Abstract
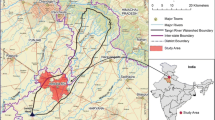
Makkah City, west of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, is considered the third main highly populated metropolitan area in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It exhibits two unique features that increase the hazardous flood consequences: (1) its topography is very complex and (2) about three million Muslims are gathered annually in Makkah to perform Hajj over a 2-week period. Floods are natural returning hydrological phenomena that have been affecting human lives. The objectives of the current study are: (1) identification of land use types and road networks in Makkah, (2) hydrological modeling of flood characteristics in Makkah based on precise up-to-date databases, (3) examination of the relationship between land use, land cover changes, transportation network expansion, and the floods' prosperities and hazards, and (4) development of digital hydrological maps for present and near future flood hazards in Makkah. The attained results show that the mean runoff depth and the total flood volume are significantly increased from 2010 to 2030. Additionally, it has been found that a great part of the road network in Makkah City is subjected to high dangerous flood impacts. The overall length of flood danger-factor roads is increased from 481 km (with almost 37 %) to 1,398 km (with 74 % approximately) between 2010 and 2030. Thus, it is concluded that urbanization has a direct strong relationship with flood hazards. Consequently, it is recommended that the attained results should be taken into account by decision makers in implementing new development planning of the Makkah metropolitan area.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ghamdi K, Elzahrany R, Mirza M, Dawod G (2012a) Impacts of urban growth on flood hazards in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. Int J Water Resour Environ Eng 4(2):23–34
Al-Ghamdi K, Mirza M, Elzahrany R, Dawod G (2012b) GIS evaluation of urban growth and flood hazards: a case study of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. The International FIG Working Week 2012, Rome, Italy, May 6–10
Amini A, Ali T, Ghazali A, Aziz A, Akib S (2011) Impacts of land-use change on stream flows in the Damansara watershed. Malays Arab J Sci Eng 36:713–720
Blanton P, Marcus A (2009) Railroads, roads and lateral disconnection in the river landscapes of the continental. US Geomorphol 112:12–227
Chen J, Hill A, Urbano L (2010) A GIS-based model for urban flood inundation. J Hydrol 373:184–192
Dawod G, Mirza M, Al-Ghamdi K (2011a) GIS-based spatial mapping of flash flood hazards in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. J Geogr Inf Syst 3(3):217–223
Dawod G, Mirza M, Al-Ghamdi K (2011b) Assessment of several flood estimation methodologies in Makkah metropolitan area, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0405-5, Published online October, 6
Fred E, Mostafa B (2008) Flood risk modeling for holy sites in Makkah. Third National Conference of GIS Applications in Saudi Arabia, April 7–9, Al Khober City, Saudi Arabia
Hansford J (2010) Impact of land use changes on floods in the Upper Waikato, New Zeeland, Final Report, January 19, 16 pp
HAMDD (Higher Authority for Makkah District Development) (2004) Master planning of Makkah City till 2030. Technical report (in Arabic), Makkah. Saudi Arabia
He M, Hogue T (2011) Integrating hydrologic modeling and land use projections for evaluation of hydrologic response and regional water supply impacts in semi-arid environments. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1144-3
Kar G, Kumar A, Singh R (2009) Spatial distribution of soil hydro-physical properties and morphometric analysis of a rainfed watershed as a tool for sustainable land use planning. Agr Water Manage 96:1449–1459
Koshak N, Dawod G (2011) A GIS morphometric analysis of hydrological basins for flood management within Makkah Metropolitan Area, Saudi Arabia, under review. Int J Geomatics Geosci 2(2):544–554
Paquier A (2010) Flood studies and effects of climate changes: two examples. Presented in the International Workshop on Impacts of Global Warming from Hydrological and Hydraulics Issues, Kyoto, Japan
Mirza M, Ahmed B (2001) Winter weather and climate conditions in Makkah (in Arabic), Geographic Messages, 253, Kuwait Geographic Association, Kuwait
Mirza M (2009) Impacts of development on spatial variations in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia (in Arabic). Presented in the Fourth Arab Geographers Meeting, Rebate, Morocco
Mirza M, Dawod G, Al-Ghamdi K (2011a) Assessment of flood hazards on road network in Makkah City and holy areas using a 3D GIS (in Arabic). Unpublished technical report, Center of Research Excellence in Hajj and Omrah, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia
Mirza M, Dawod G, Al-Ghamdi K (2011b) Accuracy and relevance of digital elevation models for geomatics applications—a case study of Makkah municipality, Saudi Arabia. Int J Geomatics Geosci 1(4):803–812
Mirza M, Dawod G, Al-Ghamdi K, Elzahrany R, Al-Harbi K, Shehata A (2011) Assessment of flood hazards on road network in Makkah City and holy areas using a 3D GIS. Unpublished technical report, Center of Research Excellence in Hajj and Omrah, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia
Mojaddadi H, Habibnejad M, Solaimani K, Abmadi M, Hadian-Amri M (2009) An investigation of efficiency of outlet runoff assessment models: Navroud watershed, Iran. J Appl Sci 9(1):105–112
Olang L, Furst J (2011) Effects of land cover change on flood peak discharges and runoff volumes: model estimates for the Nyando river basin, Kenya. Hydrol Process 25:80–89
Ragunath H (2006) Hydrology: principles, analysis, and design, 2nd edn. New Age International Limited Publications, New Delhi, India
Sheng J, Wilson J (2009) Watershed urbanization and changing flood behavior across the Los Angeles metropolitan region. Nat Hazards 48:41–57
Sherief Y (2008) Flash floods and their effects on the development in El-Qaa plain area in south Sinai, Egypt. PhD dissertation, University of Mainz, Germany
Subyani A, Qari M, Matsah M (2012) Digital elevation model and multivariate statistical analysis of morphometric parameters of some wadis, western Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 5:147–157
Versini P, Gaume E, Andrieu H (2010) Application of a distributed hydrological model to the design of a road inundation warning system for flash flood prone areas. Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 10:805–817
Youssef A, Pradhan B, Hassan A (2010) Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine road, southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0551-1
Wang L, Wehrly K, Breck J, Kraft L (2010) Landscape-based assessment of human disturbance for Michigan lakes. J Environ Manag 46:471–483
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support offered by the Technology Innovation Center on Geographic Information System (TIC-GIS), Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dawod, G.M., Mirza, M.N., Al-Ghamdi, K.A. et al. Projected impacts of land use and road network changes on increasing flood hazards using a 4D GIS: A case study in Makkah metropolitan area, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 7, 1139–1156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0876-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0876-7