Abstract
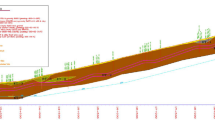
UG1B is the first underground Metro Line under construction in Jaipur which is the capital of Rajastan (India). The twin bore tunnel route pass through the historical centre of the old city of Jaipur called “Pink City”. Significant historical monuments of world’s heritage, such as Hawa Mahal, Jantar Mantar, Isarlat tower, Tripolia Gate (main entrance to the city palace) and Chandpole Gate, are within the greater influence zone of the project. Specifically, the twin bore TBM tunnel passed 4.5 m under the foundation of Chandpole Gate which is one of the main significant historical entrances to the old city, almost 300 years old. The paper addresses the main design aspects of the under-passing of Chandpole Gate in Jaipur by two EPB TBM machines, and introduces the new method which is used for designing these shallow tunnels, by combining the usage of the analytical solution of Massinas and Sakellariou (Géotechnique 59:691–701, 2009) with detailed numerical analysis; the innovative closed form solution has been applied to assess the required support pressure, whereas its results have been used as input to 3-D numerical analyses of tunnel excavation below the Gate to predict induced settlements. The route from the evaluation of the geotechnical model, to the study of the structural and foundation system of the monument, the approach to the necessary tunnel face retaining pressure to be maintained by the EPB machines during under passing and the prediction of the surface and Gate settlement due to tunneling operations is introduced and analyzed. Monitoring of TBM operation parameters and settlement measurements during construction are presented in the form of comparative diagrams and graphs, to illustrate the application of the main design recommendations and verify the design predictions, in terms of applied face pressure and resulting settlements of the Chandpole Gate. Comparison has shown that main recommendations, as derived from the new proposed method of design and followed during the tunnelling operations, resulted to a successful under-passing of Chandpole Gate, with induced settlements within the predicted, permissible limits.

(Source www.mapsofindia.com)







Reproduced with permission from (Massinas and Sakellariou 2009)

Reproduced with permission from (Massinas and Sakellariou 2009)




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostou G, Kovári K (1994) The face stability of slurry-shield-driven tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 9:165–174
Anagnostou G, Kovári K (1996) Face stability conditions with earth-pressure-balanced shields. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 11:165–174
Atkinson JH, Potts DM (1977) Stability of a shallow circular tunnel in cohesionless soil. Géotechnique 27:203–215
Broms BB, Bennermark H (1967) Stability of clay at vertical openings. J Soil Mech Found Div 93(SM1):71–95
Burd HJ, Houlsby GT, Augarde CE, Liu G (2000) Modelling tunnelling-induced settlement of masonry buildings. Proc Inst Civil Eng Geotech Eng 143(1):17–29
Burghignoli A, Di Paola F, Jamiolkowski M, Simonacci G (2010) New rome metro line C: approach for safe-guarding ancient monuments. In: Invited lecture, international conference on geotechnical challenges in megacities, Moscow, pp 1–24
Chambon P, Corté JF (1994) Shallow tunnels in cohesionless soil: stability of tunnel face. J Geotech Eng 120:1148–1165
Chen RP, Tang LJ, Ling DS, Chen YM (2011) Face stability analysis of shallow shield tunnels in dry sandy ground using the discrete element method. Comput Geotech 38(2):187–195
Davis EH, Gunn MJ, Mair RJ, Seneviratne HN (1980) The stability of shallow tunnels and underground openings in cohesive material. Géotechnique 30:397–416
Detournay E, St. John CM (1988) Design charts for a deep circular tunnel under non-uniform loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 21(2):119–137
Giardina G, DeJong MJ, Mair RJ (2015) Interaction between surface structures and tunnelling in sand: centrifuge and computational modelling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 50:465–478
Horn M (1961) Horizontaler Erddruck auf senkrechte Abschlussflaechen von Tunneln. Landeskonferenz der ungarischen Tiefbauindustrie (German translation by STUVA, Düsseldorf)
Jeffery GB (1920) Plane stress and plane strain in bipolar coordinates. Trans R Soc Lond Engl Ser A 221(1920):265–293
Kim SH, Tonon F (2010) Face stability and required support pressure for TBM driven tunnels with ideal face membrane: drained case. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 25(5):526–542
Kimura T, Mair RJ (1981) Centrifugal testing of model tunnels in soft soil. In: Publications Committee of X.ICSMEE (eds) Proceedings of the 10th international conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Stockholm, Balkema, Rotterdam, vol 1, pp 319–322
Leca E, Dormieux L (1990) Upper and lower bound solutions for the face stability of shallow circular tunnels in frictional material. Géotechnique 40(4):581–606
Liu G (1997) Numerical modelling of damage to masonry buildings due to tunnelling. In: Ph.D. Thesis, Oxford University, Oxford
Massinas S, Sakellariou MG (2006) A parametric study of the tunnelling-induced surface settlements under 3D conditions. In: 2nd international conference on from scientific computing to computational engineering, 2nd IC-SCCE, Athens, 5–8 July 2006, Greece
Massinas S, Sakellariou MG (2009) Closed-form solution for plastic zone formation around a circular tunnel in half-space obeying Mohr-Coulomb criterion. Géotechnique 59(8):691–701
Massinas S, Sakellariou MG (2010) Feasibility study for tunnel-building interaction by using the analytic solution for a circular tunnel in an elastic-plastic half space. In: Petrukhin, Ulitsky, Kolybin, Lisyuk, Kholmyansky (eds) Proceedings of the international geotechnical conference on “Geotechnical Challenges in Megacities”, Moscow, June 2010, Russia, vol 3, GRF 190005, St. Petersburg, pp 751–757
Massinas S, Singh D, Saini MIS, Bhardwaj V, Aishwarya K (2015) Settlement analysis and monitoring instrumentation of Delhi Metro’s operational Line-2 tunnels during TBM, of new Line-8, underpass. In: ITA world tunnel congress, Dubrovnik, May 2015, Croatia
Migliazza M, Chiorboli M, Giani GP (2009) Comparison of analytical method, 3D finite element model with experimental subsidence measurements resulting from the extension of the Milan underground. J Comput Geotech 36(1–2):113–124
Mirhabibi A, Soroush A (2012) Effects of surface buildings on twin tunnelling-induced ground settlements. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 29:40–51
Mollon G, Dias D, Soubra AH (2009) Probabilistic analysis and design of circular tunnels against face stability. Int J Geomech 9(6):237–249
Murayama S, Endo M, Hashiba T, Yamamoto K, Sasaki H (1966) Geotechnical aspects for the excavating performance of the shield mashines. In: The 21st annual lecture in meeting of Japan Society of Civil Engineers
Potts D, Addenbrooke TI (1997) A structure’s influence tunneling-induced ground movements. Geotech Eng 125(2):109–125
Prountzopoulos G (2012) Investigation of the excavation face stability in shallow tunnels. In: Doctoral thesis. National Technical University of Athens (NTUA), School of Civil Engineering (In Greek)
Rampello S, Callisto L, Viggianni G, Soccodato FM (2012) Evaluating the effects of tunnelling on historical buildings: the example of a new subway in Rome. Geomech Tunn 5(3):275–299
Savin GN (1961) Stress Concentration around Holes”, Pergamon Press
Strack OE (2002) Analytic solutions of elastic tunneling problems. In: PhD thesis, Delft University Press, Delft
Vermeer PA, Ruse N, Marcher T (2002) Tunnel heading stability in drained ground. Felsbau 20(6):8–18
Acknowledgements
The authors of the present study would like to express their gratitude to Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation (JMRC) and the general contractor Continental Engineering Corporation (CEC) and especially the TBM team, for providing us with the essential information during elaboration of the present study. The authors would like also to express their special gratitude to Mr. Gabriele Tidone (First Project Director of CEC) for his valuable support and guidance during the elaboration of the design.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massinas, S., Prountzopoulos, G.K., Bhardwaj, V. et al. Design Aspects of Under-Passing a City’s Heritage Landmark with EPB Machines Under Low Overburden; The Case of Chandpole Gate in Jaipur Metro, India. Geotech Geol Eng 36, 3683–3705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0565-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0565-0