Abstract
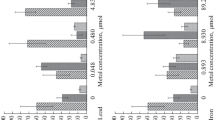
The minimum calcium requirements, relative importance of buffering and optimum ratio of calcium to magnesium, calcium to sodium, and calcium to potassium ions were determined for laboratory populations ofBiomphalaria pfeifferi and related to suggested limiting factors for the natural distribution of this species. Snails were reared in a range of concentrations of both calcium bicarbonate and unbuffered calcium sulphate from 0.5 to 20 mg/l as Ca++ and also in a series of media with a constant concentration of 2 mg/l as Ca++ but with a range of Ca/Mg, Ca/Na and Ca/K ratios of 4.0 to 0.1. Shell growth, survivorship, fecundity, egg fertility, and the net reproductive rate were compared. In calcium bicarbonate cultures a concentration of 2mg/l Ca++ appeared to be the lower limit for the survival of laboratory populations but a concentration of 4 mg/l Ca++ was needed for a population to thrive. The calcium sulphate salt gave much poorer results, emphasizing the importance of the bicarbonate buffer. In the cationic ratio experiments the low Ca/Mg ratios proved to have the most damaging effects on snail populations but the effects of very low Ca/Na and Ca/K ratios could also be measured. A parallel experiment on the hatching rate of snail eggs, using similar experimental solutions, gave comparable results. The significance of these findings to snail ecology is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrewartha, H. G. & Birch, L. C. 1954. The distribution and abundance of animals. Chicago.
Boycott, A. E. 1936. The habitats of fresh water Mollusca in Britain. J. Anim. Ecol. 5: 116–186.
Frank, G. H. & Meyling, A. H. 1966. A contribution to the conchometry of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Basommatophora: Planorbiidae). Malacologia 3: 379–398.
Harrison, A. D. 1962. Hydrobiological studies on alkaline and acid still waters in the Western Cape Province. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 36: 213–244.
Harrison, A. D. 1965. Geographical distribution of riverine invertebrates in Southern Africa. Arch. Hydrobiol. 61: 387–394.
Harrison, A. D., Keller, P. & Dimovic, D. 1957. Ecological studies on Olifantsvlei, near Johannesburg. Hydrobiologia 15: 89–134.
Harrison, A. D., Nduku, W. & Hooper, A. S. C. 1966. The effects of a high magnesium to calcium ratio on the egg-laying rate of an aquatic planorbid snail, Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Ann. trop. Med. Parasit. 60: 212–214.
Harrison, A. D., Williams, N. V. & Greigg, G. 1970. Studies on the effects of calcium bicarbonate concentrations on the biology of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss) (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). Hydrobiologia 36: 317–327.
Harry, H. W., Crumbie, B. C. & Martinez de Jesus, J. 1957. Studies on the qualities of fresh water of Puerto Rico relative to the occurrence of Australorbis glabratus (Say). Am. J. trop. Med. Hyg. 6: 315–322.
McKillop, W. B. & Harrison, A. D. 1972. Distribution of aquatic gastropods across an interface between the Canadian Shield and limestone formations. Can. J. Zool. 50: 1433–1445.
Schutte, C. H. J. & van Eeden, J. A. 1959. Contributions to the morphology of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss). I. The shell and radula. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. Series 13,2: 1–20.
Shiff, C. J. & Garnett, B. 1967. The influence of temperature on the intrinsic rate of natural increase of the freshwater snail, Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Pulmonata: Planorbiidae). Arch. Hydrobiol. 62: 429–438.
Williams, N. V. 1970A. Studies on aquatic pulmonate snails in Central Africa. 1. Field distribution in relation to water chemistry. Malacologia 10: 153–164.
Williams, N. V. 1970B. Studies on aquatic pulmonate snails in Central Africa. 2. Experimental investigation of field distribution patterns. Malacologia 10: 165–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nduku, W.K., Harrison, A.D. Calcium as a limiting factor in the biology of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss), (Gastropoda: Planorbidae). Hydrobiologia 49, 143–170 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00772685
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00772685