Background and Objectives: Heart rate variability (HRV) is defined as a physiological variation in duration between sinus beats. The aim of this study was to research and analyze the HRV between various groups of patients.
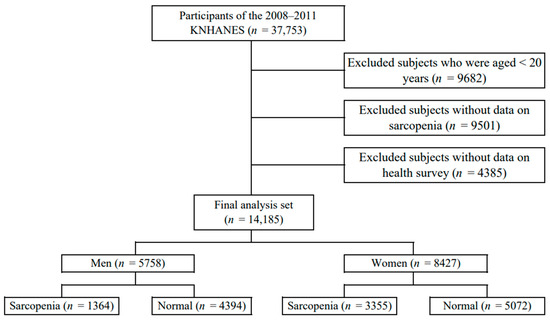
Materials and Methods: A retrospective study was conducted in an outpatient setting. Patients who had undergone a tilt-table test were selected for this study and were divided into three groups based on their self-reported health anamnesis: group 1 (
n = 84, mean age 45.8 ± 17.8) consisted of patients with no known orthostatic intolerance or neurodegenerative disease, group 2 consisted of patients with a known or suspected orthostatic intolerance (
n = 50, mean age 46.5 ± 18.6), and group 3 consisted of patients with a known or suspected neurodegenerative disorder (
n = 29, mean age 55.6 ± 20.4). During the tilt-table test, HRV frequency-domain parameters—normalized low frequency (LFnu) and high frequency (HFnu), absolute powers—absolute low frequency (LF-RRI), absolute high frequency (HF-RRI), and LF/HF ratio—were recorded during 5 min rest in the supine position.
Results: Group 1 had a reduced LFnu at 52.93% (SD: 18.00) compared to group 2 at 58.57% (18.06) and group 3 at 61.80% (SD: 17.74), and group 1 had increased HFnu: group 1—47.08% (SD: 17.97), group 2—41.41% (SD: 18.03), and group 3—38.16% (SD: 14.7). LFnu and HFnu differences were statistically significant (
p < 0.05). LF-RRI was reported as follows: group 1—531.32 ms
2 (SD: 578.57), group 2—346.2 ms
2 (SD: 447.96), and group 3—143.21 ms
2 (SD: 166.96). HF-RRI was reported as follows: group 1—835.87 ms
2 (SD: 1625.42), group 2—297.46 ms
2 (SD: 507.15), and group 3—70.83 ms
2 (SD: 75.67). LF-RRI and HF-RRI comparisons between groups were statistically significant (
p < 0.001). LF/HF ratios were reported as follows: group 1—1.91 (SD: 2.29), group 2—2.43 (SD: 2.33), and group 3–2.54 (SD: 2.17). LF/HF ratio comparisons between groups were statistically significant at
p < 0.05.
Conclusions: This study shows that patients with known or suspected orthostatic intolerance and neurodegenerative disorders have reduced HRV, possibly caused by reduced parasympathetic modulation. HRV in patients with known or suspected neurodegenerative disorders is reduced more severely than in patients with orthostatic disorders. Other studies in HRV have indicated a possible increase of risk in cardiovascular disorders in patients with reduced HRV, and therefore, HRV analysis could be a potential clinical diagnostic tool. However, the lack of universally agreed upon methodology, reference values, and possible external and internal factor influence hinders the introduction of HRV examinations into wider clinical practice.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT