Summary
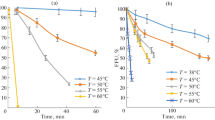
Attenuated poliovirus is inactivated in a synergistic manner when exposed simultaneously to heat and ionizing radiation. The synergistic response is observed in both the thermally labile and stable forms of the virus. A three-term kinetic model may be used to describe the inactivation response of the virus in a theral and/or radiation environment
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, K. I., Gerber, G. B., Okada, S.: Direct and indirect action. In: Radiation biochemistry (S. Okada,Ed.) Vol. 1, pp. 77–90. New York: Academic Press 1970
DiGirolamo, R., Listen, J., Matches, J.: Effects of irradiation on the survival of virus in west coast oysters. Appl. Microbiol.24, 1005–1006 (1973)
Dimmock, N. J.: Differences between the thermal inactivation of picornaviruses at “high” and “low” temperatures. Virology31, 338–353 (1967)
Hinuma, Y., Katagiri, S., Fukuda, M., Fukushi, K., Watanabe, Y.: Kinetic studies on the thermal degradation of purified poliovirus. Biken's J.8, 143–153 (1965)
Koch, G.: Influence of assay conditions on infectivity of heated poliovirus. Virology12, 601–603 (1960)
McGregor, S., Mayor, M. D.: Biophysical studies on rhinovirus and poliovirus. J. Virol.2, 149–154 (1968)
Norman, A., Veomett, R. C.: Heat inactivation of poliovirus ribonucleic acid. Virology12, 136–139 (1960)
Sullivan, R., Fassolitis, A. C., Larkin, E. P., Read, R. B., Peeler, J. T.: Inactivation of thirty viruses by gamma radiation. Appl. Microbiol.22, 61–65 (1971)
Trujillo, R., Dugan, V. L.: Synergistic inactivation of viruses by heat and ionizing radiation. Biophys. J.12, 92–113 (1972)
Trujillo, R.: Measurement of the radiation inactivation of attenuated poliovirus by the plaque assay technique. SLA-74-0065. Albuquerque, New Mexico: Sandia Laboratories
Wallis, C., Melnick, J. L.: Cationic stabilization - a new property of enteroviruses. Virology16, 504–506 (1962)
Woese, C.: Thermal inactivation of animal viruses. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.83, 741–751 (1960)
Younger, J. S.: Thermal inactivation studies with different strains of poliovirus. J. Immunol.78, 282–290 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dugan, V.L., Trujillo, R.E. Heat-acclerated radioinactivation of attenuated poliovirus. Radiat Environ Biophys 12, 187–195 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01327346
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01327346