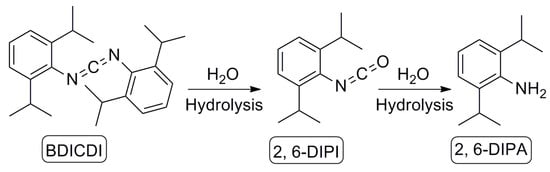
Vibrio cholerae is the etiological agent of cholera in humans. The bacterium is frequently detected in aquatic products worldwide. However, the current literature on the genome evolution of
V. cholerae of aquatic animal origins is limited. Here, we firstly characterized the growth and
[...] Read more.
Vibrio cholerae is the etiological agent of cholera in humans. The bacterium is frequently detected in aquatic products worldwide. However, the current literature on the genome evolution of
V. cholerae of aquatic animal origins is limited. Here, we firstly characterized the growth and genome features of
V. cholerae isolates with different resistance phenotypes from three species of common freshwater fish. The results revealed that the non-O1/O139
V. cholerae isolates (
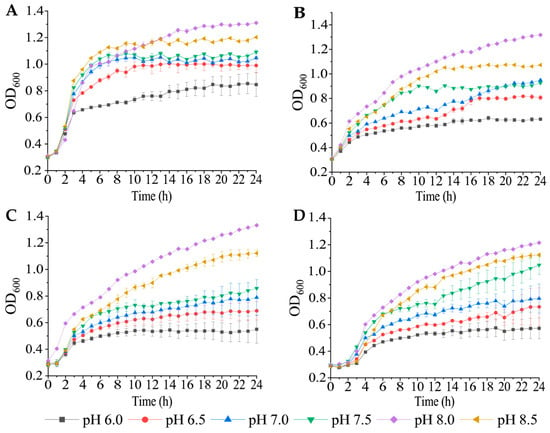
n = 4) were halophilic and grew optimally at 2% NaCl and pH 8.0. Their draft genome sequences were 3.89 Mb–4.15 Mb with an average GC content of 47.35–47.63%. Approximately 3366–3561 genes were predicted to encode proteins, but 14.9–17.3% of them were of an unknown function. A number of strain-specific genes (
n = 221–311) were found in the four
V. cholerae isolates, 3 of which belonged to none of any of the known sequence types (STs). Several putative mobile genetic elements (MGEs) existed in the
V. cholerae isolates, including genomic islands (
n = 4–9), prophages (
n = 0–3), integrons (
n = 1–1), and insertion sequences (
n = 0–3). Notably, CRISPR-Cas system arrays (
n = 2–10) were found in the
V. cholerae genomes, whereby the potential immunity defense system could be active. Comparative genomic analyses also revealed many putative virulence-associated genes (
n = 106–122) and antibiotic resistance-related genes (
n = 6–9). Overall, the results of this study demonstrate the bacterial broader-spectrum growth traits and fill prior gaps in the genomes of
V. cholerae originating from freshwater fish.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT