Summary
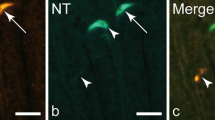
The endocrine gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) system of 10 human embryos was studied with special reference to neurotensin-immunoreactive cells. These cells are first present in the ileal and jejunal mucosa of 12 to 13 week old embryos. Thereafter the neurotensin-immunoreactive cells are found regularly in these segments of the gut with an increasing number towards the terminal ileum. At about the twentieth week of gestation, the neurotensin cells are detected also in the lower duodenum, i.e. the distribution pattern is more extensive in this age than in younger embryos or in adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björkman, N., Hellerström, C., Hellmann, B., Peterson, B.: The cell types in the endocrine pancreas of the human fetus. Z. Zellforsch. 72, 425–445 (1966)
Carraway, R., Leeman, S.E.: The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J. biol. Chem. 248, 6854–6861 (1973)
Conklin, J.L.: Cytogenesis of the human fetal pancreas. Amer. J. Anat. 111, 181–193 (1962)
Coons, A.H., Leduc, E.H., Conolly, J.M.: Studies on antibody production: Method for histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of hyperimmune rabbit. J.exp.Med. 102, 49–60 (1955)
Dubois, P.M., Paulin, C., Assan, R., Dubois, M.P.: Evidence for immunoreactive somatostatin in the endocrine cells of human foetal pancreas. Nature (Lond.) 256, 731–732 (1975)
Dubois, P.M., Paulin, C., Chayvialle, J.A.: Identification of gastrin-secreting cells and cholecystokininsecreting cells in the gastrointestinal tract of human fetus and adult man. Cell Tiss. Res. 175, 351–356 (1976a)
Dubois, P.M., Paulin, C., Dubois, M.P.: Gastrointestinal somatostatin cells in the human fetus. Cell Tiss. Res. 166, 179–184 (1976b)
Falck, B., Håkanson, R., Owman, Ch., Sjöberg, N.O.: Monoamine-storing cells of the enterochromaffine type in the gastro-intestinal tract of human fetus. Acta physiol. scand 71, 403–404 (1967)
Falkmer, S., Patent, G.J.: Comparative and embryological aspects of the pancreatic islets. In: Handbook of physiology. Sect. 7, Vol. 1: Endocrine pancreas, pp. 1–24, N. Freinkel and D.F. Steiner (editors) Washington D.C.: American Physiological Society 1972
Helmstaedter, V., Feurle, G.E., Forssmann, W.G.: Ultrastructural identification of a new cell type—the N-cell ⊕s the source of neurotensin in the gut mucosa. Cell Tiss. Res. (in press, 1977a)
Helmstaedter, V., Feurle, G.E., Taugner, Ch., Forssmann, W.G.: Demonstration of neurotensinimmunoreactive cells in the GEP-system of man and various mammals. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) (in press, 1977 b)
Helmstaedter, V., Taugner, Ch., Feurle, G.E., Forssmann, W.G.: Localisation of neurotensinimmunoreactive cells in the small intestine of man and various mammals. Histochemistry 53, 35–41 (1977c)
Kitabgi, P., Carraway, R., Leemann, S.E.: Isolation of a tridecapeptide from bovine intestinal tissue and its partial characterization as neurotensin. J. biol. Chem. 251, 7053–7058 (1976)
Larsson, L.I., Håkanson, R., Sjöberg, N.O., Sundler, F.: Fluorescence histochemistry of the gastrin cell in fetal and adult man. Gastroenterology 68, 1152–1159 (1975)
Larsson, L.I., Rehfeld, I.J., Sundler, F., Håkanson, R.: Pancreatic gastrin in fetal and neonatal rats. Nature (Lond.) 262, 609–610 (1976)
Moxey, P.C., Trier, J.S.: Endocrine cells in the human fetal small intestine. Cell Tiss. Res. (in press)
Mühlmann, G., Helmstaedter, V., Feurle, G.E., Forssmann, W.G.: Untersuchungen zur Entwicklung endokriner Zellen des menschlichen GEP-Systems. Verh. anat. Ges. (in Druck)
Orci, L., Baetens, O., Rufener, C., Brown, M., Vale, W., Guillemin, R.: Evidence for immunoreactive neurotensin in dog intestinal mucosa. Life Sci. 19, 559–562 (1976)
Pearse, A.G.E., Polak, J.M.: Neural crest origin of the endocrine polypeptide (APUD) cells of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Gut 12, 783–788 (1971)
Pictet, R.L., Rall, L.B., Phelbs, P., Rutter, W.J.: The neural crest and the origin of the insulin-producing cells. Science 191, 191–192 (1976)
Sternberger, L.A.: Immunocytochemistry, pp. 129–171 New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc. 1974
Sundler, F., Håkanson, R., Hammer, R.A., Alumets, J., Carraway, R., Leeman, S.E., Zimmerman, E.A.: Immunohistochemical localization of neurotensin in endocrine cells of the gut. Cell Tiss. Res. 178, 313–321 (1977)
Taugner, Ch., Helmstaedter, V., Mühlmann, G., Feurle, G.E., Forssmann, W.G.: Lokalisation von Neurotensin in endokrinen Zellen des GEP-Systems. Verh. Anat. Ges. (in press, 1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are indebted for technical assistance of Mrs. M.Wagner and M. Ehrbar and for preparing the manuscript by R.Botz and J.Greenberg
Supported by the German Research Foundation, Antrag Fo 77/7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helmstaedter, V., Mühlmann, G., Feurle, G.E. et al. Immunohistochemical identification of gastrointestinal neurotensin cells in human embryos. Cell Tissue Res. 184, 315–320 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219893
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219893