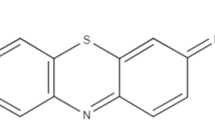
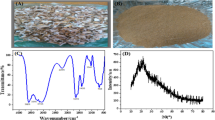
Abstract
This study prepared a biosorbent from the agricultural waste of atemoya peels, which was then used to remove the methylene blue dye. The atemoya peels were used in natura, and some were subjected to an alkaline treatment. The pH values obtained for the points of zero charge were 6.0 and 8.0 for the untreated and alkaline-treated materials, respectively. For neutral and/or alkaline pH values, the untreated and treated materials achieved average removals of approximately 80% and 90%, respectively. A kinetic study of the model dye removal profile showed a higher removal ratio over a shorter period for the alkaline-treated material. This profile is described by the pseudo-second-order model, which was the best fit for the D-R isotherm in both biosorbents. The maximum biosorption capacities were 190.18 mg g−1 (untreated) and 264.50 mg g−1 (treated) at 45 °C, and the alkaline-treated materials were shown to be reusable for at least 5 cycles. The results show that these biosorbents are efficient and cost-effective to remove the studied model molecules.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Araújo, C. S. T., Almeida, I. L. S., Rezende, H. C., Marcionilio, S. M. L. O., Léon, J. J. L., & de Matos, T. N. (2018). Elucidation of mechanism involved in adsorption of Pb (II) onto lobeira fruit (Solanum lycocarpum) using Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherms. Microchemical Journal, 137, 348–354.
Aryee, A. A., Mpatani, F. M., Kani, A. N., Dovi, E., Han, R., Li, Z., & Qu, L. (2020). Iminodiacetic acid functionalized magnetic peanut husk for the removal of methylene blue from solution: Characterization and equilibrium studies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–15
Bafana, A., Devi, S. S., & Chakrabarti, T. (2011). Azo dyes: Past, present and the future. Environmental Reviews, 19(NA), 350–371.
Balarak, D., Mostafapour, F. K., Azarpira, H., & Joghataei, A. (2017). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of ampicilin unto montmorillonite nanoparticles. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, 1–9
Baron, D., Amaro, A. C. E., Macedo, A. C., Boaro, C. S. F., & Ferreira, G. (2018). Physiological changes modulated by rootstocks in atemoya (Annona x atemoya Mabb.): Gas exchange, growth and ion concentration. Brazilian Journal of Botany, 41(1), 219–225.
Biehl, P., von der Lühe, M., & Schacher, F. H. (2018). Reversible adsorption of methylene blue as cationic model cargo onto polyzwitterionic magnetic nanoparticles. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 39(14), 1800017.
Carneiro, P. A., Umbuzeiro, G. A., Oliveira, D. P., & Zanoni, M. V. B. (2010). Assessment of water contamination caused by a mutagenic textile effluent/dyehouse effluent bearing disperse dyes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1–3), 694–699.
Carvalho, L. B., Chagas, P. M. B., Marques, T. R., Razafitianamaharavo, A., Pelletier, M., Nolis, P., ... Pinto, L. d. M. A. (2019). Removal of the synthetic hormone methyltestosterone from aqueous solution using a β-cyclodextrin/silica composite. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(6), 103492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103492
Carvalho, L. B., Chagas, P. M. B., & Pinto, L. M. A. (2018). Caesalpinia ferrea fruits as a biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous medium. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229(9), 297.
Chen, S. G., & Yang, R. T. (1994). Theoretical basis for the potential theory adsorption isotherms The Dubinin-Radushkevich and Dubinin-Astakhov Equations. Langmuir, 10(11), 4244–4249.
Chieng, H. I., Lim, L. B. L., & Priyantha, N. (2017). Enhancement of crystal violet dye adsorption on Artocarpus camansi peel through sodium hydroxide treatment. Desalination and Water Treatment, 58, 320–331.
Cooksey, C. J. (2017). Quirks of dye nomenclature. 8. Methylene blue, azure and violet. Biotechnic & Histochemistry, 92(5), 347–356.
Costa, E. V., Pinheiro, M. L. B., Xavier, C. M., Silva, J. R. A., Amaral, A. C. F., Souza, A. D. L., ... Machado, G. M. C. (2006). A pyrimidine-β-carboline and other alkaloids from Annona f oetida with antileishmanial activity. Journal of natural products, 69(2), 292-294
Cruz, L. S. D., Lima, R. Z., Abreu, C. M. P. D., Corrêa, A. D., & Pinto, L. D. M. A. (2013). Physical and chemical characterization of fractions of fruit atemoya Gefner. Ciência Rural, 43(12), 2280–2284.
Dada, A. O., Olalekan, A. P., Olatunya, A. M., & Dada, O. (2012). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3(1), 38–45.
de Souza, P. A., da Silva Freitas, R. V., Batista, E. M., da Costa, F. B., & Maracajá, P. B. (2015). Armazenamento de atemoias, Annona squamosa x Annona cherimola, recobertas com filme PVC. Revista Verde De Agroecologia e Desenvolvimento Sustentável, 10(5), 39.
Dutta, M., Islam, N., Rabha, S., Narzary, B., Bordoloi, M., Saikia, D., ... Saikia, B. K. (2020). Acid mine drainage in an Indian high-sulfur coal mining area: Cytotoxicity assay and remediation study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 389, 121851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121851
El-Naggar, N.E.-A., & Rabei, N. H. (2020). Bioprocessing optimization for efficient simultaneous removal of methylene blue and nickel by Gracilaria seaweed biomass. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–21.
Enniya, I., & Jourani, A. (2017). Study of Methylene Blue Removal by a biosorbent prepared with Apple peels. J. Mater. Environ. Sci., 8(12), 4573–4581.
Ferrari, V., Taffarel, S. R., Espinosa-Fuentes, E., Oliveira, M. L. S., Saikia, B. K., & Oliveira, L. F. S. (2019). Chemical evaluation of by-products of the grape industry as potential agricultural fertilizers. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, 297–306.
Fomina, M., & Gadd, G. M. (2014). Biosorption: Current perspectives on concept, definition and application. Bioresource Technology, 160, 3–14.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2009). An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 54–60.
Franco, D. S. P., Georgin, J., Drumm, F. C., Netto, M. S., Allasia, D., Oliveira, M. L. S., & Dotto, G. L. (2020). Araticum (Annona crassiflora) seed powder (ASP) for the treatment of colored effluents by biosorption. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(10), 11184–11194.
Freundlich, H. (1907). Über die adsorption in lösungen. Zeitschrift Für Physikalische Chemie, 57(1), 385–470.
Georgin, J., Franco, D. S. P., Netto, M. S., Allasia, D., Oliveira, M. L. S., & Dotto, G. L. (2020). Treatment of water containing methylene by biosorption using Brazilian berry seeds (Eugenia uniflora). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–13.
Georgin, J., Marques, B. S., Peres, E. C., Allasia, D., & Dotto, G. L. (2018). Biosorption of cationic dyes by Pará chestnut husk (Bertholletia excelsa). Water Science and Technology, 77(6), 1612–1621.
Gerola, G. P., Boas, N. V., Caetano, J., Tarley, C. R. T., Gonçalves, A. C., & Dragunski, D. C. (2013). Utilization of passion fruit skin by-product as lead (II) ion biosorbent. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224(2), 1446.
Ho, Y.-S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465.
Jawad, A. H., Kadhum, A. M., & Ngoh, Y. S. (2018). Applicability of dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus) peels as low-cost biosorbent for adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 109, 231–240.
Juchen, P. T., Piffer, H. H., Veit, M. T., da Cunha Gonçalves, G., Palácio, S. M., & Zanette, J. C. (2018). Biosorption of reactive blue BF-5G dye by malt bagasse: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(6), 7111–7118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.009
Kariuki, Z., Kiptoo, J., & Onyancha, D. (2017). Biosorption studies of lead and copper using rogers mushroom biomass ‘Lepiota hystrix.’ South African Journal of Chemical Engineering, 23, 62–70.
Khadir, A., Negarestani, M., & Ghiasinejad, H. (2020). Low-cost sisal fibers/polypyrrole/polyaniline biosorbent for sequestration of reactive orange 5 from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(4), 103956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103956
Kilic, M., Apaydin-Varol, E., & Pütün, A. E. (2011). Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from tobacco residues: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189(1–2), 397–403.
Kumara, P. S., Joshibaa, G. J., Feminaa, C. C., Varshinia, P., Priyadharshinia, S., Karthicka, M. A., & Jothiranib, R. (2019). A critical review on recent developments in the low-cost adsorption of dyes from wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 172, 395–416.
Kwak, J.-H., Islam, M. S., Wang, S., Messele, S. A., Naeth, M. A., El-Din, M. G., & Chang, S. X. (2019). Biochar properties and lead (II) adsorption capacity depend on feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature, and steam activation. Chemosphere, 231, 393–404.
Lagergren, S. K. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven Vetenskapsakad Handingarl, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids Part I. Solids. Journal of the American chemical society, 38(11), 2221–2295.
Lin, S.-H., & Juang, R.-S. (2002). Heavy metal removal from water by sorption using surfactant-modified montmorillonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 92(3), 315–326.
Mateo-Sagasta, J., Zadeh, S. M., Turral, H., & Burke, J. (2017). Water pollution from agriculture: A global review. Executive summary. Rome, Italy: FAO Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management ….
Meili, L., Lins, P. V. S., Costa, M. T., Almeida, R. L., Abud, A. K. S., Soletti, J. I., ... Carvalho, S. H. V. (2019). Adsorption of methylene blue on agroindustrial wastes: Experimental investigation and phenomenological modelling. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology, 141, 60-71
Mohamed, M. A., Salleh, W. N. W., Jaafar, J., Ismail, A. F., Abd Mutalib, M., Mohamad, A. B., ... Hir, Z. A. M. (2017). Physicochemical characterization of cellulose nanocrystal and nanoporous self-assembled CNC membrane derived from Ceiba pentandra. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 1892-1902
Mohtar, S. S., Busu, T. N. Z. T. M., Noor, A. M. M., Shaari, N., Yusoff, N. A., Bustam, M. A., ... Mat, H. B. (2015). Extraction and characterization of lignin from oil palm biomass via ionic liquid dissolution and non-toxic aluminium potassium sulfate dodecahydrate precipitation processes. Bioresource Technology, 192, 212-218
Mokhtar, N., Aziz, E. A., Aris, A., Ishak, W. F. W., & Mohd Ali, N. S. (2017). Biosorption of azo-dye using marine macro-alga of Euchema Spinosum. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(6), 5721–5731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.10.043
Morton, J. F. (1987). Fruits of warm climates. JF Morton.
Novais, R. M., Ascensao, G., Tobaldi, D. M., Seabra, M. P., & Labrincha, J. A. (2018). Biomass fly ash geopolymer monoliths for effective methylene blue removal from wastewaters. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 783–794.
Pérez-Morales, J. M., Sánchez-Galván, G., & Olguín, E. J. (2019). Continuous dye adsorption and desorption on an invasive macrophyte (Salvinia minima). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(6), 5955–5970.
Rafatullah, M., Sulaiman, O., Hashim, R., & Ahmad, A. (2010). Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 70–80.
Ramrakhiani, L., Ghosh, S., & Majumdar, S. (2016). Surface modification of naturally available biomass for enhancement of heavy metal removal efficiency, upscaling prospects, and management aspects of spent biosorbents: A review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(1), 41–78.
Rangabhashiyam, S., Lata, S., & Balasubramanian, P. (2018). Biosorption characteristics of methylene blue and malachite green from simulated wastewater onto Carica papaya wood biosorbent. Surfaces and Interfaces, 10, 197–215.
Regalbuto, J. R., & Robles, J. (2004). The engineering of Pt/carbon catalyst preparation. University of Illinois, Chicago, 1, 1–14.
Richardson, S. D., & Ternes, T. A. (2018). Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues. Analytical Chemistry, 90(1), 398–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04577
Rojo, E., Alonso, M. V., Domínguez, J. C., Saz‐Orozco, B. D., Oliet, M., & Rodriguez, F. (2013). Alkali treatment of viscose cellulosic fibers from eucalyptus wood: structural, morphological, and thermal analysis. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 130(3), 2198–2204.
Rudzinski, W., & Plazinski, W. (2007). Studies of the kinetics of solute adsorption at solid/solution interfaces: On the possibility of distinguishing between the diffusional and the surface reaction kinetic models by studying the pseudo-first-order kinetics. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(41), 15100–15110.
Sadaf, S., & Bhatti, H. N. (2014). Batch and fixed bed column studies for the removal of Indosol Yellow BG dye by peanut husk. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45(2), 541–553.
Schwanninger, M., Rodrigues, J. C., & Fackler, K. (2011). A review of band assignments in near infrared spectra of wood and wood components. Journal of near Infrared Spectroscopy, 19(5), 287–308.
Sellaoui, L., Hessou, E. P., Badawi, M., Netto, M. S., Dotto, G. L., Silva, L. F. O., ... Chen, Z. (2021a). Trapping of Ag+, Cu2+, and Co2+ by faujasite zeolite Y: New interpretations of the adsorption mechanism via DFT and statistical modeling investigation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 420, 127712.
Sellaoui, L., Yazidi, A., Ali, J., Dotto, G. L., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., Oliveira, L. F. S., & Chen, Z. (2021b). Theoretical study and analysis of o-nitrophenol adsorption using layered double hydroxides containing Ca-Al, Ni-Al and Zn-Al. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(32), 44547–44556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13882-x
Shanmugarajah, B., Chew, I. M., Mubarak, N. M., Choong, T. S., Yoo, C., & Tan, K. (2019). Valorization of palm oil agro-waste into cellulose biosorbents for highly effective textile effluent remediation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 210, 697–709.
Sharma, S., Hasan, A., Kumar, N., & Pandey, L. M. (2018). Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using immobilized Agrobacterium fabrum biomass along with iron oxide nanoparticles as biosorbent. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(22), 21605–21615.
Silva, G. M. C., da Silva, M. P. S., Biazatti, M. A., dos Santos, P. C., da Silva, N. M., & Mizobutsi, G. P. (2016). Uso do 1-MCP e atmosfera modificada na pós-colheita de atemoia ‘Gefner.’ Revista Brasileira De Ciências Agrárias, 11(2), 67–72.
Silva, N. F., Netto, M. S., Silva, L. F. O., Mallmann, E. S., Lima, E. C., Ferrari, V., & Dotto, G. L. (2021). Composite carbon materials from winery composted waste for the treatment of effluents contaminated with ketoprofen and 2-nitrophenol. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105421
Singh, R. L., Singh, P. K., & Singh, R. P. (2015). Enzymatic decolorization and degradation of azo dyes–A review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 104, 21–31.
Sivakumar, R., Renganathan, P. S., Helan, H. M., & Rajachandrasekar, T. (2019). Removal of copper ion from aqueous solution using seeds of sugar apple (Annona squamosa L.).
Smoczyński, L., Pierożyński, B., & Mikołajczyk, T. (2020). The effect of temperature on the biosorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. Processes, 8(6), 636.
Temkin, M., & Pyzhev, V. (1940). Kinetics of the synthesis of ammonia on promoted iron catalysts. Jour Phys Chem (USSR), 13, 851–867.
Tkaczyk, A., Mitrowska, K., & Posyniak, A. (2020). Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 717, 137222
Tran, H. N., You, S.-J., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., & Chao, H.-P. (2017). Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Research, 120, 88–116.
Tsai, W.-T., Hsu, C.-H., & Lin, Y.-Q. (2019). Highly porous and nutrients-rich biochar derived from dairy cattle manure and its potential for removal of cationic compound from water. Agriculture, 9(6), 114.
Vithanage, M., Mayakaduwa, S. S., Herath, I., Ok, Y. S., & Mohan, D. (2016). Kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanistic studies of carbofuran removal using biochars from tea waste and rice husks. Chemosphere, 150, 781–789.
Venceslau, A.F.A.; Mendonça, A.C.; Benedick, L.A.Z.; Thomasi, S.S.; Nunes, C.A.; Pinto, L.M.A. (2021). Analysis of the chemical constituents of Thompson atemoya seed oil. Revista Brasileira de Fruticultura, 43(6)
Weber, W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 89(2), 31–60.
Xia, S., Zhang, L., Pan, G., Qian, P., & Ni, Z. (2015). Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with a nanocomposite system: synthesis, photocatalysis and degradation pathways. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 17(7), 5345–5351.
Yanishpolskii, V. V., Skubiszewska-Zieba, J., Leboda, R., Tertykh, V. A., & Klischar, I. V. (2000). Methylene Blue Sorption Equilibria on Hydroxylated Silica Surfaces as Well as on Carbon–Silica Adsorbents (Carbosils). Adsorption Science & Technology, 18(2), 83–95.
Yamil, L. d. O., Georgin, J., Franco, D. S. P., Netto, M. S., Foletto, E. L., Piccilli, D. G. A., ... Dotto, G. L. (2020). Transforming pods of the species Capparis flexuosa into effective biosorbent to remove blue methylene and bright blue in discontinuous and continuous systems. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–14.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Laboratory of Electronic Microscopy and Ultrastructural Analysis of the Federal University of Lavras and Finep, Fapemig, CNPq, and Capes for supplying the equipment and technical support for the experiments involving electron microscopy, as well as the Chemical Analysis and Prospection Center (CAPQ/UFLA).
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 and Institutional Scientific Initiation Scholarship Program – PIBIC/UFLA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Adneia de Fátima Abreu Venceslau: conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing.
Andressa Campos Mendonça: methodology, validation, investigation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Lucas Bragança Carvalho: conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Guilherme Max Dias Ferreira: formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Sergio Scherrer Thomasi: conceptualization, resources.
Luciana Matos Alves Pinto: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.27 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venceslau, A.d.A., Mendonça, A.C., Carvalho, L.B. et al. Removal of Methylene Blue from an Aqueous Medium Using Atemoya Peel as a Low-cost Adsorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05414-7