Abstract
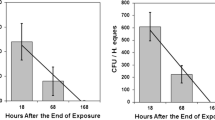
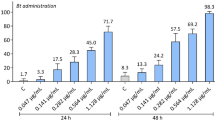
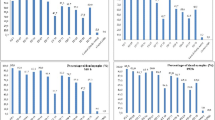
Microbial pest control agents or entomopathogens have been considered an interesting alternative to use instead of chemical insecticides. Knowledge of ecotoxicity data is very important to predict the hazard of any product released in the environment and subsidize the regulation of these products by governmental agencies. In the present study four new Brazilian strains of Bacillus and one fungus were tested to evaluate their acute toxicity to the microcrustacean Daphnia similis, the snail Biomphalaria glabrata and the dung beetle Digitonthophagus gazella. The microcrustaceans and the snails were exposed to entomopathogens in synthetic softwater and the beetles were exposed directly in cattle dung. Obtained data reveal low susceptibility of the non-target species to tested microorganisms, with lethal concentrations being observed only at much higher concentrations than that effective against target insects. These results show that the tested strains are selective in their action mode and seem to be non-hazardous to non-target species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison JA (1993) Persistence and nontarget effects of Bacillus thuringiensis in soil: a review. Can J For Res 23:2329–2342
Alves RT, Silva EAF, Sousa KM, Oliveira MAS, Pereira AV, Pereira EBC, Junqueira NTV, Icuma IM (2003) Controle biológico do percevejo-de-renda da seringueira com o uso de micoinseticida formulado em óleo emulsionável. Boletim de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento nº 113, Embrapa Cerrados, Planaltina, DF. http://bbeletronica.cpac.embrapa.br/2003/bolpd/bolpd_113.pdf. Accessed 15 April 2008
ABNT, Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2004). Ecotoxicologia aquática—Toxicidade aguda—Método de ensaio com Daphnia spp. (Cladocera, Crustacea). NBR 12713. ABNT, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Boisvert M, Boisvert J (2000) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis on target and nontarget organisms: a review of laboratory and field experiments. Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:517–561
Castro VLSS, Jonsson CM, Melo IS, Nunes FV (2001) Avaliação de risco ecotoxicológico de Trichoderma stromaticum usado como biopesticida. Ecotoxicol Environ Rest 4:18–24
Charles JF, Nielsen-LeRoux C, Delécluse A (1996) Bacillus sphaericus toxins: molecular biology and mode of action. Ann Rev Entomol 41:451–472
Diaz MP, Macias AF, Navarro SR, De La Torres M (2006) Mechanism of action of entomopathogenic fungi. Interciencia 31:856–860
Genthner FJ, Cripe GM, Crosby DJ (1994) Effect of Beauveria bassiana and its toxins on Mysidopsis bahia (Mysidacea). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 26:90–94
Genthner FJ, Chancy CA, Couch JA, Foss SS, Middaugh DP, George SE, Warren MA, Bantle JA (1998) Toxicity and pathogenicity testing of the insect pest control fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35:317–324
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman–Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Ignoffo CM (1973) Effects of entomopathogens on vertebrates. Ann NY Acad Sci 217:141–172
Jonsson CM, Genthner FJ (1997) Avaliação do potencial de patogenicidade e toxicidade do fungo entomopatógeno Colletotrichum gloeosporioides isolado de Orthezia em duas espécies de crustáceos. Boletim de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento nº1. Embrapa Meio Ambiente, Jaguariúna
Knowles BH (1994) Mechanisms of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal δ-endotoxins. In: Evans PD (ed) Advances in insect physiology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 275–308
Lacey LA, Mulla MS (1990) Safety of Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus to nontarget organisms in the aquatic environment. In: Laird M, Lacey L, Davidson E (eds) Safety of microbial insecticides. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 169–188
Lacey LA, Siegel JP (2000) Safety and ecotoxicology of entomopathogenic bacteria. In: Charles JF, Delécluse A, Nielsen-LeRoux C (eds) Entomopathogenic bacteria: from laboratory to field application. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 253–273
Martins EC, Praça LB, Dumas VF, Silva-Werneck JO, Sone EH, Waga IC, Berry C, Monnerat RG (2007) Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates toxic to cotton boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis). Biol Control 40:65–68
Mathavan S, Velpandi A (1984) Toxicity of Bacillus sphaericus strains to selected target and non-target aquatic organisms. Indian J Med Res 80:653–657
Menon AS, Mestral J (1985) Survival of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki in waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 25:265–274
Merritt RW, Walker ED, Wilzbach MA, Cummins KW, Morgan WT (1989) A broad evaluation of Bti for black fly (Diptera: Simuliidae) control in a Michigan river: efficacy, carry and nontarget effects on invertebrates and fish. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 5:397–415
Monnerat RG, Silva S, Dias D, Martins E, Praça L, Jones G, Soares CM, Dias JMCS, Berry C (2004) Screening of high toxic Brazilian Bacillus sphaericus strains against Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti. J Appl Entomol 128:469–473
Monnerat RG, Dias D, Silva S, Martins E, Berry C, Falcão R, Gomes AMM, Praça L, Soares CM (2005) Screening of Bacillus thuringiensis strains effective against mosquitoes. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 40:103–106
Monnerat RG, Batista AC, Medeiros P, Martins E, Melatti VM, Praça L (2007) Screening of Brazilian Bacillus thuringiensis isolates active against Spodoptera frugiperda, Plutella xylostella and Anticarsia gemmatalis. Biol Control 41:291–295
Navon A (1993) Control of lepidopteran pests with Bacillus thuringiensis. In: Entwistle PF, Cory JS, Bailey MJ, Higgs S (eds) Bacillus thuringiensis, an environmental biopesticide: theory and practice. Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 255–266
Nunes TLS, Graminha EBN, Maia AS, Silva GS, Varandas NP, Costa AJ (2001) Atividade anti-ixodídica dos fungos Sporothrix insectorum e Paelomyces fumosoroseus sobre Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1887): bioensaios e microscopia eletrônica de varredura. Semin Ci Agrar 22:55–60
Oliveira-Filho EC (2008) Avaliação da periculosidade ambiental de bioinseticidas como uma nova perspectiva para a ecotoxicologia no Brasil. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 3:1–7
Oliveira-Filho EC, Paumgartten FJR (2000) Toxicity of Euphorbia milii latex and niclosamide to snails and nontarget aquatic species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:342–350
Oliveira-Filho EC, Matos RL, Paumgartten FJR (2004) Comparative study on the susceptibility of freshwater species to copper-based pesticides. Chemosphere 56:369–374
Oliveira-Filho EC, Geraldino BR, Grisolia CK, Paumgartten FJR (2005) Acute toxicity of endosulfan, nonylphenol ethoxylate and ethanol to different life stages of the freshwater snail Biomphalaria tenagophila (Orbigny, 1835). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:1185–1190
Oliveira-Filho EC, Grisolia CK, Paumgartten FJR (2009a) Trans-generation study of the effects of nonylphenol ethoxylate on the reproduction of the snail Biomphalaria tenagophila. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:458–465
Oliveira-Filho EC, Grisolia CK, Paumgartten FJR (2009b) Effects of endosulfan and ethanol on the reproduction of the snail Biomphalaria tenagophila: a multigeneration study. Chemosphere 75:398–404
Pedersen JC, Damgaard PH, Eilenberg E, Hansen BM (1995) Dispersal of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki in an experimental cabbage field. Can J Microbiol 41:118–125
Polanczyk R, Alves S (2003) Bacillus thuringiensis: uma breve revisão. Agrociencia 7:1–10
Praça LB, Batista AC, Martins ES, Siqueira CB, Dias DGS, Gomes ACMM, Falcão R, Monnerat RG (2004) Estirpes de Bacillus thuringiensis efetivas contra insetos das ordens Lepidoptera, Coleoptera e Diptera. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 39:11–16
Snarski VM (1990) Interactions between Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and fathead minnows, Pimephales promelas Rafinesque, under laboratory conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2618–2622
USEPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency (1996a) Microbial pesticide test guidelines. Freswater aquatic invertebrate testing, Tier I. USEPA, Washington. EPA-712-C-96-333
USEPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency (1996b) Microbial pesticide test guidelines. Nontarget insect testing, Tier I. USEPA, Washington. EPA-712-C-96-336
USEPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency (1998) RED Facts Bacillus thuringiensis. USEPA, Washington. EPA-738-F-98-001
Acknowledgment
Research supported by SEG/Embrapa and CNPq (Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira-Filho, E.C., Muniz, D.H.F., Freire, I.S. et al. Susceptibility of non-target invertebrates to Brazilian microbial pest control agents. Ecotoxicology 20, 1354–1360 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0691-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0691-4