Abstract
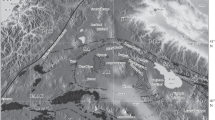
The intraplate Cameroon Volcanic Line (CVL) straddles the African-South Atlantic continent-ocean boundary and is composed mainly of alkaline basic volcanic rocks. Voluminous silicic volcanics characterize the continental sector of the CVL. We present here new geochemical, isotopic (Sr-Nd-O) and 40Ar/39Ar geochronological data on the main silicic volcanic centres of the Western (Mt. Oku, Sabga and Mt. Bambouto) and Eastern (Ngaoundere plateau) Cameroon Highlands. The silicic volcanism of Mt. Oku, Sabga and Mt. Bambouto occurred between 25 and 15 Ma and is represented by voluminous quartz-normative trachytes and minor rhyolitic ignimbrites. At Mt. Bambouto central volcano about 700 m of silicic volcanics erupted in less than 2.7 million years. These silicic volcanics are associated with slightly to moderately alkaline basalts and minor basanites. In general, onset of the silicic volcanism migrated from NE (Oku: 25 Ma) to SW (Sabga: 23 Ma; Bambouto: 18 Ma; and Mt. Manengouba: 12 Ma). The silicic volcanism of the Ngaoundere plateau (eastern branch of the CVL) is instead dominated by nepheline-normative trachytes which are associated with strongly alkaline basalts and basanitic rocks. These Ne-trachytes are younger (11-9 Ma) than the Q-trachytes of the Western Highlands. The least differentiated silicic volcanics are isotopically similar (87Sr/86Sr < 0.70380; 143Nd/144Nd > 0.51278) to the associated alkaline basalts suggesting differentiation processes without appreciable interaction with crustal materials. Such interactions may, however, have played some role in the genesis of the most evolved silicic volcanics which have 87Sr/86Sr as high as 0.705–0.714. Fractional crystallization is the preferred mechanism for genesis of the silicic melts of both Western and Eastern Highlands, as shown by modeling major and trace element variations. The genesis of the least evolved Q-trachytes from the Western Highlands, starting from slightly to moderately alkaline basalts, is compatible with fractionation of dominantly plagioclase, clinopyroxene and magnetite. Crystal fractionation may have occurred at low pressure and at QFM buffer f O2conditions. Parental magmas of the Ngaoundere Ne-trachytes are likely instead to have been strongly alkaline basalts which evolved through crystal fractionation at higher P (6-2 kbar) and f O2 (QFM + 2). The migration (25 to 12 Ma) of the silicic volcanism from NE to SW in the continental sector of the CVL is reminiscent of that (31-5 Ma) of the onset of the basic volcanism in the oceanic sector (Principe to Pagalu islands) of the CVL. These ages, and that (11-9 Ma) of the silicic volcanism of the Ngaoundere plateau, indicate that the Cameroon Volcanic Line as a whole may not be easily interpreted as the surface expression of hot-spot magmatism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 February 1998 / Accepted: 22 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marzoli, A., Renne, P., Piccirillo, E. et al. Silicic magmas from the continental Cameroon Volcanic Line (Oku, Bambouto and Ngaoundere): 40Ar-39Ar dates, petrology, Sr-Nd-O isotopes and their petrogenetic significance. Contrib Mineral Petrol 135, 133–150 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050502
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050502