Abstract
This paper investigates the relationship between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in the G-7 countries from a historical perspective. To this end, taking time-varying interaction and business cycle into account, we use the historical decomposition method for the first time in the literature. Our results provide evidence that Canada, Italy, Japan and partly the USA need to sacrifice economic growth if they aim to reduce CO2 emissions by decreasing fossil-based energy use. This situation is not valid since the early 1990s for France, throughout the analysis period for Germany and a few exceptions in all periods for the UK. Furthermore, empirical results provide evidence contrary to the EKC hypothesis for Canada, Germany, Japan, the UK and the USA. We found BC-shaped and N-shaped curves for France and Italy, respectively. Although the EKC hypothesis is not valid for Germany and the UK, economic growth has no damaging effect on environmental quality. Also, this effect seems to be cyclical for the USA.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
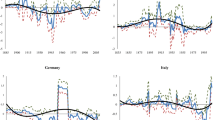
Although there seems to be a difference between our calculation and World Bank data regarding CO2 emissions per capita, both data moved together exactly after 1991, which is the beginning year of the World Bank data. It is clear that this small detail is of no significance considering the 30-year data gain for Germany.
These explanations are valid for the same figures shown below for the other countries.
The shape of the relationship with respect to the per capita output is indirectly inferred from the observation that the per capita output was increasing through the study period.
References
Acaravci, A., & Ozturk, I. (2010). On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy, 35(12), 5412–5420.
Ahmad, A., Zhao, Y., Shahbaz, M., Bano, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, S., et al. (2016). Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: An aggregate and disaggregate analysis of the Indian economy. Energy Policy, 96, 131–143.
Akarca, A. T., & Long, T. V. (1980). On the relationship between energy and GNP: A reexamination. The Journal of Energy and Development, 5(2), 326–331.
Akbostancı, E., Türüt-Aşık, S., & Tunç, Gİ. (2009). The relationship between income and environment in Turkey: Is there an environmental Kuznets curve? Energy Policy, 37(3), 861–867.
Alam, M. J., Begum, I. A., Buysse, J., Rahman, S., & Van Huylenbroeck, G. (2011). Dynamic modeling of causal relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in India. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(6), 3243–3251.
Al-mulali, U., & Che Sab, C. N. B. (2018). Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and development in the UAE. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning and Policy, 13(4), 1–6.
Al-Mulali, U., & Ozturk, I. (2016). The investigation of environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the advanced economies: The role of energy prices. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 54, 1622–1631.
Ang, J. B. (2007). CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy, 35(10), 4772–4778.
Antonakakis, N., Chatziantoniou, I., & Filis, G. (2017). Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: An ethical dilemma. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 68, 808–824.
Apergis, N., Christou, C., & Gupta, R. (2017). Are there Environmental Kuznets Curves for US state-level CO2 emissions? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69, 551–558.
Apergis, N., & Payne, J. E. (2009). Energy consumption and economic growth in Central America: Evidence from a panel cointegration and error correction model. Energy Economics, 31(2), 211–216.
Apergis, N., & Payne, J. E. (2010). Renewable energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from a panel of OECD countries. Energy Policy, 38(1), 656–660.
Appiah, M. O. (2018). Investigating the multivariate Granger causality between energy consumption, economic growth and CO 2 emissions in Ghana. Energy Policy, 112, 198–208.
Aslan, A., Destek, M. A., & Okumus, I. (2018). Bootstrap rolling window estimation approach to analysis of the Environment Kuznets Curve hypothesis: Evidence from the USA. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(3), 2402–2408.
Bakirtas, T., & Akpolat, A. G. (2018). The relationship between energy consumption, urbanization, and economic growth in new emerging-market countries. Energy, 147, 110–121.
Balcilar, M., & Ozdemir, Z. A. (2013a). The export-output growth nexus in Japan: A bootstrap rolling window approach. Empirical Economics, 44(2), 639–660.
Balcilar, M., & Ozdemir, Z. A. (2013b). The causal nexus between oil prices and equity market in the US: A regime switching model. Energy Economics, 39, 271–282.
Balcilar, M., & Ozdemir, Z. A. (2013c). Asymmetric and time-varying causality between inflation and inflation uncertainty in G-7 countries. Scottish Journal of Political Economy, 60(1), 1–42.
Balcilar, M., & Ozdemir, Z. A. (2019). The nexus between the oil price and its volatility risk in a stochastic volatility in the mean model with time-varying parameters. Resources Policy, 61, 572–584.
Balcilar, M., Ozdemir, Z. A., & Arslanturk, Y. (2010). Economic growth and energy consumption causal nexus viewed through a bootstrap rolling window. Energy Economics, 32(6), 1398–1410.
Balcilar, M., Ozdemir, Z. A., Ozdemir, H., & Shahbaz, M. (2018). The renewable energy consumption and growth in the G-7 countries: Evidence from historical decomposition method. Renewable Energy, 126, 594–604.
Balcilar, M., Ozdemir, Z. A., & Shahbaz, M. (2019). On the time-varying links between oil and gold: New insights from the rolling and recursive rolling approaches. International Journal of Finance & Economics, 24, 1047–1065. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijfe.
Balcilar, M., Ozdemir, Z. A., & Yetkiner, H. (2014). Are there really bubbles in oil prices? Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 416, 631–638.
Bayramoglu, A. T., & Yildirim, E. (2017). The relationship between energy consumption and economic growth in the USA: A non-linear ARDL bounds test approach. Energy and Power Engineering, 9(03), 170.
Bekhet, H. A., & Othman, N. S. (2018). The role of renewable energy to validate dynamic interaction between CO2 emissions and GDP towards sustainable development in Malaysia. Energy Economics, 72, 47–61.
Bildirici, M. E., & Gökmenoğlu, S. M. (2017). Environmental pollution, hydropower energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from G7 countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 75, 68–85.
Bilgili, F., Koçak, E., & Bulut, Ü. (2016). The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: A revisited environmental Kuznets curve approach. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 54, 838–845.
Chen, P. Y., Chen, S. T., Hsu, C. S., & Chen, C. C. (2016). Modeling the global relationships among economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 65, 420–431.
Chontanawat, J., Hunt, L. C., & Pierse, R. (2006). Causality between energy consumption and GDP: Evidence from 30 OECD and 78 non-OECD countries (No. 113). Surrey Energy Economics Centre (SEEC), School of Economics, University of Surrey.
Cole, M. A., Rayner, A. J., & Bates, J. M. (1997). The environmental Kuznets curve: An empirical analysis. Environment and Development Economics, 2(4), 401–416.
Day, K. M., & Grafton, R. Q. (2003). Growth and the environment in Canada: An empirical analysis. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue canadienne d’agroeconomie, 51(2), 197–216.
De Bruyn, S. M., van den Bergh, J. C., & Opschoor, J. B. (1998). Economic growth and emissions: Reconsidering the empirical basis of environmental Kuznets curves. Ecological Economics, 25(2), 161–175.
Destek, M. A., & Aslan, A. (2017). Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth in emerging economies: Evidence from bootstrap panel causality. Renewable Energy, 111, 757–763.
Dogan, E., & Ozturk, I. (2017). The influence of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and real income on CO2 emissions in the USA: Evidence from structural break tests. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(11), 10846–10854.
Dogan, E., & Turkekul, B. (2016). CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: Testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(2), 1203–1213.
Eden, S. H., & Hwang, B. K. (1984). The relationship between energy and GNP: Further results. Energy Economics, 6(3), 186–190.
Efron, B. (1982). The jackknife, the bootstrap, and other resampling plans (Vol 38). Philadelphia: SIAM.
Erol, U., & Yu, E. S. (1987). On the causal relationship between energy and income for industrialized countries. The Journal of Energy and Development, 13(1), 113–122.
Fang, Z., & Chang, Y. (2016). Energy, human capital and economic growth in Asia Pacific countries—Evidence from a panel cointegration and causality analysis. Energy Economics, 56, 177–184.
Ghali, K. H., & El-Sakka, M. I. (2004). Energy use and output growth in Canada: A multivariate cointegration analysis. Energy economics, 26(2), 225–238.
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1991). Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement (No. w3914). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1995). Economic growth and the environment. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 110(2), 353–377.
Halicioglu, F. (2009). An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy, 37(3), 1156–1164.
Jebli, M. B., Youssef, S. B., & Ozturk, I. (2016). Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecological Indicators, 60, 824–831.
Katircioglu, S., Katircioglu, S., & Kilinc, C. C. (2018). Investigating the role of urban development in the conventional environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from the globe. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 1–7.
Kilian, L., & Lütkepohl, H. (2017). Structural vector autoregressive analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kourtzidis, S. A., Tzeremes, P., & Tzeremes, N. G. (2018). Re-evaluating the energy consumption-economic growth nexus for the United States: An asymmetric threshold cointegration analysis. Energy, 148, 537–545.
Kraft, J., & Kraft, A. (1978). On the relationship between energy and GNP. The Journal of Energy and Development, 3(2), 401–403.
Lee, C. C. (2006). The causality relationship between energy consumption and GDP in G-11 countries revisited. Energy Policy, 34(9), 1086–1093.
Lütkepohl, H. (2005). New introduction to multiple time series analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Menegaki, A. N., & Tugcu, C. T. (2017). Energy consumption and Sustainable Economic Welfare in G7 countries; A comparison with the conventional nexus. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69, 892–901.
Mutascu, M. (2016). A bootstrap panel Granger causality analysis of energy consumption and economic growth in the G7 countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 63, 166–171.
Narayan, P. K., Saboori, B., & Soleymani, A. (2016). Economic growth and carbon emissions. Economic Modelling, 53, 388–397.
Narayan, S., & Doytch, N. (2017). An investigation of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth nexus using industrial and residential energy consumption. Energy Economics, 68, 160–176.
Olale, E., Ochuodho, T. O., Lantz, V., & El Armali, J. (2018). The environmental Kuznets curve model for greenhouse gas emissions in Canada. Journal of Cleaner Production, 184, 859–868.
Ouyang, Y., & Li, P. (2018). On the nexus of financial development, economic growth, and energy consumption in China: New perspective from a GMM panel VAR approach. Energy Economics, 71, 238–252.
Ozatac, N., Gokmenoglu, K. K., & Taspinar, N. (2017). Testing the EKC hypothesis by considering trade openness, urbanization, and financial development: The case of Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(20), 16690–16701.
Ozokcu, S., & Ozdemir, O. (2017). Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 639–647.
Pablo-Romero, M. P., Cruz, L., & Barata, E. (2017). Testing the transport energy-environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in the EU27 countries. Energy Economics, 62, 257–269.
Pao, H. T., & Tsai, C. M. (2010). CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in BRIC countries. Energy Policy, 38(12), 7850–7860.
Phillips, P. C. (1987). Time series regression with a unit root. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 55(2), 277–301.
Phillips, P. C., & Perron, P. (1988). Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika, 75(2), 335–346.
Rafindadi, A. A., & Ozturk, I. (2017). Impacts of renewable energy consumption on the German economic growth: Evidence from combined cointegration test. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 75, 1130–1141.
Rodríguez-Caballero, C. V., & Ventosa-Santaulària, D. (2017). Energy-growth long-term relationship under structural breaks. Evidence from Canada, 17 Latin American economies and the USA. Energy Economics, 61, 121–134.
Saboori, B., Sapri, M., & Bin Baba, M. (2014). Economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development)’s transport sector: A fully modified bi-directional relationship approach. Energy, 66, 150–161.
Saidi, K., & Mbarek, M. B. (2017). The impact of income, trade, urbanization, and financial development on CO 2 emissions in 19 emerging economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(14), 12748–12757.
Saidi, K., Rahman, M. M., & Amamri, M. (2017). The causal nexus between economic growth and energy consumption: New evidence from global panel of 53 countries. Sustainable Cities and Society, 33, 45–56.
Selden, T. M., & Song, D. (1994). Environmental quality and development: Is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 27(2), 147–162.
Shafik, N. (1994). Economic development and environmental quality: An econometric analysis. Oxford Economic Papers, 46, 757–773.
Shafik, N., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (1992). Economic growth and environmental quality: Time-series and cross-country evidence (Vol. 904). Washington: World Bank Publications.
Shahbaz, M., Balcilar, M., & Ozdemir, Z. A. (2017). Does oil predict gold? A nonparametric causality-in-quantiles approach. Resources Policy, 52, 257–265.
Shahbaz, M., Zakaria, M., Shahzad, S. J. H., & Mahalik, M. K. (2018). The energy consumption and economic growth nexus in top ten energy-consuming countries: Fresh evidence from using the quantile-on-quantile approach. Energy Economics, 71, 282–301.
Soytas, U., & Sari, R. (2003). Energy consumption and GDP: Causality relationship in G-7 countries and emerging markets. Energy Economics, 25(1), 33–37.
Soytas, U., Sari, R., & Ewing, B. T. (2007). Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecological Economics, 62(3–4), 482–489.
Tamazian, A., Chousa, J. P., & Vadlamannati, K. C. (2009). Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: Evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy, 37(1), 246–253.
Tang, C. F., Tan, B. W., & Ozturk, I. (2016). Energy consumption and economic growth in Vietnam. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 54, 1506–1514.
Tiba, S., & Omri, A. (2017). Literature survey on the relationships between energy, environment and economic growth. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69, 1129–1146.
UN. (2017). The sustainable development goals report 2017. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/files/report/2017/TheSustainableDevelopmentGoalsReport2017.pdf.
Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Lu, A., Li, L., He, Y., ToJo, J., et al. (2017). A disaggregated analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve for industrial CO2 emissions in China. Applied Energy, 190, 172–180.
Wu, Y., & Yan, H. (2018). The decoupling analysis between regional building energy consumption and economic growth in China. In Proceedings of the 21st international symposium on advancement of construction management and real estate (pp. 1385–1395). Springer, Singapore.
Yang, G., Sun, T., Wang, J., & Li, X. (2015). Modeling the nexus between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy, 86, 104–117.
Zaman, K., & Abd-el Moemen, M. (2017). Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and economic development: Evaluating alternative and plausible environmental hypothesis for sustainable growth. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 74, 1119–1130.
Zhang, X. P., & Cheng, X. M. (2009). Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecological Economics, 68(10), 2706–2712.
Zhang, Q., Sornette, D., Balcilar, M., Gupta, R., Ozdemir, Z. A., & Yetkiner, H. (2016). LPPLS bubble indicators over two centuries of the S&P 500 index. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 458, 126–139.
Zoundi, Z. (2017). CO2 emissions, renewable energy and the environmental Kuznets curve, A panel cointegration approach. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 1067–1075.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balcilar, M., Ozdemir, Z.A., Tunçsiper, B. et al. On the nexus among carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in G-7 countries: new insights from the historical decomposition approach. Environ Dev Sustain 22, 8097–8134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00563-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00563-6