Abstract
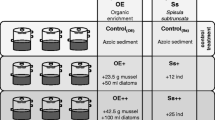
Experimental manipulations of food supply were performed on soft sediment cores from two European estuaries, the Westerscheldt and the Gironde, with a view to determining benthic macrofaunal community response. Over a period of twenty weeks in a laboratory mesocosm system, both communities showed losses in terms of numbers of individuals and small, but non-significant, losses in terms of numbers of species. Whereas no effect of the different types of foods or the dose levels at which they were supplied was detected for the Westerscheldt benthic community, that of the Gironde showed some significant response. This was largely attributed to the differential mortality of spionid polychaetes across the dose levels used, with the highest dose, equivalent to 200 g C m−2 yr−1, only just maintaining their initial population densities. The results are discussed in terms of the importance of lateral advection of food particles at the benthic boundary layer and the general insufficiency of many estimates of carbon input to shallow benthic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austen, M. A. & R. M. Warwick, 1995. Effects of manipulation of food supply on estuarine meiobenthos. Hydrobiologia 311 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 110): 175–184.
Beukema, J. J. & G. C. Cadee, 1986. Zoobenthos responses to eutrophication of the Dutch Wadden Sea. Ophelia 26: 55–64.
Clarke, K. R., 1993. Non parametric multivariate analysis of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 18: 117–143.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 1994. Similarity based testing for community pattern: the two-way layout with no replication. Mar. Biol. 118: 167–176.
Creutzberg, F., P. Wapenaar, G. Duineveldt & N. L. Lopez, 1984. Distribution and density of the benthic fauna in the southern North Sea in relation to bottom characteristics and hydrographic conditions. P-V Réun. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer 183: 101–110.
Gee, J. M., R. M. Warwick, M. Schanning, J. A. Berge & W. G. Ambrose, 1985. Effects of organic enrichment on meiofaunal abundance and community structure in sublittoral soft sediments. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 91: 247–262.
Graf, G., 1992. Benthic-Pelagic coupling: a benthic view. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. annu. Rev. 30: 149–190.
Heip, C., 1989; The ecology of the estuaries of the Rhine. In Ros, J. D. (ed.), Meuse and Scheldt in the Netherlands. Topics in Marine Biology. Scient. Mar. 53: 457–463.
Laane, R. W. P. M., H. Etcheber & J. C. Relexans, 1987. Particulate organic matter in estuaries and its ecological implications for macrobenthos. SCOPE/UNEP Sonderband 64: 71–91.
Levin, L. A. & E. L. Creed, 1986. Effect of temperature and food availability on reproductive responses of Streblospio benedicti (Polychaeta: Spionidae) with planktotrophic or lecithotrophic development. Mar. Biol. 92: 103–113.
Levinton, J. S. & S. Stewart, 1988. Effects of sediment organics, detrital input and temperature on demography, production and body size of a deposit feeder. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 49: 259–266.
Lopez, G. R. & J. S. Levinton, 1987. Ecology of deposit feeding animals in marine sediments. Quart. Rev. Biol. 62: 235–260.
Pearson, T. H. & R. Rosenberg, 1978. Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 16: 229–311.
Taghon, G. L., A. R. M. Nowell & P. A. Jumars, 1980. Induction of suspension feeding in spionid polychaetes by high particulate fluxes Science, N.Y. 210: 562–564.
Whitlach, R. B., 1980. Patterns of resource utilization and coexistence in marine intertidal deposit feeding communities. J. mar. Res. 38: 743–765.
Whitlach, R. B., 1981. Animal-sediment relationships in intertidal marine benthic habitats: some determinants of deposit-feeding species diversity. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 53: 31–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kendall, M.A., Davey, J.T. & Widdicombe, S. The response of two estuarine benthic communities to the quantity and quality of food. Hydrobiologia 311, 207–214 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00008581
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00008581