Abstract
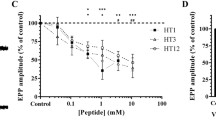
Two neuropeptides were isolated from synganglia (central nervous system) of the hard tick, Ixodes sinensis. Their primary sequences were established as Leu-Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Thr-Lys and Trp-Glu-Lys-Leu-Gly-Ser-Met-Glu-Thr-Leu. By hot plate bioassay, neuropeptide a displayed strong antinociceptive effect in mice by a dose-dependent behavior, while neuropeptide b had some relaxant effects on the isolated rat strip. These neuropeptides might be involved in down-regulating the host’s defensive reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bior A D, Essenberg R C, Sauer J R. Comparison of differentially expressed genes in the salivary glands of male ticks, Amblyomma americanum and Dermacentor anderson. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2002, 32: 645–655
Balashov Y S. Blood sucking ticks (Ixodidae): Vectors of disease of man and animals. Misc Publ Entomol Soc Am, 1972, 8, 161–376
Iwanaga S, Okada M, Isawa H, et al. Identification and characterization of novel salivary thrombin inhibitors from the ixodidae tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Eur J Biochem, 2003, 270: 1926–1934
Ribeiro J M, Evans P M, MacSwain J L, et al. Amblyomma americanum: Characterization of salivary prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha by RP-HPLC/bioassay and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Exp Parasitol, 1992, 74(1): 112–116
Bowman A S, Sauer J R, Zhu K, et al. Biosynthesis of salivary prostaglandins in the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 1995, 25(6): 735–741
Arocha-Pinango C L, Marchi R, Carvajal Z, et al. Invertebrate compounds acting on the hemostatic mechanism. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis, 1999, 10(2): 43–68
Iwanaga S, Okada M, Isawa H, et al. Identification and characterization of novel salivary thrombin inhibitors from the ixodidae tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Eur J Biochem, 2003, 270(9): 1926–1934
Lai R, Takeuchi H, Jonczy J, et al. A thrombin inhibitor from the ixodid tick, Amblyomma hebraeum. Gene, 2004, 342(2): 243–249
Ribeiro J M. Role of saliva in tick/host interactions. Exp Appl Acarol, 1989, 7(1): 15–20
Lawrie C H, Randolph S E, Nuttal P A. Ixodes ticks: Serum species sensitivity of anticomplement activity. Exp Parasitol, 1999, 93(4): 207–214
Lawrie C H, Sim R B, Nuttall P A. Investigation of the mechanisms of anti-complement activity in Ixodes ricinus ticks. Mol Immunol, 2005, 42(1): 31–38
Liang J G, Zhang J, Lai R, et al. An opioid peptide from synganglia of the tick, Amblyomma testindinarium. Peptides, 2005, 26(4): 603–606
Cao Y Q, Mantyh P W, Carlson E J, et al. Primary afferent tachykinins are required to experience moderate to intense pain. Nature, 1998, 392: 390–394
Caterina M J, Leffler A, Malmberg A B, et al. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science, 2000, 288: 306–313
Girard F, Bachelard H, St-Pierre S, et al. The contractile effect of bombesin, gastrin releasing peptide and various fragments in the rat stomach strip. Eur J Pharmacol, 1984, 102(3–4): 489–497
Fred N, Katarina S, Eva-lena G. The Hemorphins: A new class of opioid peptides derived from the blood protein hemoglobin. Biopoly, 1997, 43: 147–156
Laurent V, Salzet B, Verger-Bocquet M, et al. Morphine-like substance in leech ganglia. Evidence and immune modulation. Eur J Biochem, 2000, 267: 2354–2361
Singh S K, Girschick H J. Tick-host interactions and their immunological implications in tick-borne diseases. Curr Sci, 2003, 85: 1284–1298
McMillen M A, Sumpio B E. Endothelins: Polyfunctional cytokines. J Am Coll Surg, 1995, 180: 621–637
Yakubu M A, Shibata M, Leffler C W. Hematoma-induced enhanced cerebral vasoconstrictions to leukotriene C4 and endothelin-1 in piglets: Role of prostanoids. Pediatr Res, 1995, 38: 119–123
Silldorff E P, Yang S, Pallone T L, Prostaglandin E2 abrogates endothelin-induced vasoconstriction in renal outer medullary descending vasa recta of the rat. J Clin Invest, 1995, 95: 2734–2740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors equally contributed to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Liu, T., Yang, H. et al. Two neuropeptides from synganglia of the hard tick, Ixodes sinensis (Acari: Ixodidae). CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 2743–2747 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2200-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2200-3