Abstract
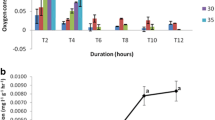
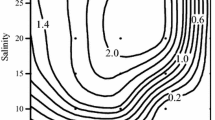
The effects of temperature, salinity and oxygen tension on the rates of oxygen consumption of three different strains of Artemia nauplii have been studied. When acclimated to a salinity of 30‰, nauplii from each of the three strains were able to maintain approximately constant rates of oxygen consumption over a wide range of oxygen tension. The ability to maintain respiratory independence during hypoxia was reduced, however, with an increase in either temperature or salinity. Nauplii of two of the strains (parthenogenetic diploid and tetraploid) showed a progressive increase in the rate of oxygen consumption with increasing temperature up to 35°C. Nauplii of the bisexual strain appeared to be less tolerant of exposure to temperatures >30°C, since at higher temperatures their oxygen consumption declined slightly. The differences between the nauplii of the different strains in their physiological responses to changing environmental conditions appear to correlate well with their seasonal occurrence in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu-Grobois F. A. (1987). A review of the genetics of Artemia. In: Sorgeloos, P. A., Bengtson, Decleir, W., Jaspers, E. (eds.) Artemia research and its applications. Vol. 1 Morphology, genetics, strain characterization, toxicology. Universa Press, Wetteren, p. 61–100
Abreu-Grobois F. A., Beardmore, J. A. (1980). International study on Artemia. II. Genetic characterization of Artemia populations —an electrophoretic approach. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. 1. Morphology, genetics, radiobiology, toxicology. Universa Press, Wetteren, p. 133–146
Amat, F. (1983). Zygogenetical and parthenogenetical Artemia in the Cádiz sea side salterns. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 13: 291–293
Amat, F. (1985). Utilización de Artemia en acuicultura. Infms téc. Inst. Invest. pesq. 128–129: 1–60
Artom, C. (1931). L'origine e l'evoluzione della partenogenesi attraverso i differenti biotipi di uma specie collectiva (Artemia salina L.) con special riferimento al biotipo diploid partenogenetico di Ste. Memorie R. Accad. Ital. 2: 1–57
Browne, R. A., Macdonald, G. (1982). Biogeography of the brine shrimp, Artemia: Distribution of parthenogenetic and sexual populations. J. Biogeogr. 9: 331–338
Chapman, J. (1968). The relative adaptive values of parthenogenesis and zygogenesis. M.Sc. thesis. San Francisco State College, California.
Conte, F. P., Lowry, J., Carpenter, J., Edwards, A., Smith, R., Ewing, R. D. (1980). Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of Artemia nauplii as a function of salinity. In: Persoone, G.: Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp of Artemia. Vol. 2, Physiology, biochemistry, molecular biology. Universa Press, Wetteren, p. 125–136
Croghan, P. C. (1958). The osmotic and ionic regulation of Artemia salina (L.). J. exp. Biol. 35: 219–223
Decleir, W., Wolf, G., De Watcher, B. (1989). Adaptation to hypoxia in Artemia. In: Cell and molecular biology of Artemia development. Plenum Press, New York, p. 47–54
Eliassen, E. (1952). The energy-metabolism of Artemia salina in relation to body-size, seasonal rhythms and different salinities, Årbok (Matem.-naturvit. ser.) Univ. Bergen 11: 1–17
Engel, D. W., Angelovic, J. W. (1968). The influence of salinity and temperature upon the respiration of brine shrimp nauplii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 26:749–752
Heip, J., Moens, L., Kondo, M. (1977). Ontogeny of haemoglobins in the brine shrimp Artemia salina (L.). Archs int. Physiol. Biochim. 85: 177–178
Herreid, C. F. (1980). Hypoxia in invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 67: 311–320
Kratowich, N. R. (1964). The effect of metabolic inhibitors on osmoregulation by nauplii of Artemia salina at various salinities. Am. Zool. 4: 389–390
Russler, D., Mangos, J. (1978). Micropuncture studies of the osmoregulation in the nauplius of Artemia salina. Am. J. Physiol. 234: 216–222
Schmidt-Nielsen, K. (1990). Animal physiology. 4th edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Van Den Branden C., D'Hondt, J., Moens, L., Decleir, W. (1978). Functional properties of the haemoglobins of Artemia salina (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 60: 185–187
Vanhaecke, P., Siddal, S. E., Sorgeloos, P. (1984). International study on Artemia. XXXII. Combined effects of temperature and salinity on the survival of Artemia of various geographical origins. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 80: 259–275
Vanhaecke, P., Tackaert, W., Sorgeloos, P. (1987). The biogeography of Artemia: an updated review. In: Sorgeloos, P., Bengtson, Decleir, W., Jaspers, E. (eds.) Artemia research and its applications. Vol. 1. Morphology, genetics, strain characterization, toxicology. Universa Press, Wetteren, p. 129–155
Varó I., Taylor, A. C., Amat, F. (1993). Comparison of two methods for measuring the rates of oxygen consumption of small aquatic animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. (in press)
Varó, I., Taylor, A. C., Navarro, J. C., Amat, F. (1991). Effects of temperature and oxygen tension on oxygen consumption rates of nauplii of different Artemia strains. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 76: 25–31
Vos, J., Bernaerts, F., Gabriels, I., Decleir, W. (1979). Aerobic and anaerobic respiration of adult Artemia salina L., acclimated to different oxygen concentration. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62: 545–548
Zhang, L., Lefcort, H. (1991). The effect of ploidy level on the thermal distribution of brine shrimp Artemia parthenogenetica and its ecological implication. Heredity, Lond. 66: 445–452
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varó, I., Taylor, A.C. & Amat, F. Comparative study of the effects of temperature, salinity and oxygen tension on the rates of oxygen consumption of nauplii of different strains of Artemia . Marine Biology 117, 623–628 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349774