Abstract
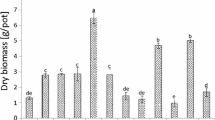
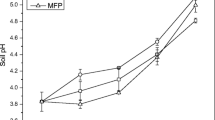
Excessive leaching of herbicides affects their efficacy against target weeds and results in contamination of groundwater. Use of adjuvants that can weakly bind herbicides and in turn release them slowly is a valuable technique to prolong the efficacy of herbicides and to minimize their leaching into groundwater. Effects of activated charcoal, three humic substances (Enersol SP 85%, Enersol 12%, and Agroliz), or a synthetic polymer (Hydrosorb) on the leaching of bromacil, dicamba, and simazine were investigated in leaching columns using a Candler fine sand (Typic Quartzipsamment). The addition of adjuvants had no harmful effects on physical properties of the soil as evident from lack of its affects on water percolation. When no adjuvants were used, 69%, 37%, and 4% of applied dicamba, bromacil, and simazine, respectively, were leached in the first pore volume of leachate (⋍3.2 cm rainfall). With five pore volumes of leachate (⋍16 cm rainfall), bromacil and dicamba were leached completely and only 80% of simazine was leached. Using Enersol 12% adjuvant resulted in a 13%–18% reduction in leaching of dicamba and bromacil in five pore volumes of leachate. The leaching of simazine was significantly decreased when any of the five adjuvants mentioned above were used. However, the decrease in leaching was significantly greater when using Enersol SP 85% or Enersol 12% (24%–28%) than when using the other adjuvants (12%–16%).
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Alva, A. K., and M. Singh. 1990a. Sorption of bromacil, diuron, norflurazon, and simazine at various horizons in two soils.Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 45:365–371.
Alva, A. K., and M. Singh. 1990b. Dicamba reactions in Myakka and Candler soils.Agronomy Abstract 1990:32.
Blair, A. M., C. Parker, and L. Kasasian, 1976. Herbicide protectants and antidotes—a review. ARC Weed Research Organization.PANS 22:65N80.
Burnside, O. C. 1971. Prevention and detoxilication of pesticide residues in soils. Pages 387–420in W. D. Guenzi (ed.), Pesticides in soil and water. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin.
Carlisle, V. W., F. Sodek, M. E., Collins, L. C. Hammond, and W. G. Harris. 1989. Characterization data for selected Florida soils. University of Florida. Institute of Food and Agricultural Science. Soil Science Research Report No. 89-1.
Carringer, R. D., J. B. Weber, and T. J. Monaco. 1975. Adsorption-desorption of selected pesticides by organic matter and montmorillouite.Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 23:568–572.
Cohen, S. Z., C. Eiden, and M. N. Lorber. 1986. Monitoring groundwater for pesticides. Pages 170–196in W. Y. Garner (ed.), Evaluation of pesticides in ground water. American Chemical Society Symposium Series 315. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Gamble, D. S., and S. U. Khan. 1988. Atrazine hydrolysis in aqueous suspensions of humic acid at 25°C.Canadian Journal of Chemistry 60:2605–2617.
Grover, R. 1971. Adsorption and desorption of trifluralin, triallate, and diallate by various adsorbants.Weed Science 22:405–408.
Harris, C. I. 1967. Movement of herbicides in soil.Weeds 15:214–216.
Harris, C. L., S. O. Norris, and L. K. Post. 1973. Factors influencing release of fenae from polyethylene materials.Weed Science 21:318–325.
Harris, F. W., A. E. Aulabaugh, R. D. Case, M. Dykes, and W. A. Field. 1977. Polymers containing pendent herbicide substitutes: Preliminary hydroysis studies. Pages 222–250in D. R. Paul and F. W. Harris (eds.), Controlled release polymeric formulations. American Chemical Society Symposium Series 53. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Holden, P. 1986. Pesticides and groundwater quality. Issues and problems in four states. National Research Council. Agricultural National Academy Press, Washington, DC.
Hornsby, A. G., T. M. Butler, D. P. H. Tucker, J. L. Knapp, and J. W. Noling. 1990. Managing pesticides for crop production and water quality protection.Florida Grover and Rancher 83:34–38.
Hurle, K., and A. Walker. 1980. Persistence and its prediction. Pages 83–122in R. J. Hance (ed.), Interactions between herbicides and the soil. Academic Press, New York.
Jain, R., and M. Singh, 1990. Effect of synthetic polymer on adsorption and leaching of herbicides in soil.In C. L. Foy (ed.), Adjuvants and agrochemicals. CRC Press, Boca Roton, Florida, (in press).
Kham, S. U. 1974. Adsorption of bihydridylium herbicides by humic acid.Journal of Environmental Quality 3:202–206.
Kozak, J., J. B. Weber, and T. J. Sheets. 1983. Adsorption of prometryn and metolachlor by selected soil organic matter fractions.Soil Science 136:94–101.
Lamoreaux, R. J., V. L. Corbin, and B. S. Johl. 1989. Adsorption and deactivation of norflurazon by activated charcoal.Weed Technology 3:297–305.
Madhun, Y. A., J. L. Young, and V. H. Freed. 1986. Binding of herbicides by water-soluble organic materials from soil.Journal of Environmental Quality 15:61–68.
Mehlich, A. 1953. Determination of P, Ca, Mg, K, Na, NH4-North Carolina soil test mimeo. North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Rao, P. S. C., A. G. Hornsby, and R. G. Jessup. 1985. Indices for ranking the potential for pesticide contamination of groundwater.Proceedings of the Soil and Crop Science Society of Florida 44:1–8.
Shea, P. J. 1985. Detoxification of herbicide in soil.Weed Science 33:33–41.
Steward, K. K., and L. L. Nelson. 1972. Evaluation of controlled release PVD and attaclay formulations of 2,4-D on Furasiun watermilfoil.Hyacinth Control Journal 10:35–44.
Upchurch, R. P., and D. D. Mason. 1961. The influence of soil organic matter on the phytotoxicity of herbicides.Weeds 9:9–13.
Walker, A. 1980. Activity and selectivity in the field. Pages 203–235in R. J. Hance (ed.), Interactions between herbicides and the soil. Academic Press, New York.
Walkley, A., and I. A. Black. 1931. An examination of the degrjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chronic acid titration method.Soil Science 37:29–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alva, A.K., Singh, M. Use of adjuvants to minimize leaching of herbicides in soil. Environmental Management 15, 263–267 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02393858
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02393858