Abstract
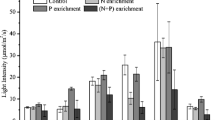
Control of phytoplankton production in the Great Lakes can be achieved most efficiently by limiting inputs of biologically available P. We report the results of studies performed to characterize the chemical forms and availability of particulate P in wastewater and tributaries which enter the lower Lakes, the eroding bluffs which border Lake Erie, and bottom samples from the near-shore of western Lake Erie. Rates of release of available P were estimated from a simple first-order model of the process, as observed during algal bioassays. Available P in wastewater samples, as a fraction of total particulate P, was affected minimally by wastewater treatment, including chemical precipitation and filtration; it correlated well with levels of total particulate P. Available particulate P levels in fluvial suspended sediments showed regional uniformity, but appeared to be strongly dependent on levels of both NaOH-P and CDB-P. Rates of release of available P decreased during wastewater treatment to values which were similar in magnitude to those observed for fluvial sediments. Release rates, however, were not related to any of the particulate P fractions which were measured. Analysis of the bluff and bottom samples indicated that P availability in the former was negligible, but the latter contained levels which approached those of wastewater particulates, though available P was released from the bottom sediments at relatively low rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, D. E., Perry, J. R. & Flatness, D., 1979. Availability of pollutants associated with suspended or settled river sediments which gain access to the Great Lakes. Final Report, Vol. 11, Menomenee River Pilot Watershed Study. Water Resources Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison. 96 pp.
Bierman, V. J., 1980. A comparison of models developed for phosphorus management in the Great Lakes. In: Loehr, R. C., Martin, C. S. & Rast, W. (Eds.). Phosphorus Management Strategies for Lakes, pp. 235–255. Ann Arbor Sci. Publ.
Chang, S. C. & Jackson, M. L., 1957. Fractionation of soil phosphorus. Soil Sci. 84: 133–144.
Cowen, W. F. & Lee, G. F., 1976. Phosphorus available in particulate materials transported by urban runoff. J. Wat. Pollut. Control Fed. 48: 580–591.
DePinto, J. V., 1982. An experimental apparatus for evaluating kinetics of available phosphorus release from aquatic particulates. Water Res. (G.B.) 16 (in press).
DePinto, J. V., Edzwald, J. K., Switzenbaum, M. S. & Young, T. C., 1980. Phosphorus removal in lower Great Lakes municipal treatment plants. EPA-600/2–80–117, MERL-Cincinnati. 147 pp.
DePinto, J. V., Young, T. C. & Martin, S. C., 1981. Algal-available phosphorus in suspended sediments of lower Great Lakes tributaries, J. Great Lakes Res. 7: 311–325.
Dorich, R. A., Nelson, D. W. & Sommers, L. E., 1980. Algal availability of sediment phosphorus in drainage water of the Black Creek watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 9: 557–563.
Fitzgerald, G. P., 1970. Aerobic lake muds for the removal of phosphorus from lake waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15: 550–555.
Golterman, H. L., 1977. Sediments as a sources of phosphate for algal growth. In: Golterman, H. L. (Ed.), Interactions between Sediments and Fresh Water, pp. 286–293. Junk, The Hague.
Golterman, H. L., Bakels, H. L. & Jakobs-Mögelin, J., 1969. Availability of mud phosphates for the growth of algae. Verb. int. Verein. Limnol. 17: 465–479.
Logan, T. J., 1978. Chemical extraction as an index of bioavailability of phosphate in Lake Erie basin suspended sediments. Lake Erie Wastewater Management Study Report. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Buffalo District, 42 pp.
Logan, T. J., Verhoff, F. H. & DePinto, J. V., 1979. Biological availability of total phosphorus. Lakes Erie Wastewater Management Study, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Buffalo District. 62 pp.
Murphy, J.&Riley, J. P., 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analyt. chim. Acta. 27: 31–36.
PMSTF, 1980. Phosphorus management for the Great Lakes; Final report of the phosphorus management strategies task force. International Joint Commission, Windsor, 129 pp.
Rhee, G-Y., 1978. Effects of N:P atomic ratios and nitrate limitation on algal growth, cell composition, and nitrate uptake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23: 10–25.
Sonzogni, W. C., Chesters, G., Coote, D. R., Jeffs, D. N., Konrad, J. C., Ostry, R. C. & Robinson, J. B., 1980. Pollution from land runoff. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14: 148–153.
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, 1979. Lake Erie wastewater management study methodology report. Lake Erie Wastewater Management Study; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Buffalo District, 146 pp.
Vallentyne, J. R. & Thomas, N. A., 1978. Fifth-year review of Canada-United States Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. Report of Task Group III. U. S. Department of State, Washington, D. C., 84 pp.
Williams, J. D. H., Jaquet, J.-M. & Thomas, R. L., 1976. Forms of phosphorus in the surficial sediments of Lake Erie. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 33: 413–429.
Williams, J. D. H., Murphy, J. P. & Mayer, T., 1976. Rates of accumulation of phosphorus forms in Lake Erie sediments. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 33: 430–439.
Williams, J. D. H., Shear, H. & Thomas, R. L., 1980. Availability to Scenedesmus quadricanda of different forms of phosphorus in sedimentary materials in the Great Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 1–11.
Young, T. C. & King, D. L., 1980. Interacting limits to algal growth: light, phosphorus, and carbon dioxide availability. Wat. Res. 14: 409–412.
Young, T. C., DePinto, J. V., Flint, S. E., Switzenbaum, M. S. & Edzwald, J. K., 1981. Algal availability of phosphorus in municipal wastewaters. J. Wat. Pollut. Control Fed. 54 (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, T.C. Algal-availability of particulate phosphorus from diffuse and point sources in the lower Great Lakes basin. Hydrobiologia 91, 111–119 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02391926
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02391926