson JE, Gabrielson PW, Jeong HJ, Reimer JD, Voolstra CR, Santos SR (2018) Systematic revision of Symbiodiniaceae highlights the antiquity and diversity of coral endosymbionts. Curr Biol 28:2570–2580
Lee S, Fuhrman JA (1987) Relationships between biovolume and biomass of naturally derived marine bacterioplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1298–1303
Lee S, Davy SK, Tang S-L, Kench PS (2016) Mucus sugar content shapes the bacterial community structure in thermally stressed Acropora muricata. Front Microbiol 7:371
Levitan DR, Fukami H, Jara J, Kline D, McGovern TM, McGhee KE, Swanson CA, Knowlton N (2004) Mechanisms of reproductive isolation among sympatric broadcast-spawning corals of the Montastraea annularis species complex. Evolution 58:308–323
Levitan DR, Boudreau W, Jara J, Knowlton N (2014) Long-term reduced spawning in Orbicella coral species due to temperature stress. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 515:1–10
Louca S, Polz MF, Mazel F, Albright MB, Huber JA, O’Connor MI, Ackermann M, Hahn AS, Srivastava DS, Crowe SA (2018) Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nature Ecology & Evolution 2:936–943
Mahaffey C, Reynolds S, Davis CE, Lohan MC (2014) Alkaline phosphatase activity in the subtropical ocean: insights from nutrient, dust and trace metal addition experiments. Front Mar Sci 1:73
Malfatti F, Lee C, Tinta T, Pendergraft MA, Celussi M, Zhou Y, Sultana CM, Rotter A, Axson JL, Collins DB (2019) Detection of active microbial enzymes in nascent sea spray aerosol: Implications for atmospheric chemistry and climate. Environ Sci Technol Lett 6:171–177
Mao-Jones J, Ritchie KB, Jones LE, Ellner SP (2010) How microbial community composition regulates coral disease development. PLoS Biol 8:e1000345
Martinez J, Smith DC, Steward GF, Azam F (1996) Variability in ectohydrolytic enzyme activities of pelagic marine bacteria and its significance for substrate processing in the sea. Aquat Microb Ecol 10:223–230
Meikle P, Richards G, Yellowlees D (1988) Structural investigations on the mucus from six species of coral. Mar Biol 99:187–193
Naher L, Tan SG, Yusuf UK, Ho CL, Siddiquee S (2012) Activities of chitinase enzymes in the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) in interactions with pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi. Plant Omics 5:333–336
Ochsenkühn MA, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Harir M, Amin SA (2018) Coral metabolite gradients affect microbial community structures and act as a disease cue. Commun Biol 1:1–10
Osman EO, Suggett DJ, Voolstra CR, Pettay DT, Clark DR, Pogoreutz C, Sampayo EM, Warner ME, Smith DJ (2020) Coral microbiome composition along the northern Red Sea suggests high plasticity of bacterial and specificity of endosymbiotic dinoflagellate communities. Microbiome 8:1–16
Peng G, Xue J, Liu W, Xie Y (2009) Role of protease and chitinase of Verticillium lecanii in infecting scale insect cuticle. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 15:220–225
Porter KG (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Pruzzo C, Vezzulli L, Colwell RR (2008) Global impact of Vibrio cholerae interactions with chitin. Environ Microbiol 10:1400–1410
Rädecker N, Pogoreutz C, Voolstra CR, Wiedenmann J, Wild C (2015) Nitrogen cycling in corals: the key to understanding holobiont functioning? Trends Microbiol 23:490–497
Raz-Bahat M, Douek J, Moiseeva E, Peters E, Rinkevich B (2017) The digestive system of the stony coral Stylophora pistillata. Cell Tissue Res 368:311–323
Rohwer F, Kelley S (2004) Culture-independent analyses of coral-associated microbes. In: Rosenberg E, Loya Y (eds) Coral health and disease. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 265–277
Rohwer F, Breitbart M, Jara J, Azam F, Knowlton N (2001) Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi. Coral Reefs 20:85–91
Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Azam F, Knowlton N (2002) Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 243:1–10
Rosenberg E, Koren O, Reshef L, Efrony R, Zilber-Rosenberg I (2007) The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat Rev Micro 5:355–362
Rosenberg E, Kushmaro A, Kramarsky-Winter E, Banin E, Yossi L (2009) The role of microorganisms in coral bleaching. ISME J 3:139–146
Rosset S, Wiedenmann J, Reed AJ, D’Angelo C (2017) Phosphate deficiency promotes coral bleaching and is reflected by the ultrastructure of symbiotic dinoflagellates. Mar Pollut Bull 118:180–187
Rougerie F, Wauthy B (1993) The endo-upwelling concept: from geothermal convection to reef construction. Coral Reefs 12:19–30
Rypien KL, Ward JR, Azam F (2010) Antagonistic interactions among coral-associated bacteria. Environ Microbiol 12:28–39
Sebastian M, Ammerman JW (2009) The alkaline phosphatase PhoX is more widely distributed in marine bacteria than the classical PhoA. ISME J 3:563–572
Smith DC, Simon M, Alldredge AL, Azam F (1992) Intense hydrolytic enzyme activity on marine aggregates and implications for rapid particle dissolution. Nature 359:139–142
Sommer F, Bäckhed F (2013) The gut microbiota—masters of host development and physiology. Nat Rev Micro 11:227–238
Staley TJ, Konopka A (1985) Measurement of in situ activities of nonphotosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Annu Rev Microbiol 39:321–346
Subramoni S, Suárez-Moreno Z, Venturi V (2010) Lipases as pathogenicity factors of plant pathogens. In: Timmis KN (ed) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 3269–3277
Thompson JR, Randa MA, Marcelino LA, Tomita-Mitchell A, Lim E, Polz MF (2004) Diversity and dynamics of a North Atlantic coastal Vibrio community. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4103–4110
Tout J, Siboni N, Messer LF, Garren M, Stocker R, Webster NS, Ralph PJ, Seymour JR (2015) Increased seawater temperature increases the abundance and alters the structure of natural Vibrio populations associated with the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Front Microbiol 6:432
Unanue M, Azúa I, Barcina I, Egea L, Iriberri J (1993) Size distribution of aminopeptidase activity and bacterial incorporation of dissolved substrates in three aquatic ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 11:175–183
Wambeke F, Christaki U, Giannakourou A, Moutin T, Souvemerzoglou K (2002) Longitudinal and vertical trends of bacterial limitation by phosphorus and carbon in the Mediterranean Sea. Microb Ecol 43:119–133
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole- genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Ziervogel K, Arnosti C (2008) Polysaccharide hydrolysis in aggregates and free enzyme activity in aggregate-free seawater from the north-eastern Gulf of Mexico. Environ Microbiol 10:289–299
ZoBell C (1941) Studies on marine bacteria. I. The cultural requirements of heterotrophic aerobes. J Mar Res 42–75
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grant #4827 from Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to FA, Project 42076150 supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) to XM, Project 41877352 (NSFC), Shenzhen Fundamental Research and Discipline Layout project (JCYJ20180507182227257) and the Guangdong MEPP fund (GDOE[2019]A06) to XZ, China Scholarship Council (CSC) and #LMB20191102 from South China Sea Institute of Oceanology Chinese Academy of Sciences to YZ and NSF OCE (1442206) to MM. Lastly, we would like to thank our editor and the reviewers for their great advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. The views expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views or policies of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Any mention of trade names, products, or services does not imply an endorsement by the U.S. Government or the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The EPA does not endorse any commercial products, services, or enterprises.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Topic Editor Steve Vollmer
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Guillemette, R., Malfatti, F. et al. Ectohydrolytic enzyme activities of bacteria associated with Orbicella annularis coral. Coral Reefs 40, 1899–1913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-021-02188-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-021-02188-6