Abstract
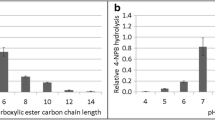
A recombinant polyester-degrading hydrolase from Thermobifida sp. BCC23166 targeting on aliphatic-aromatic copolyester (rTfH) was produced in Streptomyces rimosus R7. rTfH was expressed by induction with thiostrepton as a C-terminal His6 fusion from the native gene sequence under the control of tipA promoter and purified from the culture supernatant to high homogeneity by a single step affinity purification on Ni-Sepharose matrix. The enzyme worked optimally at 50–55°C and showed esterase activity on C3-C16 p-nitrophenyl alkanoates with a specific activity of 76.5 U/mg on p-nitrophenyl palmitate. Study of rTfH catalysis on surface degradation of polyester films using surface plasmon resonance analysis revealed that the degradation rates were in the order of poly-ε-caprolactone > Ecoflex® > polyhydroxybutyrate. Efficient hydrolysis of Ecoflex® by rTfH was observed in mild alkaline conditions, with the highest activity at pH 8.0 and ionic strength at 250 mM sodium chloride, with the maximal specific activity of 0.79 mg−1min−1mg−1 protein. Under the optimal conditions, rTfH showed a remarkable 110-time higher specific activity on Ecoflex® in comparison to a lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus, while less difference in degradation efficiency of the two enzymes was observed on the aliphatic polyesters, suggesting greater specificities of rTfH to the aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. This study demonstrated the use of streptomycetes as an alternative expression system for production of the multi-polyester-degrading enzyme of actinomycete origin and provided insights on its catalytic properties on surface degradation contributing to further biotechnological application of this enzyme.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beki E, Nagy I, Vanderleyden J, Jager S, Kiss L, Fulop L, Hornok L, Kukolya J (2003) Cloning and heterologous expression of a beta-d-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.25)-encoding gene from Thermobifida fusca TM51. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1944–1952
Brawner M, Poste G, Rosenberg M, Westpheling J (1991) Streptomyces: a host for heterologous gene expression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2:674–681
Calabia BP, Tokiwa Y (2004) Microbial degradation of poly(d-3-hydroxybutyrate) by a new thermophilic streptomyces isolate. Biotechnol Lett 26:15–19
Champreda V, Kanokratana P, Sriprang R, Tanapongpipat S, Eurwilaichitr L (2007) Purification, biochemical characterization, and gene cloning of a new extracellular thermotolerant and glucose tolerant malto-oligosaccharide forming α-amylase from an endophytic ascomycete Fusicoccum sp. BCC4124. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:2010–2020
Deckwer W-D, Müller RJ, Van den Heuvel J, Kleeberg I (2001) Enzyme which cleaves ester groups and which is derived from Thermomonospora fusca. GBF patent W001123581A1
Díaz M, Ferreras E, Moreno R, Yepes A, Berenguer J, Santamaría R (2008) High-level overproduction of Thermus enzymes in Streptomyces lividans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:1001–1008
Dresler K, van den Heuvel J, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (2006) Production of a recombinant polyester-cleaving hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca in Escherchia coli. Bioprocess Biosys Eng 29:169–183
Eberl A, Heumann S, Kotek R, Kaufmann F, Mitsche S, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gübitz GM (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of polymers and oligomers. J Biotechnol 135:45–51
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith CP (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 135:223–229
Gilbert M, Morosoli R, Shareck F, Kluepfel D (1995) Production and secretion of proteins by streptomycetes. Crit Rev Biotechnol 15:13–39
Gouda MK, Kleeberg I, van den Heuvel J, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (2002) Production of a polyester degrading extracellular hydrolase from Thermomonospora fusca. Biotechnol Prog 18:927–934
Heumann S, Eberl A, Pobeheim H, Liebminger S, Fischer-Colbrie G, Almansa E, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gübitz GM (2006) New model substrates for enzyme hydrolyzing polyethyleneterepthalate and polyamide fibers. J Biochem Biophys Methods 69:89–99
Hoang K-C, Tseng M, Shu W-J (2007) Degradation of polyethylene succinate (PES) by a new thermophilic Microbispora strain. Biodegradation 18:333–342
Hobbs G, Frazer CM, Gardner DCJ, Cullum JA, Oliver SG (1989) Dispersed growth of Streptomyces in liquid culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:272–277
Hranueli D, Pigac J, Vesligaj M (1979) Characterization and persistence if actinophage RP2 isolated from Streptomyces rimosus ATCC10970. J Gen Microbiol 114:295–303
Jendrossek D (2007) Peculiarities of PHA granules preparation and PHA depolymerase activity determination. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1186–1196
Kalabia BP, Tokiwa Y (2004) Microbial degradation of poly(d-3-hydroxybutyrate) by a new thermophilic Streptomyces isolate. Biotechnol Lett 26:15–19
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces Genetics. Society for General Microbiology, Reading UK
Kleeberg I, Hetz C, Kroppenstedt RM, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (1998) Biodegradation of aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters by Thermomonospora fusca and other thermophilic compost isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1731–1735
Kleeberg I, Welzel K, VandenHeuvel J, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (2005) Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters. Biomacromolecules 6:262–270
Luengo JM, Garsia B, Sandoval A, Naharro G, Olivera ER (2003) Bioplastics from microorganisms. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:251–260
MacNeil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL, Dezeny G, Gibbons PH, MacNeil T (1992) Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene 111:61–68
Marten E, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (2003) Studies on the enzymatic hydrolysis of polyesters I. Low molecular mass model esters and aliphatic polyesters. Polym Degrad Stab 80:485–501
Mazodier P, Petter R, Thompson C (1989) Intergeneric conjugation between Escherichia coli and Streptomyces species. J Bacteriol 171:3583–3585
Müller RJ, Kleeberg I, Deckwer W-D (2001) Biodegradation of polyesters containing aromatic constituents. J Biotechnol 86:87–95
Müller RJ, Schrader H, Profe J, Dresler K, Deckwer W-D (2005a) Enzymatic degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate): rapid hydrolyse using a hydrolase from T. fusca. Macromol Rapid Commun 26:1400–1405
Müller I, Welzel K, VandenHeuvel J, Müller R-J, Deckwer WD (2005b) Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters. Biomacromolecules 6:262–270
Phithakrotchanakoon C, Rudeekit Y, Tanapongpipat S, Leejakpai T, Aiba S, Noda I, Champreda V (2009a) Microbial degradation and physico-chemical alteration of polyhydroxyalkanoates by a thermophilic Streptomyces sp. Biologia 64:246–251
Phithakrotchanakoon C, Daduang R, Thamchaipenet A, Wangkam T, Srikhirin T, Eurwilaichitr L, Champreda V (2009b) Heterologous expression of polyhydroxyalkanoate depolymerase from Thermobifida sp. in Pichia pastoris and catalytic analysis by surface plasmon resonance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:131–140
Sambrook J, Russell DW (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Schmidt-Dannert C, Sztajer H, Stocklein W, Menge U, Schmid RD (1994) Screening, purification and properties of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1214:43–53
Sun J, Kelemen GH, Fernandez-Abalos JM, Bibb MJ (1999) Green fluorescent protein as a receptor for spatial and temporal gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 145:2221–2227
Tokiwa Y, Calabia BP (2004) Degradation of microbial polyesters. Biotechnol Lett 26:1181–1189
van Wezel GP, Krabben P, Traag BA, Keijser BJF, Kerste R, Vijgenboom E, Heijnen JJ, Kraal B (2006) Unlocking Streptomyces spp. for use as sustainable industrial production platforms by morphological engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5283–5288
Vrancken K, Anné J (2009) Secretory production of recombinant proteins by Streptomyces. Future Microbiol 4:181–188
Witt U, Müller RJ, Deckwer WD (1997) Biodegradation behavior and material properties of aliphatic-aromatic polyesters of commercial importance. J Environ Polym Degrad 5:81–89
Yang Y, Malten M, Grote A, Jahn D, Deckwer W-D (2006) Codon optimized Thermobifida fusca hydrolase secreted by Bacillus megaterium. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:780–794
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF). The authors would like to thank Dr. Phillip James Shaw for manuscript proofreading. N.S. was granted YSTP senior project studentship from NSTDA. T.W. was granted the Development and Promotion of Science and Technology Talents Project (DPST) Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinsereekul, N., Wangkam, T., Thamchaipenet, A. et al. Recombinant expression of BTA hydrolase in Streptomyces rimosus and catalytic analysis on polyesters by surface plasmon resonance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1775–1784 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2465-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2465-y