Abstract
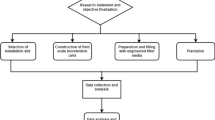
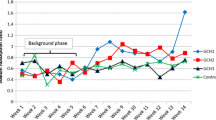
The TREENET inlet is an emerging water-sensitive urban design technology that consists of a novel kerb side inlet coupled with a leaky well infiltration system. The inlets have been retrofitted to existing roads since 2006; however, there is currently little information available on the effectiveness of these inlet and leaky well systems. This study investigated the performance of the kerb side inlets and leaky well system for water quality improvement prior to infiltration to native soil. The leaky wells included four filter media types, namely gravel, water treatment solids, sandy loam and clay. To compare the performance of the four filter media types, batch and column studies were performed in the laboratory. The best performance was observed using the sandy loam as a filter media, followed by clay, water treatment solids and then gravel. The selection of effective media for removal of heavy metals is important as each media type has different pollutant removal capacity, infiltration and clogging performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahiablame LM, Engel BA, Chaubey I (2013) Effectiveness of low impact development practices in two urbanized watersheds: retrofitting with rain barrel/cistern and porous pavement. J Environ Manag 119:151–161
ANZECC, ARMCANZ (2000) Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh and marine water quality. The Guidelines Australian Water Association, Artarmon, p 314
Ashworth DJ, Alloway BJ (2004) Soil mobility of sewage sludge-derived dissolved organic matter, copper, nickel and zinc. Environ Pollut 127:137–144
ASTM (2008) Standard test method for 24-h batch-type measurement of contaminant sorption by soils and sediments. D4646-03
Beecham S, Chowdhury R (2012) Effects of changing rainfall patterns on WSUD in Australia. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers. Water Management 165:285–285
Bond NR, Lake PS, Arthington AH (2008) The impacts of drought on freshwater ecosystems: an Australian perspective. Hydrobiologia 600:3–16
Boyd MJ, Bufill MC, Knee RM (1993) Pervious and impervious runoff in urban catchments. Hydrol Sci J 38:463–478
Bravin MN, Garnier C, Lenoble V, Gérard F, Dudal Y, Hinsinger P (2012) Root-induced changes in pH and dissolved organic matter binding capacity affect copper dynamic speciation in the rhizosphere. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 84:256–268
Brien CJ (2018) ASremlPlus: Augments the use of ASreml-R in fitting mixed models. https://github.com/briencj/asremlPlus
Butler D, Cullis B, Gilmour A, Gogel B (2009) Analysis of mixed models for S-language environments: ASreml-R Reference Manual. Queensland DPI, Brisbane, Australia
Chen G, Zeng G, Du C, Huang D, Tang L, Wang L, Shen G (2010) Transfer of heavy metals from compost to red soil and groundwater under simulated rainfall conditions. J Hazard Mater 181:211–216
City of Austin (1994) Developments in sand filter technology to improve stormwater runoff quality. In: Techniques WP (Hrsg.). The City of Austin, Texas, pp. 47–54
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Ni S (2001a) Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 44:997–1009
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Sharma H, Minami C (2001b) Laboratory study of biological retention for urban stormwater management. Water Environ Res 73:5–14
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Sharma H, Minami C, Winogradoff D (2003) Water quality improvement through bioretention: lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ Res 75:73–82
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Sharma H, Minami C (2006) Water quality improvement through bioretention media: nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Water Environ Res 78:284–293
Drapper D, Tomlinson R, Williams P (2000) Pollutant concentration in road runoff: Southeast Queensland case study. J Environ Eng 126:314–320
Dunphy AJ, Beecham SC, Vigneswaran S, Ngo HH, McLaughlan RG, Collins A (2006) Development of a confined water sensitive urban design (WSUD) system using engineered soils, 7th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling and the 4th International Conference on Water Sensitive Urban Design; Book of Proceedings. Monash University, pp. 596
Ellis J, Lundy L (2016) Implementing sustainable drainage systems for urban surface water management within the regulatory framework in England and Wales. J Environ Manag 183:630–636
Fan J, He Z, Ma LQ, Yang Y, Yang X, Stoffella PJ (2011) Immobilization of copper in contaminated sandy soils using calcium water treatment residue. J Hazard Mater 189:710–718
Gong C, Donahoe R (1996) An experimental study of heavy metal attenuation and mobility in sandy loam soils. Appl Geochem 12:243–254
Hatt BE, Deletic A, Fletcher TD (2007a) Stormwater reuse: designing biofiltration systems for reliable treatment. Water Sci Technol 55:201–209
Hatt BE, Fletcher TD, Deletic A (2007b) Treatment performance of gravel filter media: implications for design and application of stormwater infiltration systems. Water Res 41:2513–2524
Hidalgo AM, Murcia MD, Gomez E, Garcia-Izquierdo C, Solano C (2017) Possible uses for sludge from drinking water treatment plants. J Environ Eng 143:1–7
Hsieh C, Davis A (2005) Evaluation and optimization of bioretention media for treatment of urban storm water runoff. J Environ Eng 131:1521–1531
Jayasuriya LNN, Kadurupokune N, Othman M, Jesse K (2007) Managing stormwater productivity using pervious pavements, NOVATECH-2007 6th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management. NOVATECH, Lyon, France
Johnson T, Lawry D, Sapdhare H (2016) The council verge as the next wetland: TREENET and the cities of Mitcham and Salisbury investigate. 29th International Horticultural Congress on Horticultural : Sustaining Lives, Livelihoods and Landscapes 1:63–69
Kondili E, Kaldellis JK, Papapostolou C (2010) A novel systemic approach to water resources optimisation in areas with limited water resources. Desalination 250:297–301
Lehman RM, Mills AL (1994) Field evidence for copper mobilization by dissolved organic matter. Water Res 28:2487–2497
Leterme SC, Allais L, Jendyk J, Hemraj DA, Newton K, Mitchell J, Shanafield M (2015) Drought conditions and recovery in the Coorong wetland, south Australia in 1997–2013. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 163:175–184
Lin L, Xu X, Papelis C, Cath TY, Xu P (2014) Sorption of metals and metalloids from reverse osmosis concentrate on drinking water treatment solids. Sep Purif Technol 134:37–45
Mao L, Young SD, Bailey EH (2015) Lability of copper bound to humic acid. Chemosphere 131:201–208
Mesquita ME, Carranca C (2005) Effect of dissolved organic matter on copper - zinc competitive adsorption by a sandy soil at different pH values. Environ Technol 26:1065–1072
Mouni L, Merabet D, Robert D, Bouzaza A (2009) Batch studies for the investigation of the sorption of the heavy metals Pb2+ and Zn2+ onto Amizour soil (Algeria). Geoderma 154:30–35
Myers B, Beecham S, van Leeuwen J (2011) Water quality with storage in permeable pavement basecourse. Proc Inst Civ Eng Water Manag 164:361–372
Niemczynowicz J (1999) Urban hydrology and water management – present and future challenges. Urban Water 1:1–14
NRMMC, EPHC, AHMC NRMMC, Environment Protection and Heritage Council and Australian Health Minister Conference (2006) Australian guidelines for water recycling: managing health and environmental risks (Phase-1), Canberra
O’Neill SW, Davis AP (2012) Water treatment residual as a bioretention amendment for phosphorus. I: evaluation studies. J Environ Eng 138:318–327
Pavelic P, Dillon PJ, Mucha M, Nakai T, Barry KE, Bestland E (2011) Laboratory assessment of factors affecting soil clogging of soil aquifer treatment systems. Water Res 45:3153–3163
Phillips IR, Lamb DT, Hawker DW, Burton ED (2004) Effects of pH and salinity on copper, lead, and zinc sorption rates in sediments from Moreton Bay, Australia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73:1041–1048
Pitt R, Field R, Lalor M, Brown M (1995) Urban stormwater toxic pollutants: assessment, sources, and treatability. Water Environ Res 67:260–275
Pyke C, Warren MP, Johnson T, LaGro J Jr, Scharfenberg J, Groth P, Freed R, Schroeer W, Main E (2011) Assessment of low impact development for managing stormwater with changing precipitation due to climate change. Landsc Urban Plan 103:166–173
R Core Team (2018) A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.https://www.R-project.org/
Reddy KR, Xie T, Dastgheibi S (2014) Removal of heavy metals from urban stormwater runoff using different filter materials. J Environ Chem Eng 2:282–292
Siemens G, Bathurst RJ (2010) Numerical parametric investigation of infiltration in one-dimensional sand–geotextile columns. Geotext Geomembr 28:460–474
Soleimanifar H, Deng Y, Wu L, Sarkar D (2016) Water treatment residual (WTR)-coated wood mulch for alleviation of toxic metals and phosphorus from polluted urban stormwater runoff. Chemosphere 154:289–292
Tang Q, Wang H, Chen H, Tang X (2015) A characterization study of hydraulic conductivity of compacted clay and fine sand treated with landfill leachate and nutrient solution. Electron J Geotech Eng 20:1–14
Vijayakumar G, Tamilarasan R, Dharmendrirakumar M (2012) Adsorption, kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on the removal of basic dye Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution by the use of natural adsorbent perlite. J Mater Environ Sci 3:157–170
Walsh CJ, Roy AH, Feminella JW, Cottingham PD, Groffman PM, Morgan RP (2005) The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:706–723
Wella-Hewage CS, Alankarage Hewa G, Pezzaniti D (2016) Can water sensitive urban design systems help to preserve natural channel-forming flow regimes in an urbanised catchment? Water Sci Technol 73:78–87
Whiting J (2008) Drought kills trees across Mitcham Hills. Eastern Courier, South Australia
Xu J, Tan W, Xiong J, Wang M, Fang L, Koopal LK (2016) Copper binding to soil fulvic and humic acids: NICA-Donnan modeling and conditional affinity spectra. J Colloid Interface Sci 473:141–151
Zhou LX, Wong JWC (2001) Effect of dissolved organic matter from sludge and sludge compost on soil copper sorption. J Environ Qual 30:878–883
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge and appreciate the support of the Australian Government Research Training Program, the Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges Natural Resources Management Board, the City of Mitcham, the Environment Protection Authority South Australia, the University of South Australia and TREENET Incorporated.
Funding
The authors are grateful for funding received from the Australian Research Council under grant LP120200678 including the collaboration and funding from the industry partner for this grant, Sunshine Coast Regional Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sapdhare, H., Myers, B., Beecham, S. et al. Performance of a kerb side inlet to irrigate street trees and to improve road runoff water quality: a comparison of four media types. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 33995–34007 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3083-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3083-y