Abstract
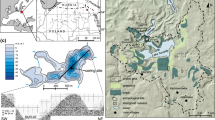
The accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements has been investigated in a well laminated sequence of Holocene and late Pleistocene lake sediments composed of diatomaceous gyttja, tuff and silt and clay sediments. Varve chronology of the annually deposited gyttja yielded a continuous high-resolution time sequence and allowed the absolute age dating of the sediment.
Fluxes of elements remained largely uniform from the late Pleistocene into the Holocene (12 867–2 364 VT years ago; VT: varve time, years before 1950). Higher trace element and heavy metal fluxes occur from 2 322 to 862 VT years ago and reached their maxima in the uppermost sediments (<845 VT years ago). These increasing element fluxes correlate with increasing inputs of clastic material. The changing accumulation rates are the result of elevated soil erosion in the lake catchment caused by human settlement, deforestation and agricultural activities. Thus disturbances of the natural geochemical cycles of the Holzmaar region have occurred since the beginning of the Iron Age and especially since the beginning of the Middle Ages.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 May 1996 · Accepted: 19 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lottermoser, B., Schütz, U., Boenecke, J. et al. Natural and anthropogenic influences on the geochemistry of Quaternary lake sediments from Holzmaar, Germany. Environmental Geology 31, 236–247 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050185
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050185