Abstract
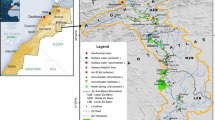
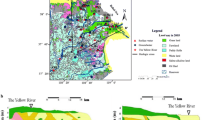
The deterioration of groundwater quality, particularly due to salinization, because of the overexploitation of groundwater in the Lower Central Plain of Thailand remains a major concern. With increasing demand for water there is a growing need for sustainable management of the resource, which would benefit from an improved understanding of the sources of chloride contamination. Thus, a hydrochemical and isotopic study was carried out to chemically characterize groundwater and to investigate possible sources of salinization, and in particular of chloride contamination, in the multi-layered Bangkok aquifer system. Groundwater samples were taken from four topmost aquifers (Bangkok, Phra Pradaeng, Nakhon Luang, and Nonthaburi). Additionally, short-term rainwater sampling, as well as river and seawater sampling was performed and later analyzed for ionic composition and stable water isotopes. Ionic and isotopic data indicate at least three different recharge sources for groundwater. The major recharge source is rainwater. The influence of seawater is limited to the coastal region and tidally influenced areas of the two main rivers (Chao Phraya and Tha Chin). Bromide data also suggest the influence of saline water in deeper aquifers due to trapped water. Most importantly, although the influence of seawater on groundwater is recognizable, the surrounding geology contributes a significant number of dissolved ions detected in the groundwater.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlai P (2007) Numerical modeling of possible saltwater intrusion mechanisms in the multiple-layer coast aquifer system of the Gulf of Thailand. Unpublished PhD dissertation. University of Kassel, Germany, p 148
Asian Institute of Technology (2007) Sustainable water management policy (SWMP) study on groundwater management—Bangkok, Thailand. Research report submitted to the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies, Japan. Bangkok: Asian Institute of Technology (AIT)
Babel MS, Rivas AA (2008) Groundwater quality management policy research in Bangkok and vicinity. Research report submitted to the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies, Japan
Das Gupta A (1985) Simulated salt-water movement in the Nakhon Luang aquifer, Bangkok, Thailand. Ground Water 23(4):512–522
Das Gupta A, Babel MS (2005) Challenges for sustainable management of groundwater use in Bangkok, Thailand. Int J Water Resour Dev 21(3):453–464
Das Gupta A, Siddique M (1981) Hydrodynamic response of Nakhon Luang aquifer, Bangkok, Thailand. Ground Water 19(5):469–475
Das Gupta A, Yapa P (1982) Saltwater encroachment in an aquifer: a case study. Water Resour Res 18(3):546–556
Das Gupta A, Arbhabhirama A, Ahmad B (1979) Preliminary investigation of saltwater encroachment into the Nakhon Luang aquifer, Bangkok, Thailand. Geotech Eng 10:141–157
Das Gupta A, Jayakrishnan R, Onta P, Ramnarong V (1995) Assessment of groundwater quality for the Bangkok aquifer system. Models for Assessing and Monitoring Groundwater Quality, IAHS publication no. 227: 3–10
Demirel Z (2004) The history and evaluation of saltwater intrusion into a coastal aquifer in Mersin, Turkey. J Environ Manage 70:275–282
Department of the Air Force (1965) Climate of Thailand. Department of the air force, San Francisco
Edmunds WM, Ma J, Aeschbach-Hertig W, Kipfer R, Darbyshire DPF (2006) Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin, North West China. Applied geochemistry 21(12):2148–2170
FAO (1997) Retrieved August 01, 2008, from Aquastat—FAO’s Information System on Water and agriculture. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/countries/index.stm
IAEA (2008) Retrieved November 11, 2008, from Wiser—Water isotope system for data analysis, visualization and electronic retrieval. http://nds121.iaea.org/wiser/index.php
JICA (1995) The study on management of groundwater and land subsidence in the Bangkok metropolitan area and its vicinity. Kokusai Kogyo Co., Ltd., Tokyo
Kasetsart University (KU) (2004) Effect of groundwater over-pumping mitigation: mathematical model study. Final project report submitted to the department of groundwater resources, Bangkok
Kim Y, Lee K, Koh D, Lee D, Lee S, Park W, Koh G, Woo N (2003) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: a case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea. J Hydrol 270:282–294
Lee K, Wenner DB, Lee I (1999) Using H- and O-isotopic data for estimating the relative contributions of rainy and dry season precipitation to groundwater: example from Cheju Island, Korea. J Hydrogeol 222:65–74
Mazor E (2004) Chemical and Isotopic groundwater hydrology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, p 453
Metrix Associates Co. Ltd (2004) Executive summary report—the study on groundwater protection in the central plain. Department of groundwater resources (DGR), Bangkok
Nozaki Y, Yamamoto Y, Manaka T, Amakawa H, Snidvongs A (2001) Dissolved barium and radium isotopes in the Chao Phraya estuarine mixing zone Thailand. Cont Shelf Res 21(13–14):1435–1448
Panno S, Hackley K, Hwang H, Greenberg S, Krapac I, Landsberger S, O’Kelly D (2006) Characterization and identification of Na–Cl sources in ground water. Ground Water 44(2):176–187
Park S, Yun S, Chae G, Yoo I, Shin K, Heo C, Lee S (2005) Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. J Hydrol 313:182–194
Rau J, Nutalaya P (1981) Chloride contamination in aquifers of the Central Plain, Thailand. Geotech Eng 12:123–151
Sampat P (2000) Deep trouble: the hidden threat of groundwater pollution. Worldwatch Paper 154. http://www.worldwatch.org/system/files/EWP154.pdf
Sinsakul S (2000) Late quaternary geology of the lower central plain, Thailand. J Asian Earth Sci 18:415–426
Wichakul, S (2007) Estimation of safe yield for the Bangkok aquifer system. Unpublished Master Thesis. Asian Institute of Technology, Pathumthani, Thailand
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Leuphana University of Lueneburg, Germany; the Asian Institute of Technology in Bangkok, Thailand; the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES), Japan; and the Yamanashi University, Kofu, Japan. The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. A. Toeppe for her comments and assistance. Also, sincere appreciation is extended to the laboratory members and the students of the Yamanashi University, especially Ms. U. Hiraga and Mr. S. K. Chapagain. Further, the authors are deeply grateful to Mr. P. Tibkaew, Mr. V. Kanganapongporn, Mr. K. Pimsak, and Mr. P. Chutipattarasakul for the assistance during fieldwork. Moreover, Ms. S. Hanmeng deserves a lot of thanks for her assistance with the Thai language and Ms. S. Wichakul for providing additional data and information. Thankful acknowledgement is also extended to Ms. M. Franks for editing the earlier version of this manuscript. Thanks are also due to Ms. K. J. McElhinney for her assistance with the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoecker, F., Babel, M.S., Gupta, A.D. et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterization of groundwater salinization in the Bangkok aquifer system, Thailand. Environ Earth Sci 68, 749–763 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1776-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1776-y