Abstract
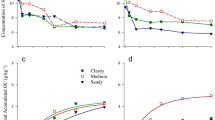
A continuous flow soil respirometer was used to evaluate the effect of nutrient addition, application rate, and application frequency on biodegradation of 2 complex oily sludges in soil. The most rapid biodegradation of the refinery sludge occurred when nitrogen was added to reduce the carbon to nitrogen (C∶N) ratio to 9∶1. The petrochemical sludge was degraded most rapidly when nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium were added at a rate of 124∶1, C∶NPK; CO2evolution from both wastes increased with increasing application rates, but the fraction of applied sludge which degraded decreased with increasing application rates. Small frequent applications resulted in a slight increase in respiration rate per unit applied over a single equivalent application, indicating that repeated applications of smaller amounts of sludge result in a more rapid rate of decomposition. The population of total soil bacteria was greatest when 1% of either sludge was added to the soil, whereas 5 and 10% sludge additions resulted in slightly lower microbial populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M (1981) Biodegradation of chemicals of environmental concern. Science 211:123–138
Atlas RM (1977) Stimulated petroleum biodegradation. Crit Rev Microbiol 5:271–386
Baruah JN, Alroy Y, Mateles RL (1967) The incorporation of liquid hydrocarbons into agar media. Appl Microbiol 15(4):961
Bremner JM (1965) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, pp 1149–1176
Brown KW, Brawand H, Thomas JC, Evans GB (1982) Impact of simulated land treatment with oily sludges on ryegrass emergence and yield. Agro J 74(2):257–261
Cook FD, Westlake DWS (1974) Microbial degradation of Northern crude oils. Information Canada Cat No R72-12774
Dibble JT, Bartha R (1979a) Effect of environmental parameters on biodegradation of oil sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:729–738
Dibble JT, Bartha R (1979b) Leaching aspects of oil sludge biodegradation in soil. Soil Sci 127:365–370
EPA (1979) Subtitle C. Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976. Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Office of Soild Waste, Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Francke JC, Clark FE (1974) Disposal of oily waste by microbial assimilation. US Atomic Energy Report Y-1934
Jobson A, McLaughlin M, Cook FD, Westlake DWS (1974) Effect of amendments on the microbial utilization of oil applied to soil. Appl Microbiol 27:166–171
Kincannon CN (1972) Oily waste disposal by soil cultivation process. Report EPA-R2-72-100. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Maunder BR, Ward JS Disposal of waste oil by landspreading. In: 3rd Intl. Biodegradation Symposium. August 17–23, 1975. University of Rhode Island, Kingston, TS XXV-5
Odu CTI, Adeoye KB (1969) Heterotrophic nitrification in soils—A preliminary investigation. Soil Biol Biochem 2:41–45
Poglazova MN, Fedoseeva GE, Khesina AJ, Meissel MN, Shabad LM (1967) Destruction of benzo(a)pyrene by soil bacteria. Life Sciences 6:1053–1062
Raymond RL, Hudson JO, Jamison VW (1976) Oil degradation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:522
Stotzky G (1965) Microbial respiration. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, pp 1550–1572
Warner JS (1976) Determination of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in marine organisms. Anal Chem 48:578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, K.W., Donnelly, K.C. & Deuel, L.E. Effects of mineral nutrients, sludge application rate, and application frequency on biodegradation of two oily sludges. Microb Ecol 9, 363–373 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019025
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019025