Abstract
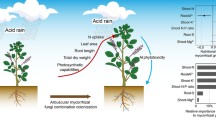
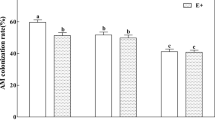
Acid rain (AR) is a frequent environmental issue in southern China that causes damage to the growth and photosystems of subtropical tree species. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) can improve plant tolerance to acidic conditions; however, how AMF mediate the detrimental effects of AR on the growth and photosynthetic parameters of tree species is yet to be understood. In this study, we inoculated Zelkova serrata, an important economic tree species in China, with Rhizophagus irregularis, and Diversispora versiformis, alone and in combination, under three simulated AR regimes (pH 2.5, 4.0, and 5.6). Mycorrhizal colonization, the concentrations of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in hyphae, leaf chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthetic parameters, and growth were all subsequently measured. Our results revealed that AR sharply reduced photosynthetic ability and total biomass of non-mycorrhizal plants, whereas AMF inoculation significantly improved ALP, SDH, total biomass, net photosynthetic rate, and acid tolerance under acidic conditions compared to the non-mycorrhizal controls. Moreover, the acid tolerance of Z. serrata was positively correlated with net photosynthetic rate. Furthermore, our results indicated that mycorrhizal efficiencies varied with the intensity of AR and AMF identities, with D. versiformis proving much more efficient than the other fungi under acidic conditions. Overall, our findings highlight the significance of AMF associations for tree species suffering from AR stress and provide insight into strategies for improving the acid tolerance of plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera P, Cumming J, Oehl F, Cornejo P, Borie F (2015) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in acidic soils and their contribution to aluminum phytotoxicity alleviation. In: Panda SK, Baluška F (eds) Aluminum stress adaptation in plants, signaling and communication in plants. Springer, Switzerland, pp 203–228
Albornoz FE, Dixon KW, Lambers H (2020) Revisiting mycorrhizal dogmas: are mycorrhizas really functioning as they are widely believed to do? Soil Ecol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42832-020-0070-2
Al-Karaki GN (2006) Nursery inoculation of tomato with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and subsequent performance under irrigation with saline water. Sci Hortic 109:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.02.019
Amanifar S, Toghranegar Z (2020) The efficiency of arbuscular mycorrhiza for improving tolerance of Valeriana officinalis L. and enhancing valerenic acid accumulation under salinity stress. Ind Crops Prod 147:112234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112234
Andrade GC, Castro LN, da Silva LC (2020) Micromorphological alterations induced by simulated acid rain on the leaf surface of Joannesia princeps Vell. (Euphorbiaceae). Ecol Indic 116:106526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106526
Anwar G, Lilleskov EA, Chimner RA (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation has similar benefits to fertilization for Thuja occidentalis L. seedling nutrition and growth on peat soil over a range of pH: implications for restoration. New Forest 51:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09732-x
Bao GZ, Tang WY, An QR, Liu YX, Tian JQ, Zhao N, Zhu SN (2020) Physiological effects of the combined stresses of freezing-thawing, acid precipitation and deicing salt on alfalfa seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 20:204. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02413-4
Bertness MD, Callaway R (1994) Positive interactions in communities. Trends Ecol Evol 9:191–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(94)90088-4
Bussotti F, Pollastrini M (2021) Revisiting the concept of stress in forest trees at the time of global change and issues for stress monitoring. Plant Stress 2:100013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2021.100013
Cao Y, Wang S, Zhang G, Luo J, Lu S (2009) Chemical characteristics of wet precipitation at an urban site of Guangzhou, South China. Atmos Res 94:462–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.07.004
Chen L, Lei N (2019) Effect of soil microbe inoculation on Koelreuteria paniculata seedlings growth under simulated acid rain stress. Ecol Environ Sci 28:438–445. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:TRYJ.0.2019-03-002
Clark RB (1997) Arbuscular mycorrhizal adaptation, spore germination, root colonization, and host plant growth and mineral acquisiiton at low pH. Plant Soil 192:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004218915413
da Fonseca SS, da Silva BRS, Lobato AKD (2020) 24-Epibrassinolide positively modulate leaf structures, antioxidant system and photosynthetic machinery in rice under simulated acid rain. J Plant Growth Regul 39:1559–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10167-4
Date RA, Grundon NJ, Rayment GE, Probert ME (1995) Plant-soil interactions at low pH: principles and management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Dovrat G, Meron E, Shachak M, Golodets C, Osem Y (2019) Plant size is related to biomass partitioning and stress resistance in water-limited annual plant communities. J Arid Environ 165:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2019.04.006
Du EZ, Dong D, Zeng XT, Sun ZZ, Jiang XF, de Vries W (2017) Direct effect of acid rain on leaf chlorophyll content of terrestrial plants in China. Sci Total Environ 605:764–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.044
Evelin H, Giri B, Kapoor R (2012) Contribution of Glomus intraradices inoculation to nutrient acquisition and mitigation of ionic imbalance in NaCl-stressed Trigonella foenum-graecum. Mycorrhiza 22:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-011-0392-0
Gilani MM, Tigabu M, Liu B, Farooq TH, Rashid MHU, Ramzan M, Ma XQ (2020) Seed germination and seedling emergence of four tree species of southern China in response to acid rain. J for Res 32:471–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01102-0
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 84:489–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1980.tb04556.x
Gosling P, Jones J, Bending GD (2016) Evidence for functional redundancy in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and implications for agroecosystem management. Mycorrhiza 26:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-015-0651-6
Grilli G, Urcelay C, Longo MS, Galetto L (2014) Mycorrhizal fungi affect plant growth: experimental evidence comparing native and invasive hosts in the context of forest fragmentation. Plant Ecol 215:1513–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-014-0410-3
He L, Xu J, Hu LL, Ren ML, Tang JJ, Chen X (2019) Nurse effects mediated by acid-tolerance of target species and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization in an acid soil. Plant Soil 441:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04103-z
Huang K, Zhuang G, Xu C, Wang Y, Tang A (2008) The chemistry of the severe acidic precipitation in Shanghai, China. Atmos Res 89:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2008.01.006
Jakobsen I, Abbott LK, Robson AD (1992) External hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Trifolium subterraneum L.: 1. Spread of hyphae and phosphorus inflow into roots. New Phytol 120:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1992.tb01077.x
Jansa J, Smith FA, Smith SE (2008) Are there benefits of simultaneous root colonization by different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? New Phytol 177:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02294.x
Jiang HW, Jiang HW, Li JH, Li X (2012) Research progress of Zelkova Spach. J Jiangsu for Sci Technol 39:51–54. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2012.05.012
Jiao L, Wang L, Zhou Q, Huang X (2017) Stomatal and non-somatal factors regulated the photosynthesis of soybean seedligns in the present of exogenous bisphenol A. Ecotox Environ Safe 145:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.028
Johnson NC, Wilson GWT, Wilson JA, Miller RM, Bowker MA (2015) Mycorrhizal phenotypes and the law of the minimum. New Phytol 205:1473–1484. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13172
Koide RT (2000) Functional complementary in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytol 147:233–235. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00710.x
Larssen T, Seip HM, Semb A, Mulder J, Muniz IP, Vogt RD, Lydersen E, Angell V, Dagang T, Eilertsen O (1999) Acid deposition and its effects in China: an overview. Environ Sci Policy 2:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1462-9011(98)00043-4
León-Sánchez L, Nicolás E, Nortes PA, Maestre FT, Querejeta JI (2016) Photosynthesis and growth reduction with warming are driven by nonstomatal limitations in a Mediterranean semi-arid shrub. Ecol Evol 6:2725–2738. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2074
Li X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Pei C (2021) Response of soil chemical properties and enzyme activity of four species in the three gorges reservoir area to simulated acid rain. Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111457
Liang G, Hui D, Wu X, Wu J, Liu J, Zhou G, Zhang D (2016) Effects of simulated acid rain on soil respiration and its components in a subtropical mixed conifer and broadleaf forest in southern China. Environ Sci-Proc Imp 18:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EM00434A
Liang C, Ma Y, Li L (2020) Comparison of plasma membrane H+-ATPase response to acid rain stress between rice and soybean. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:6389–6400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07285-2
Liu Z, Yang J, Zhang J, Xiang H, Wei H (2019) A bibliometric analysis of research on acid rain. Sustainability 11:3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113077
Liu X, Feng Z, Zhao Z, Zhu H, Yao Q (2020) Acidic soil inhibits the functionality of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by reducing arbuscule formation in tomato roots. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 66:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2020.1721320
Macaulay BM, Enahoro GE (2015) Effects of simulated acid rain on the morphology, phenology and dry biomass of a local variety of maize (Suwan-1) in Southwestern Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 187:622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4844-4
Maestre FT, Valladares F, Reynolds JF (2005) Is the change of plant-plant interactions with abiotic stress predictable? A meta-analysis of field results in arid environments. J Ecol 93:748–757. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2005.01017.x
McNamara NP, Black HIJ, Beresford NA, Parekh NR (2003) Effects of acute gamma irradiation on chemical, physical and biological properties of soils. Appl Soil Ecol 24:117–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(03)00073-8
Medeiros CAB, Clark RB, Ellis JR (1994) Growth and nutrient uptake of sorghum cultivated with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza isolates at varying pH. Mycorrhiza 4:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206778
Niu YW, Pu JJ, Deng FP, Qi B (2017) Analysis on spatial and temporal evolution of acid rain and its causes from 1992 to 2012 in Zhejiang. Environ Monitor China 33:55–62. https://doi.org/10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2017.06.08
Qiu YJ, Zhang NL, Zhang LL, Zhang XL, Wu AP, Huang JY, Yu SQ, Wang YH (2020) Mediation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and biochemical parameters of Ligustrum vicaryi in response to salinity. Physiol Mol Plant P 112:101522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2020.101522
Raju PS, Clark RB, Ellis JR, Maranville JW (1988) Effects of Va mycorrhizae on growth and mineral uptake of sorghum grown at varied levels of soil acidity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:919–931. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628809367985
Rengel Z (2003) Handbook of soil acidity. CRC Press, New York
Rodriguez-Sanchez VM, Rosas U, Calva-Vasquez G, Sandoval-Zapotitla E (2020) Does acid rain alter the leaf anatomy and photosynthetic pigments in urban trees? Plants 9:862. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070862
Rohyadi A (2008) Growth responses of external hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to acidic soil conditions and their effects on cowpea growth. Microbiol Indones 2:22–26. https://doi.org/10.5454/mi.2.1.5
Rohyadi A, Smith FA, Murray RS, Smith SE (2004) Effects of pH on mycorrhizal colonization and nutrient uptake in cowpea under conditions that minimise confounding effects of elevated available aluminium. Plant Soil 260:283–290
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Porcel R, Azcon C, Aroca R (2012) Regulation by arbuscular mycorrhizae of the integrated physiological response to salinity in plants: new challenges in physiological and molecular studies. J Exp Bot 63:4033–4044. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers126
Saif SR (1987) Growth responses of tropical forage plant species to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae: I. Growth, mineral uptake and mycorrhizal dependency. Plant Soil 97:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02149820
Sieverding E (1991) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza management in tropical agrosystems. Deutsche Gesellschaft Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Eschborn
Singh A, Agrawal M (2008) Acid ran and its ecological consequences. J Environ Biol 29:15–24. https://doi.org/10.2112/07A-0018.1
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic press, London
Smith SE, Smith FA, Jakobsen I (2004) Functional diversity in arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbioses: the contribution of the mycorrhizal P uptake pathway is not correlated with mycorrhizal responses in growth or total P uptake. New Phytol 162:511–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01039.x
Song XZ, Zhou GM, Gu HH, Qi LH (2015) Management practices amplify the effect of N deposition on leaf litter cecomposition of the Moso bamboo forest. Plant Soil 395:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2578-2
Tisserant B, Gianiazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S, Gollotte A (1993) In planta histochemical staining of fungal alkaline phosphatase activity for analysis of efficienty arbuscular mycorrhizal infections. Mycol Res 97:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80248-7
Tong S, Zhang L (2014) Differential sensitivity of growth and net photosynthetic rates in five tree species seedlings under simulated acid rain stress. Pol J Environl Stud 23:2259–2264. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/24930
van der Heijden MGA, Sanders IR (2003) Mycorrhizal ecology. Springer, Heiderlberg, pp 184–185
Vosátka M, Dodd JC (1998) The role of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the growth of Calamagrostis villosa and Deschampsia flexuosa, in experiments with simulated acid rain. Plant Soil 200:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1004366822682
Vosátka M, Batkhuugyin E, Albrechtová J (1999) Response of three arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to simulated acid rain and aluminium stress. Biol Plant 42:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002125005497
Wang JP, Fu ZY, Ren Q, Zhu LJ, Lin J, Zhang JC, Cheng XF, Ma JY, Yue JM (2019) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake of Zelkova serrata (Thunb.) Makino seedlings under salt stress. Forests 10:186-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020186
Wang LH, Sun JW, Wang W, Zhou Q (2017) Research advances in effects of acid arin on plant photosynthesis. J Saf Environ 17:775–780. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.02.069
Wang YH, Wang MQ, Li Y, Wu AP, Huang JY (2018) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and nitrogen uptake of Chrysanthemum morifolium under salt stress. PLoS ONE 13:e0196408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196408
Wei H, Liu W, Zhang J, Qin Z (2017) Effects of simulated acid rain on soil fauna community composition and their ecological niches. Environ Pollut 220:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.088
Wen K, Liang C, Wang L, Hu G, Zhou Q (2011) Combined effects of lanthanum ion and acid rain on growth, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure in soybean seedlings. Chemosphere 84:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.054
Wu QS, Zou YN, He XH (2010) Contributions of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to growth, photosynthesis, root morphology and ion balance of citrus seedlings under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 32:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0407-z
Xia LN, Shao CL, Zhang NL, Wu AP, Xie JB, Qiu YJ, He XB, Pei J, Wang XD, Wang YH (2021) Improved tolerance of mycorrhizal Torreya grandis seedlings to sulfuric acid rain related to phosphorus and zinc contents in shoots. J Fungi 7:296. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7040296
Zhang M, Wang S, Wu F, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2007) Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in southeastern China. Atmos Res 84:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.09.003
Zhang CY, Yi XQ, Gao XZ, Wang MH, Shao CY, Lv ZD, Chen JJ, Liu ZH, Shen CW (2020) Physiological and biochemical responses of tea seedlings (Camellia sinensis) to simulated acid rain conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:110315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110315
Zhao B, Trouvelot A, Gianiazzi S, Gianiazzi-Pearson V (1997) Influence of two legume species on hyphal production and activity of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 7:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050179
Zhejiang Ecology and Environment Bureau (2016) Ecological and environmental status bulletin of Zhejiang Province in 2016. http://sthjt.zj.gov.cn/art/2017/6/2/art_1201912_13471748.html
Zhu LJ, Fu ZY, Zhang JC, Wang JP, Lin J, Yuan ZM, Cheng XF, Chu DS (2018) Effects of mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthetic characteristics of Zelkova serrata Thunb. J Nanjing for Univ 42:121–127. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201801031
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32071644; 31400366), Special Foundation for National Science and Technology Basic Research Program of China (2019FY102000), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB 31030000) and the Key Research and Development Plan of Zhejiang Province (No. 2017C02028). We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments for the improvement of the manuscript in the revision process. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by George Yan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liu, S., Shao, C. et al. Enhancement of photosynthetic parameters and growth of Zelkova serrata by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under simulated sulfuric acid rain. Plant Ecol 222, 1361–1374 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-021-01184-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-021-01184-8