Abstract
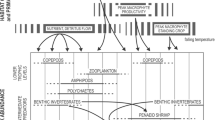
The Patagonian Shelf is a very productive region with different ecosystem structures. A long history of fishing in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean combined with a complex hydrographic structure, with a permanent front over the shelf-break and different coastal frontal regions, and a wide non-frontal area in between have made the food web in this area more complex and have resulted in changes to the spatialtemporal scale. Stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen were used to determine the trophic structure of the Patagonian shelf break which was previously poorly understood. The results indicated that the average δ15N value of pelagic guild (Illex argentinus) was remarkable lower than those of the other guilds. The δ13C values of almost all species ranged from -17‰ to -18‰, but Stromateus brasiliensis had a significant lower δ13C value. Compared with the southern Patagonian shelf, short food chain length also occurred. The impact of complex oceanographic structures has resulted in food web structure change to the temporal-spatial scale on the Patagonian shelf. The Patagonian shelf break can be considered as a separated ecosystem structure with lower δ13C values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acha E M, Mianzan H W, Guerrero R A, Favero M, Bava J. 2004. Marine fronts at the continental shelves of austral South America: physical and ecological processes. J. Mar. Syst., 44 (1–2): 83–105.
Agersted M D, Bode A, Nielsen T G. Trophic position of coexisting krill species: A stable isotope approach. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser., 516:139-151.
Alemany D, Acha E M, Iribarne O O. 2014. Marine fronts are important fishing areas for demersal species at the Argentine Sea (Southwest Atlantic Ocean). J. Sea Res., 87: 56–67.
Arkhipkin A, Brickle P, Laptikhovsky V. 2013. Links between marine fauna and oceanic fronts on the Patagonian Shelf and Slope. Arquipelago-Life Mar. Sci., 30: 19–37.
Bligh E G, Dyer W J. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol., 37 (8): 911–917.
Boltovskoy D. 2000. South Atlantic Zooplankton. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden. 1706p.
Botto F, Gaitán E, Mianzan H, Acha M, Giberto D, Schiarit A, Iribarne O. 2011. Origin of resources and trophic pathways in a large SW Atlantic estuary: an evaluation using stable isotopes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 92 (1): 70–77.
Calvert S E, Nielsen B, Fontugne M R. 1992. Evidence from nitrogen isotope ratios for enhanced productivity during formation of eastern Mediterranean sapropels. Nature, 359 (6392): 223–225.
Chen X J, Liu B L, Chen Y. 2008. A review of the development of Chinese distant-water squid jigging fisheries. Fish. Res., 89 (3): 211–221.
Ciancio J E, Pascual M A, Botto F, Frere E, Iribarne O. 2008. Trophic relationships of exotic anadromous salmonids in the southern Patagonian Shelf as inferred from stable isotopes. Limnol. Oceanogr., 53 (2): 788–798.
Clarke K R. 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust r. Ecol., 18 (1): 117–143.
DeNiro M J, Epstein S. 1977. Mechanism of carbon isotope fractionation associated with lipid synthesis. Science, 197 (4300): 261–263.
Drago M, Crespo E A, Aguilar A, Cardona L, García N, Dans S L, Goodall N. 2009. Historic diet change of the South American sea lion in Patagonia as revealed by isotopic analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog r. Ser., 384: 273–286.
Fisk A T, Tittlemier S A, Pranschke J L, Norstrom R J. 2002. Using anthropogenic contaminants and stable isotopes to assess the feeding ecology of Greenland sharks. Ecology, 83 (8): 2 162–2 172.
Forero M G, Bortolotti G R, Hobson K A, Donazar J A, Bertelloti M, Blanco G. 2004. High trophic overlap within the seabird community of Argentinean Patagonia: a multiscale approach. J. Anim. Ecol., 73 (4): 789–801.
Froese R, Pauly D. 2011. FishBase. June 2011 version, http://www.fishbase.org. (Accessed on 2016-05-30.
Haimovici M. 1998. Present state and perspectives for the southern Brazil shelf demersal fisheries. Fish. Manag. Ecol., 5 (4): 277–289.
Jackson G D, Bustamante P, Cherel Y, Fulton E A, Grist E P M, Jackson C H, Nichols P D, Pethybridge H, Phillips K, Ward R D, Xavier J C. 2007. Applying new tools to cephalopod trophic dynamics and ecology: perspectives from the Southern Ocean Cephalopod Workshop, February 2–3, 2006. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish., 17 (2–3): 79–99.
Laptikhovsky V V. 2004. A comparative study of diet in three sympatric populations of Patagonotothen species (Pisces: Nototheniidae). Polar Biol., 27 (4): 202–205.
Laptikhovsky V, Arkhipkin A, Brickle P. 2013. From small bycatch to main commercial species: explosion of stocks of rock cod Patagonotothen ramsayi (Regan) in the Southwest Atlantic. Fish. Res., 147: 399–403.
Leichter J J, Witman J D. 2009. Basin-scale oceanographic influences on marine macroecological patterns. In: Witman J D, Roy K eds. Marine Macroecology. University of Chicago Press, London. p. 205–226.
Mann K H, Lazier J R N. 2006. Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the Oceans. 3 rd edn. Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, USA. 512p.
Mouat B, Collins M A, Pompert J. 2001. Patterns in the diet of Illex argentin u s (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) from the Falkland Islands jigging fishery. Fish. Res., 52 (1–2): 41–49.
Nakamura I, Inada T, Takeda M, Hatanaka H. 1986. Important Fishes Trawled offPatagonia. Japan Marine Fishery Resource Research Centre, Tokyo. 369p.
Nyegaard M, Arkhipkin A, Brickle P. 2004. Variation in the diet of Genypterus blacodes (Ophidiidae) around the Falkland Islands. J. Fish Biol., 65 (3): 666–682.
Olson D B. 2002. Biophysical dynamics of ocean fronts. In:Robinson A R, McCarthy J J, Rothschild B J eds. The Sea, Volume 12: Biological-Physical Interactions in the Sea. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, USA. p.187-218.
Park J I, Kang C K, Suh H L. 2011. Ontogenetic diet shift in the euphausiid Euphausia pacifica quantified using stable isotope analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog r. Ser., 429: 103–109.
Patterson K R. 1998. Life history of Patagonian squid Loligo gahi and growth parameter estimates using least-squares fits to linear and von Bertalanffy models. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser., 47: 65–74.
Pauly D, Christensen V, Froese R, Palomares M L. 2000. Fishing down aquatic food webs. Am. Sci., 88 (1): 46–51.
Post D M. 2002. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology, 83 (3): 703–718.
Quillfeldt P, Cherel Y, Masello J F, Delord K, McGill R A R, Furness R W, Moodley Y, Weimerskirch H. 2015. Half a world apart? Overlap in nonbreeding distributions of Atlantic and Indian Ocean thin-billed prions. PLoS One, 10 (5): e0125007.
Ramírez F, Afán I, Hobson K A, Bertellotti M, Blanco G, Forero M G. 2014. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the feeding ecology of a top marine predator, the Magellanic penguin. Ecosphere, 5 (4): 1–21.
Santos R A, Haimovici M. 1997. Food and feeding of the short-finned squid Illex argentinus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) offSouthern Brazil. Fish. Res., 33 (1–3): 139–147.
Saporiti F, Bearhop S, Vales D G, Silva L, Zenteno L, Tavares M, Crespo E A, Cardona L. 2015. Latitudinal changes in the structure of marine food webs in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog r. Ser., 538: 23–34.
Sielfeld W, Vargas M. 1999. Review of marine fish zoogeography of Chilean Patagonia (42°-57°S). Sci. Mar., 63 (S1): 451–463.
Van Der Zanden M J, Rasmussen J B. 2001. Variation in δ 15 N and δ 13 C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol. Oceanogr., 46 (8): 2 061–2 066.
Waser N A D, Harrison W G, Head E J H, Nielsen B, Lutz V A, Calvert S E. 2000. Geographic variations in the nitrogen isotope composition of surface particulate nitrogen and new production across the North Atlantic Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. I, 47 (7): 1 207–1 226.
WoRMS Editorial Board. 2014. World register of marine species. www.marinespecies.org. Accessed on 2016-08-30.
Wu J P, Calvert S E, Wong C S. 1997. Nitrogen isotope variations in the subarctic northeast pacific: relationships to nitrate utilization and trophic structure. Deep-Sea Res. I, 44 (2): 287–314.
Zenteno L, Crespo E, Vales D, Silva L, Saporiti F, Oliveira L R, Secchi E R, Drago M, Aguilar A, Cardona L. 2015. Dietary consistency of male South American sea lions (Otaria flavescens) in southern Brazil during three decades inferred from stable isotope analysis. Mar. Bio l., 162 (2): 275–289.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the fisheries observers, crew and the officers of the trawler Longfa, LIU Zijun, CHEN Lvfen, WANG Rui, SONG Qi and REN Zeqian at the College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University for their helps in processing the samples. We acknowledge Mr Alan Coughtrey of the Shanghai Ocean University for his help in polishing the language. Finally, we would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their contributions to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (No. 2013BAD13B03), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41776185), and the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (No. 201203018)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Zhang, H., Yang, Y. et al. Upper trophic structure in the Atlantic Patagonian shelf break as inferred from stable isotope analysis. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 717–725 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-6340-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-6340-5