Abstract
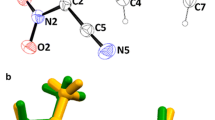
A supermolecular approach combined with an iterative electrostatic scheme was employed to investigate the nonlinear optical properties of the hybrid L-arginine phosphate monohydrate crystal, the procedure being aided by DFT calculations. The supermolecular scheme basically treated the molecules surrounding the unit cell as point charges; this approximation results in rapid convergence, making it a feasible method. DFT functionals of different flavors were considered: B3LYP, B2PLYP, CAM-B3LYP, ωB97, and M06HF, utilizing the 6-311 + G(d) basis set. All functionals gave sufficiently accurate values for the dipole moment (μ) with respect to the experimental value 32(2) D. For the average linear polarizability (\( \overline{\alpha} \)) and the total first hyperpolarizability (β tot), good agreement was observed between the DFT-calculated values and MP2-derived results reported in the literature. For the second hyperpolarizability, both static and dynamic regimes were considered. The point-charge embedding approach led to an attenuation of the second hyperpolarizability γ for all frequencies considered. Excitations of γ were not observed for frequencies smaller than 0.1 a.u. For the second hyperpolarizability (both static and dynamic), computational results showed that L-arginine phosphate monohydrate exhibits a large nonlinear optical effect, which implies the occurrence of microscopic third-order NLO behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chemla DS, Zyss J (1987) Nonlinear optical properties of organic molecules and crystals, vol 1. Academic, London
Nalwa HS, Miyata S (1996) Nonlinear optics of organic molecules and polymers. CRC, Boca Raton
de Wergifosse M, Castet F, Champagne B (2015) Frequency dispersion of the first hyperpolarizabilities of reference molecules for nonlinear optics. J Chem Phys 142:194102. doi:10.1063/1.4920977
de Wergifosse M, Champagne B (2011) Electron correlation effects on the first hyperpolarizability of push-pull π-conjugated systems. J Chem Phys 134:74113. doi:10.1063/1.3549814
Quertinmont J, Champagne B, Castet F, Hidalgo Cardenuto M (2015) Explicit versus implicit solvation effects on the first hyperpolarizability of an organic biphotochrome. J Phys Chem A 119:5496–5503. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.5b00631
Champagne B, Botek E, Nakano M et al (2005) Basis set and electron correlation effects on the polarizability and second hyperpolarizability of model open-shell pi-conjugated systems. J Chem Phys 122:114315. doi:10.1063/1.1880992
Nakano M, Nakagawa N, Kishi R et al (2007) Second hyperpolarizabilities of singlet polycyclic diphenalenyl radicals: effects of the nature of the central heterocyclic ring and substitution to diphenalenyl rings. J Phys Chem A 111:9102–9110. doi:10.1021/jp0734676
Machado DFS, Lopes TO, Lima IT et al (2016) Strong solvent effects on the nonlinear optical properties of Z and E isomers from azo-enaminone derivatives. J Phys Chem C 120:17660–17669. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01567
Manivannan S, Dhanuskodi S, Kirschbaum K, Tiwari SK (2005) Design of an efficient solution grown semiorganic NLO crystal for short wavelength generation: 2-amino-5-nitropyridinium tetrafluoroborate. Cryst Growth Des 5:1463–1468. doi:10.1021/cg049562a
Bi W, Louvain N, Mercier N et al (2008) A switchable NLO organic-inorganic compound based on conformationally chiral disulfide molecules and Bi(III)I5 iodobismuthate networks. Adv Mater 20:1013–1017. doi:10.1002/adma.200701753
Castro AN, Almeida LR, Anjos MM et al (2016) Theoretical study on the third-order nonlinear optical properties and structural characterization of 3-acetyl-6-bromocoumarin. Chem Phys Lett 653:122–130
Vaz WF, Custodio JMF, Silveira RG et al (2016) Synthesis, characterization, and third-order nonlinear optical properties of a new neolignane analogue. RSC Adv 6:79215–79227. doi:10.1039/C6RA14961H
Seidler T, Champagne B (2015) Which charge definition for describing the crystal polarizing field and the χ(1) and χ(2) of organic crystals? Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:19546–19556. doi:10.1039/C5CP03248B
Seidler T, Stadnicka K, Champagne B (2014) Evaluation of the linear and second-order NLO properties of molecular crystals within the local field theory: electron correlation effects, choice of XC functional, ZPVA contributions, and impact of the geometry in the case of 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline. J Chem Theory Comput 10:2214–2124
Seidler T, Stadnicka K, Champagne B (2014) Second-order nonlinear optical susceptibilities and refractive indices of organic crystals from a multiscale numerical simulation approach. Adv Opt Mater 2:1000–1006. doi:10.1002/adom.201400245
Seidler T, Stadnicka K, Champagne B (2013) Investigation of the linear and second-order nonlinear optical properties of molecular crystals within the local field theory. J Chem Phys 139:114105. doi:10.1063/1.4819769
Seidler T, Stadnicka K, Champagne B (2014) Linear and second-order nonlinear optical properties of ionic organic crystals. J Chem Phys 141:104109. doi:10.1063/1.4894483
Santos OL, Fonseca TL, Sabino JR et al (2015) Polarization effects on the electric properties of urea and thiourea molecules in solid phase. J Chem Phys 143:234503. doi:10.1063/1.4937481
Fonseca TL, Sabino JR, Castro MA, Georg HC (2010) A theoretical investigation of electric properties of L-arginine phosphate monohydrate including environment polarization effects. J Chem Phys 133:144103. doi:10.1063/1.3501237
Fonseca TL, De Oliveira HCB, Amaral OAV, Castro MA (2005) MP2 static first hyperpolarizability of azo-enaminone isomers. Chem Phys Lett 413:356–361
Fonseca TL, Castro MA, de Oliveira HCB, Cunha S (2007) Static and dynamic first hyperpolarizabilities of azo-enaminone isomers. Chem Phys Lett 442:259–264
de Oliveira HCB, Fonseca TL, Castro MA et al (2003) Theoretical study of the static first hyperpolarizability of azo-enaminone compounds. J Chem Phys 119:8417. doi:10.1063/1.1612474
Ribeiro GC, Almeida LR, Napolitano HB et al (2016) Polarization effects on the third-order nonlinear optical properties of two polymorphs of enamine derivative. Theor Chem Acc 135:244. doi:10.1007/s00214-016-1999-1
Almeida L, Anjos M, Ribeiro G et al (2017) Synthesis, structural characterization and computational study of a novel amino chalcone: a potential nonlinear optical material. New J Chem 41:1744–1754. doi:10.1039/C5NJ03214H
Guillaume M, Champagne B, Bégué D, Pouchan C (2009) Electrostatic interaction schemes for evaluating the polarizability of silicon clusters. J Chem Phys 130:134715. doi:10.1063/1.3104629
Kanoun MB, Botek E, Champagne B (2010) Electrostatic modeling of the linear optical susceptibilities of 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline, m-nitroaniline, 3-methyl-4-nitropyridine N-oxide and 2-carboxylic acid-4-nitropyridine-1-oxide crystals. Chem Phys Lett 487:256–262. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2010.01.021
Bishop DM (1998) Molecular vibrations and nonlinear optics. In: Prigogine I, Rice SA (eds) Advances in chemical physics, vol 104. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1–40
Levenson MD, Bloembergen N (1974) Dispersion of the nonlinear optical susceptibility tensor in centrosymmetric media. Phys Rev B 10:4447–4463
Bishop DM, Gu FL (2000) Ab initio and semi-empirical studies of the static polarizability and the second hyperpolarizability of diamond: finite Td symmetry models from CH4 to C281H172. Chem Phys Lett 317:322–329. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(99)01337-8
Tsiaousis D, Munn RW, Smith PJ, Popelier PLA (2004) Polarizability of acetanilide and RDX in the crystal: effect of molecular geometry. Chem Phys 305:317–323. doi:10.1016/j.chemphys.2004.07.013
Monaco SB, Davis LE, Velsko SP et al (1987) Synthesis and characterization of chemical analogs of L-arginine phosphate. J Cryst Growth 85:252–255. doi:10.1016/0022-0248(87)90231-4
Hickey AL, Rowley CN (2014) Benchmarking quantum chemical methods for the calculation of molecular dipole moments and polarizabilities. J Phys Chem A 118:3678–3687. doi:10.1021/jp502475e
Grimme S (2006) Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J Comput Chem 27:1787–1799. doi:10.1002/jcc.20495
Maekawa S, Moorthi K (2014) Polarizabilities from long-range corrected DFT calculations. J Chem Eng Data 59:3160–3166. doi:10.1021/je500224e
Blair SA, Thakkar AJ (2013) How often is the minimum polarizability principle violated? Chem Phys Lett 556:346–349. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2012.11.048
Champagne B, Perpète EA, van Gisbergen SJA et al (1998) Assessment of conventional density functional schemes for computing the polarizabilities and hyperpolarizabilities of conjugated oligomers: an ab initio investigation of polyacetylene chains. J Chem Phys 109:10489. doi:10.1063/1.477731
Garza AJ, Wazzan NA, Asiri AM, Scuseria GE (2014) Can short- and middle-range hybrids describe the hyperpolarizabilities of long-range charge-transfer compounds? J Phys Chem A 118:11787–11796. doi:10.1021/jp510062b
Günter P (2000) Nonlinear optical effects and materials, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-49713-4
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the following Brazilian agencies for financial support: Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Empreendimentos Científicos (FINATEC), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal (FAPDF), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Goiás (FAPEG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This paper belongs to Topical Collection VI Symposium on Electronic Structure and Molecular Dynamics—VI SeedMol
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valverde, C., Rodrigues, R.F.N., Machado, D.F.S. et al. Effect of the crystalline environment on the third-order nonlinear optical properties of L-arginine phosphate monohydrate: a theoretical study. J Mol Model 23, 122 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3274-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3274-3