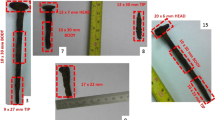
Abstract
The phase composition and the microstructure of four ferrous Japanese arrows of the Edo period (17th-19th century) has been determined through two complementary neutron techniques: Position-sensitive wavelength-resolved neutron transmission analysis (PS-WRNTA) and time-of-flight neutron diffraction (ToF-ND). Standard ToF-ND technique has been applied by using the INES diffractometer at the ISIS pulsed neutron source in the UK, while the innovative PS-WRNTA one has been performed at the J-PARC neutron source on the BL-10 NOBORU beam line using the high spatial high time resolution neutron imaging detector. With ToF-ND we were able to reach information about the quantitative distribution of the metal and non-metal phases, the texture level, the strain level and the domain size of each of the samples, which are important parameters to gain knowledge about the technological level of the Japanese weapon. Starting from this base of data, the more complex PS-WRNTA has been applied to the same samples. This experimental technique exploits the presence of the so-called Bragg edges, in the time-of-flight spectrum of neutrons transmitted through crystalline materials, to map the microstructural properties of samples. The two techniques are non-invasive and can be easily applied to archaeometry for an accurate microstructure mapping of metal and ceramic artifacts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Kapp, The Craft of the Japanese Sword (Kodansha International, 1998).
K. Nagayama, The Connoisseurs Book of Japanese Swords (Kodansha International, 1997).
M. Chkashige, Oriental Alchemy (Samuel Weiser Press, 1974).
F. Grazzi, L. Bartoli, F. Civita, M. Zoppi, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 395, 1961 (2009).
F. Grazzi, F. Civita, A. Williams, A. Scherillo, E. Barzagli, L. Bartoli, D. Edge, M. Zoppi, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 400, 1493 (2011).
F. Grazzi, L. Bartoli, F. Civita, R. Franci, A. Paradowska, A. Scherillo, M. Zoppi, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 26, 1030 (2011).
F. Salvemini, F. Grazzi, S. Peetermans, F. Civita, R. Franci, S. Hartmann, E. Lehmann, M. Zoppi, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 27, 1494 (2012).
F. Grazzi, M. Celli, S. Siano, M. Zoppi, Nuovo Cimento C 30, 59 (2007).
A.C. Larson, R.B. Von Dreele General Structure Analysis System (GSAS), Los Alamos National Laboratory Report, LAUR (2004) 86-748.
B.H. Toby, J. Appl. Cryst. 34, 210 (2001).
A. Steuwer, P.J. Withers, J.R. Santisteban, L. Edwards, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 074903 (2005).
J.R. Santisteban, L. Edwards, M.E. Fizpatrick, A. Steuwer, P.J. Withers, Appl. Phys. A 74, S1433 (2002).
M. Harada, K. Oikawa, Y. Kasugai, F. Maekawa, Prog. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1, 94 (2011).
A.S. Tremsin, J.B. McPhate, J.V. Vallerga, O.H.W. Siegmund, W.B. Feller, E. Lehmann, M. Dawson, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 628, 415 (2011).
S. Siano, L. Bartoli, J.R. Santisteban, W. Kockelmann, M.R. Daymond, M. Miccio et al., Archaeometry 48, 77 (2006).
E. Barzagli, F. Grazzi, F. Civita, A. Scherillo, A. Pietropaolo, G. Festa, M. Zoppi, Appl. Phys. A 113, 1143 (2013).
W. Kockelmann, A. Kirfel, Neutron Diffraction Imaging of cultural heritage objects (Archeometriai Muhel, 2006).
G. Artioli, Appl. Phys. A 89, 899 (2007).
E.H. Lehmann, P. Vontobel, E. Deschler-Erb, M. Soares, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 542, 68 (2005).
F. Grazzi, A. Scherillo, M. Zoppi, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 093704 (2009).
D.A. Scott, Metallography and microstructure of ancient andhistoric metals (Getty Conservation Institute, Singapore, 1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzagli, E., Grazzi, F., Salvemini, F. et al. Wavelength resolved neutron transmission analysis to identify single crystal particles in historical metallurgy. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 158 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2014-14158-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2014-14158-3