Abstract
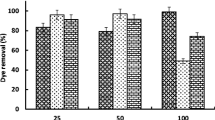
In this work, Aspergillus terreus GS28 and Aspergillus flavus CR500 isolated from industrial waste sludge examined for the decolorization of Congo red (CR) dye. The rate of CR decolorization raised due to optimum pH, temperature, carbon, nitrogen, and heavy metals. In the comparative study, A. terreus has the maximum ability (95%) to decolorize CR (≈ 100 mg L−1) as compared with A. flavus (92.96%) under optimized condition after 120 h. GC–MS and FTIR analysis of the fungal-metabolite and fungal-biomass shows bio-degradation and biosorption processes respectively. The degraded products were benzenepropanic (Rt-26.147), 3, 4-diaminonapthelene-1-sulfonic acid, and benzenedicarboxylic acid (Rt-26.660) by A. terreus, and benzenedicarboxylic acid (Rt-41.467) by A. flavus. The phytotoxicity assay revealed that a decrease in toxicity of the degraded product towards the growth and germination rate of two plant seeds compared to CR. Thus, the finding suggests that both the fungi act promising CR remediation candidates, induces restoration of CR polluted wastewater and save soil-land.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan LA, Yusoff ARM, Hadibarata T, Khudhair AB (2014) Biodegradation of bis-azo dye reactive black 5 by white-rot fungus Trametes gibbosa sp. WRF 3 and its metabolite characterization. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(10):1–11
Almeida EJR, Corso CR (2014) Comparative study of toxicity of azo dye Procion Red MX-5B following biosorption and biodegradation treatments with the fungi Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus terreus. Chemosphere 112:317–322
Asses N, Ayed L, Hkiri N, Hamdi M (2018) Congo red decolorization and detoxification by Aspergillus niger: removal mechanisms and dye degradation pathway. Int J Biomed Res 7:1–9
Bankol OP, Adekunle AA, Govindwar SP (2018) Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of Acid Red 88 dye by newly isolated fungus, Achaetomium strumarium. J Environ Chem Eng 6:1589–1600
Basak B, Bhunia B, Mukherjee S, Dey A (2013) Optimization of Physic-chemical parameters for phenol biodegradation by Candida tropicalis PHB5 using Taguchi Methodology. Desalin Water Treat 51:6846–6862
Bosco F, Mollea C, Ruggeri B (2016) Decolorization of congo red by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: the role of biosorption and biodegradation. J Environ Technol 38:2581–2588
Chakraborty S, Basak B, Dutta S, Bhunia B, Dey A (2013) Decolorization and biodegradation of congo red dye by a novel white rot fungus Alternaria alternata CMERI F6. Biores Technol 147:662–666
Cheng ZZ, Yang ZP, Hu R et al (2012) Decolorization of 12 kinds of dyes by the mycelium pellets of Trametes gallica under non-sterile condition. Mycosystema 31(6):878–889
Gao D, Du L, Yang J, Wu WM, Liang H (2010) A critical review of the application of white rot fungus to environmental pollution control. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:70–77
Gautam A, Rawat S, Verma L, Singh J, Sikarwarb S et al (2018) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticle from extract of waste tea: an application for phenol red removal from aqueous solution. J Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 10:377–387
He XL, Song C, Li Y, Wang N, Xu L, Han X, Wei D (2018) efficient degradation of Azo dyes by a newly isolated fungus Trichoderma tomentosum under non-sterile conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150(15):232–239
Iark D, dos Reis Buzzo AJ, Garcia JAA (2019) Enzymatic degradation and detoxification of azo dye Congo red by a new laccase from Oudemansiella canarii. Bioresour Technol 289:121655
Kannan A, Upreti RK (2008) Influence of distillery effluent on germination and growth of mung bean (Vigna radiata) seeds. J Hazard Mater 153:609–615
Kumar V, Dwivedi SK (2019) Hexavalent chromium reduction ability and bioremediation potential of Aspergillus flavus CR500 isolated from electroplating wastewater. Chemosphere 237:124567
Kumar K, Dastidar MG, Sreekrishnan TR (2009) Effect of process parameters on aerobic decolourization of reactive azo dye using mixed culture. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 58:952–955
Kumar V, Singh S, Singh G, Dwivedi SK (2019) Exploring the cadmium tolerance and removal capability of a filamentous fungus Fusarium solani. Geomicrobiol J 36(9):782–791
Levin L, Melignani E, Ramos AM (2010) Effect of nitrogen sources and vitamins on ligninolytic enzyme production by some white-rot fungi. Dye decolorization by selected culture filtrates. Bioresour Technol 101:4554–4563
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biologic Chem 193:265–275
Mahmud AA, Upadhyay SK, Srivastava AK, Bhojiya AA (2021) Biofertilizers: a Nexus between soil fertility and crop productivity under abiotic stress. Curr Res Environ Sustain 3:100063
Mnif I, Maktouf S, Fendri R, Kriaa M et al (2016) Improvement of methyl orange dye biotreatment by a novel isolated strain, Aeromonas veronii GRI, SPB1biosurfactant addition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1742–1754
Nouren S, Bhatti HN (2015) Mechanistic study of degradation of basic violet 3 by Citrus limon peroxidase and phytotoxicity assessment of its degradation products. Biochem Eng J 95:9–19
Pandi A, Kamini NR, Saravanan P, Gowthaman MK (2018) A sustainable approach for degredation of leather dyes by a new fungal laccase. J Clean Prod 211:590–597
Sen SK, Raut S, Bandyopadhyay P, Raut S (2016) Fungal decolouration and degradation of azo dyes: a review. Fungal Biol Rev 30(3):112–133
Singh G, Dwivedi SK (2020) Decolorization and degradation of Direct Blue-1 (Azo dye) by newly isolated fungus Aspergillus terreus GS28, from sludge of carpet industry. Environ Technol and Innovat 18:100751
Singh G, Upadhyay SK, Singh MP (2015) Dye-decolorization by native bacterial isolates, isolated from sludge of carpet industries Bhadohi-India. J Environ Sci Technol 2(6):81–85
Singh G, Kumar V, Dwivedi SK (2021) Comparative Investigation of Congo Red and Direct Blue-1 Adsorption on Mycosynthesized Iron Nanoparticle. J Clust Sci 2021:1–17
Srinu A, Vijaya LD, Murali S, Prasad DVR (2017) Decolorization of anthraquinone dyes by Aspergillus strains and also optimization of lignolytic enzymes. Int J Rec Sci Res 8(7):18547–18553
Srivastava AK, Upadhyay SK, Vishwakarma SK (2019) Mycodecolorization activity of Pleurotus Citrinopileatus for chemically different textile dye under varied aromatic amino acids and trace elements G. J Environ Sci Technol 6(4):14–17
Syafiuddin A, Fulazzaky MA (2021) Decolorization kinetics and mass transfer mechanisms of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye mediated by different fungi. Biotechnol Rep 29:e00573
Tan L, Xu B, Hao J, Wang J, Shao Y, Mu G (2019) Biodegradation and detoxification of azo dyes by a newly isolated halotolerant yeast Candida tropicalis SYF-1. Environ Eng Sci 36(9):999–1010
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some anti oxidant system in acid rain treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Vitor V, Corso CR (2008) Decolorization of textile dye by Candida albicans isolated from industrial effluents. J Ind Microbiol and Biotechnol 35:1353–1357
Wang N, Chu Y, Wu F, Zhao Z, Xu X (2017) Decolorization and degradation of congo red by a newly isolated White rot fungus, Ceriporia lacerate, from decayed mulberry branches. Int J Biodetor Biodegrad 117:236–244
Zhang H, Zhang X, Geng A (2020) Expression of a novel manganese peroxidase from Cerrena unicolor BBP6 in Pichia pastoris and its application in dye decolorization and PAH degradation. Biochem Eng J 153:107402
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Head, Department of Environmental Science, BBAU, Lucknow, U.P., India for facilitating all required laboratory facilities during experimental work. The help provided by USIC, B.B.A. University, Lucknow for FTIR analysis and AIRF of JNU, New Delhi for GC-MS analysis are greatly acknowledged. One of us (Garima Singh) would also like to thank University Grants Commission (UGC), Government of India for providing UGC-NON NET University fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Dwivedi, S.K. Biosorptive and Biodegradative Mechanistic Approach for the Decolorization of Congo Red Dye by Aspergillus Species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108, 457–467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03380-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03380-8