Abstract
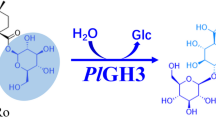
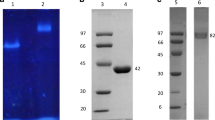
A novel protodioscin-(steroidal saponin)-glycoside hydrolase, named protodioscin-glycosidase-1 (PGase-1), was purified and characterized from the Aspergillus oryzae strain. The molecular mass of this enzyme was determined to be about 55 kDa based on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. PGase-1 was able to hydrolyze the terminal 26-O-β-d-glucopyranoside of protodioscin (furostanoside) to produce dioscin (spirostanoside), and then further hydrolyze the terminal 3-O-(1 → 4)-α-l-rhamnopyranoside of dioscin to form progenin III. However, PGase-1 could hardly hydrolyze the 3-O-(1 → 2)-α-l-rhamnopyranoside of progenin III, 3-O-β-d-glucoside of trillin, and the 1-O-glycosides of ophiopogonin D (steroidal saponin). In addition, PGase-1 also could hydrolyze the α-d-galactopyranoside, β-d-glucopyranoside, and β-d-galactopyranoside of p-nitrophenyl-glycosides, but the enzyme could not hydrolyze the α-d-mannopyranoside, α-l-arabinopyranoside, α-d-glucopyranoside, β-d-xylopyranoside, and α-l-rhamnopyranoside of p-nitrophenyl-glycosides. These new properties of PGase-1 were significantly different from those of previously described steroidal saponin-glycosidases and the glycosidases currently described in Enzyme Nomenclature by the NC-IUBMB. The gene (termed as pgase-1) encoding PGase-1 was cloned, sequenced, and expressed in Pichia pastoris GS115. The complete nucleotide sequence of pgase-1 consists of 1,725 bp. The recombinant PGase-1 from recombinant P. pastoris GS115 strain also showed the activity hydrolyzing glycosides of steroidal saponins which was similar to that of the wild-type PGase-1 from A. oryzae. The PGase-1 gene is highly similar to Aspergilli α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1), and PGase-1 should be classified as glycoside hydrolase family 13 by the method of gene sequence-based classification. But the enzyme properties of PGase-1 are different from those of α-amylase in this family.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beit-Yannai E, Ben-Shabat S, Goldschmidt N, Chapagain BP, Liu RH, Wiesman Z (2011) Antiproliferative activity of steroidal saponins from Balanites aegyptiaca—an in vitro study. Phytochem Lett 4:43–47
Dong M, Feng XZ, Wu LJ, Wang BX, Ikejima T (2001) Two new steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Dioscorea panthaica and their cytotoxic activity. Planta Med 67:853–857
Feng B, Hu W, Ma BP, Wang YZ, Huang HZ, Wang SQ, Qian XH (2007a) Purification, characterization, and substrate specificity of a glucoamylase with steroidal saponin-rhamnosidase activity from Curvularia lunata. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1329–1338
Feng B, Kang LP, Ma BP, Quan B, Zhou WB, Wang YZ, Zhao Y, Liu YX, Wang SQ (2007b) The substrate specificity of a glucoamylase with steroidal saponin-rhamnosidase activity from Curvularia lunata. Tetrahedron 63:6796–6812
Feng B, Huang HZ, Zhou WB, Kang LP, Zou P, Liu YX, Yu HS, Han BQ, Li YY, Zhang LL, Zhang T, Ma BP (2010) Substrate specificity, purification and identification of a novel pectinase with the specificity of hydrolyzing the α-1,4-glycosyl residue in steroidal saponin. Process Biochem 45:1383–1392
Fu YY, Yu HS, Tang SH, Hu XC, Wang YH, Liu B, Yu CX, Jin FX (2010) New dioscin-glycosidase hydrolyzing multi-glycosides of dioscin from Absidia strain. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:1011–1017
Inoue K, Ebizuka Y (1996) Purification and characterization of furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase from Costus speciosus rhizomes. FEBS Lett 378:157–160
Jin FX, Li Y, Zhang CZ, Yu HS (2001) Thermostable α-amylase and α-galactosidase production from the thermophilic and aerobic Bacillus sp. JF strain. Process Biochem 36:559–564
Kwon CS, Sohn HY, Kim SH, Kim JH, Son KH, Lee JS, Lim JK, Kim JS (2003) Anti-obesity effect of Dioscorea nipponica Makino with lipase-inhibitory activity in rodents. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1451–1456
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lin SH, Wang DM, Yang DP, Yao JH, Tong Y, Chen JP (2007) Characterization of steroidal saponins in crude extract from Dioscorea nipponica Makino by liquid chromatography tandem multi-stage mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 599:98–106
Lineweaver H, Burk D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc 56:658–666
Liu CZ, Zhou HY, Yan Q (2007) Fingerprint analysis of Dioscorea nipponica by high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. Anal Chim Acta 582:61–68
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Manzanares P, De Graaff LH, Visser J (1997) Purification and characterization of an α-L-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol Lett 157:279–283
Mimaki Y, Yokosuka A, Kuroda M, Sashida Y (2001) Cytotoxic activities and structure–cytotoxic relationships of steroidal saponins. Biol Pharm Bull 24:1286–1289
Qian S, Yu HS, Zhang CZ, Lu MC, Wang HY, Jin FX (2005) Purification and characterization of dioscin-α-L-rhamnosidase from pig liver. Chem Pharm Bull 53:934–937
Racape J, Belbahri L, Engelhardt S, Lacombe B, Lee J, Lochman J, Marais A, Nicole M, Nürnberger T, Parlange F, Puverel S, Keller H (2005) Ca2+-dependent lipid binding and membrane integration of PopA, a harpin-like elicitor of the hypersensitive response in tobacco. Mol Microbiol 58:1406–1420
Rao AV, Gurfinkel DM (2000) The bioactivity of saponins: triterpenoid and steroidal glycosides. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 17:211–235
Sparg SG, Light ME, Van Staden J (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethnopharmacol 94:219–243
Wang YB, Zhang YC, Zhu ZY, Zhu SL, Li YX, Li M, Yu B (2007) Exploration of the correlation between the structure, hemolytic activity, and cytotoxicity of steroid saponins. Bioorg Med Chem 15:2528–2532
Wang DM, Yu HS, Song JG, Xu YF, Liu CY, Jin FX (2011) A novel ginsenosidase from an Aspergillus strain hydrolyzing 6-O-multi-glycosides of protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides, named ginsenosidase type IV. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1057–1063
Xiao J, Wang NL, Sun B, Cai GP (2010) Estrogen receptor mediates the effects of pseudoprotodiocsin on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:128–138
Acknowledgments
M.Q. Tang and X.D. Yuan (TaKaRa Biotechnology (Dalian) Co., Ltd. China) are thanked for sequencing determination. This work was supported by Program for Liaoning Innovative Research Team in University (LNIRT: 2009 T007) and National Science of Foundation of P.R. China (NSFC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Yu, H., Liu, C. et al. Protodioscin-glycosidase-1 hydrolyzing 26-O-β-d-glucoside and 3-O-(1 → 4)-α-l-rhamnoside of steroidal saponins from Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 10035–10043 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4791-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4791-3