Summary
-
1.
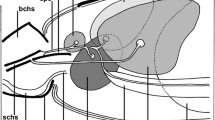
The diverting system in the salivary glands of diplopoda begins at the intercellulary spaces between the secretory cells. Here extrusion of the secretory vacuoles takes place. Sometimes microvilli of secretory cells protrude into the intercellulary spaces.
-
2.
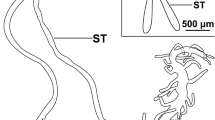
Lateral ducts unite and open into the intercellulary spaces. They are formed occasionally by a single wall-cell and represent intercellulary tubes lined with a cuticle. They run throughout the cell into a wide, common main efferent channel.
-
3.
The main efferent channel is composed of many wall-cells lined with a cuticle, and usually opens into the preoral cavity.
-
4.
The ultrastructure of the wall-cells is described. They give the impression of inactive cells, however discernible free ribosomes are numerous. Some glands possess characteristic myeline-like bodies.
-
5.
As a rule, wall-cells represent a single-layered epithelium resting on the secretory cells of the salivary gland. At the efferent duct between wall-cell and a secretory cell a zonula adhaerens is always developed, subsequently to it septate desmosomes. Neighbouring wall-cells are linked together by septate desmosomes.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Das Sekret ableitende System in den Speicheldrüsen der Diplopoden beginnt mit den Interzellularräumen zwischen den sezernierenden Zellen. In these wird das Sekret ausgeschleust. In die apikalen Endabschnitte entsenden benachbarte Parenchymzellen manchmal Mikrovilli.
-
2.
An die Interzellularräume schließen offen die Seitenkanäle an. Diese sind von jeweils einer Kanalwandzelle gebildete intrazolluläre Rohre, die von einer kutikularen Intima ausgekleidet werden. Sie durchziehen die Zelle und münden in einen weitlumigen Hauptausführkanal.
-
3.
Der Hauptausführkanal wird von vielen Kanalwandzellen aufgebaut. Auc er ist von einer kutikularen Intima ausgekleidet. Er mündet meist in den Präoralraum aus.
-
4.
Die Ultrastruktur der Kanalwandzellen wird beschrieben. Sie vermittelt den Eindruck von stoffwechsel-inaktiven Zellen. Auffällig sind die zahlreichen freien Ribosomen und in manchen Drüsen komplexe, myelinartige Körper.
-
5.
Die Kanalwandzellen sitzen meist als einschichtiges Epithel den sezernierenden Zellen auf. Am Lumen des ableitenden Systems sind zwischen beiden Zellen immer eine Zonula adhaerens, daran anschließend septierte Desmosomen ausgebildet. Benachbarte Kanalwandzellen sind durch Schlußleisten verzahnt, die als septierte Desmosomen entwickelt sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bargmann, W.: Histologic und mikroskopische Anatomic des Menschen, 3. Aufl. Stuttgart: Thieme 1959
Bargmann, W., Knoop, A.: Über die Morphologie der Milchsekretion. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Studien an der Milchdrüse der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 49, 344–388 (1959)
El-Hifnawi, E.: Die Speicheldrüsen der Diplopoden. II. Ultrastruktur der Sekret bildenden Zellen. Z. Morph. Tiere 75, 297–314 (1973)
El-Hifnawi, E., Seifert, G.: Die Speicheldrüsen der Diplopoden. I. Topographic und Histologie der Speicheldrüsen von Polyxenus lagurus, Craspedosoma rawlinsii und Schizophyllum sabulosum. Z. Morph. Tiere 74, 323–348 (1973)
Moericke, V., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E.: Zur funktionellen Morphologie der Speicheldrusen von Homopteren. IV. Mitteilung: Die Ausführgänge der Speicheldrüsen von Myzus persicae (Sulz.), Aphididae. Z. Zellforsch. 53, 25–49 (1960)
Seifert, G.: Die Cuticula von Polyxenus lagurus L. (Diplopoda, Pselaphognata). Z. Morph. Ökol. Tiere 59, 42–53 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Hifnawi, ES. Die speicheldrüsen der diplopoden. Z. Morph. Tiere 77, 221–233 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389905
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389905