Abstract
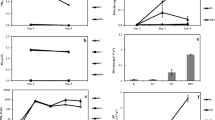
We studied the competition between larval mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) and naturally occurring populations of marine bacteria (Menai Straits, North Wales) for dissolved glycine and glocose. Laboratory reared larvae were placed in natural seawater containing populations of bacteria ranging from 2x105 to 7x105 ml-1 and the rates of uptake of 14C-labeled substrates into an equal biomass of larvae and bacteria were determined. The larvae always accumulated dissolved nutrients at rates comparable to those of the equivalent biomass of bacteria. When uptake experiments were conducted with larvae and bacteria separately, the uptake rates were not greatly different from those observed when tested together. Direct counts of bacteria showed no significant increase or decrease in bacterial numbers during the 100 min time-course of any experiment, showing that entry of 14C-labeled substrate into the larvae did not occur by ingestion of bacteria. It was shown that, although larvae have a lower affinity for substrate (higher K t) than bacteria, larvae also have a higher maximum uptake rate (V max). Effective larval uptake in the presence of bacteria relies on the high values of V max. It is invalid to assume that one transport system cannot compete with another solely because one has a lower K t.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Crawford, C. C., J. E. Hobbie and K. L. Webb: The utilization of dissolved free amino acids by estuarine microorganisms. Ecology 55, 551–563 (1974)
Crisp, D. J.: The role of the pelagic larva. In: Perspectives in experimental biology, Vol. 1. pp 145–155. Ed. by P. Spencer Davis. Oxford and New York: Pergamon Press 1976
Hobbie, J. E.: Activity and bacterial biomass. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Beih. Ergebn. Limnol.) 12, 59–63 (1979)
Hobbie, J. E., R. J. Daley and S. Jasper: Use of Nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl. envirl Microbiol. 33, 1225–1228 (1977)
Jørgensen, C. B.: August Pütter, August Krogh, and modern ideas on the use of dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments. Biol. Rev. 51, 291–328 (1976)
Loosanoff, V. L. and H. C. Davis: Rearing of bivalve molluscs. Adv. mar. Biol. 1, 1–136 (1963)
Manahan, D. T.: The uptake and metabolism of dissolved amino acids by bivalve larvae. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 164, 236–250 (1983)
Manahan, D. T. and D. J. Crisp: The role of dissolved organic material in the nutrition of pelagic larvae: amino acid uptake by bivalve veligers. Am. Zool. 22, 635–646 (1982)
Manahan, D. T., J. Davis and G. C. Stephens: Bacteria-free sea urchin: selective uptake of neutral amino acids from seawater. Science N.Y. 220, 204–206 (1983a)
Manahan, D. T., S. H. Wright and G. C. Stephens: Simultaneous determination of net uptake of 16 amino acids by a marine bivale. Am. J. Physiol. 244 (Regul. integrat. comp. Physiol. 13), R832-R838 (1983b)
Manahan, D. T., S. H. Wright, G. C. Stephens and M. A. Rice: Transport of dissolved amino acids by the mussel, Mytilus edulis: demonstration of net uptake from natural seawater. Science N.Y. 215, 1253–1255 (1982)
Newell, R. C.: Biology of intertidal animals. 781 pp. 3rd ed. Kent, UK: Marine Ecological Surveys Ltd. 1979
North, B. B.: Primary amines in California coastal waters: utilization by phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr 20, 20–27 (1975)
Sepers, A. B. J.: The utilization of dissolved organic compounds in aquatic environments. Hydrobiologia 52, 39–54 (1977)
Siebers, D.: Transintegumentary uptake of dissolved amino acids in the sea star Asterias rubens. A reassessment of its nutritional role with special reference to the significance of heterotrophic bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1, 169–178 (1979)
Sorokin, Yu. I.: Microheterotrophic organisms in marine ecosystems. In: Analysis of marine ecosystems, pp 293–341. Ed. by A. L. Longhurst. London: Academic Press 1981
Stephens, G. C.: The trophic role of dissolved organic material. In: Analysis of marine ecosystems, pp 271–291. Ed. by A. L. Longhurst, London: Academic Press 1981
Stewart, M. G.: Absorption of dissolved organic nutrients by marine invertebrates. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 17, 163–192 (1979)
Williams, P. J. Le B.: Biological and chemical aspects of dissolved organic material in seawater. In: Chemical oceanography, Vol. 2, pp 301–363. Ed. by J. P. Riley and G. Skirrow. London: Academic Press 1975
Williams, P. J. Le B., T. Berman and O. Holm-Hansen: Amino acid uptake and respiration by marine heterotrophs. Mar. Biol. 35, 41–47 (1976)
Zeuthen, E.: Body size and metabolic weight in the animal kingdom with special regard to the marine microfauna. C. r. Trav. Lab. Carlsberg (Sér. chim.) 26, 1–161 (1947)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. D. Holland, La Jolla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manahan, D.T., Richardson, K. Competition studies on the uptake of dissolved organic nutrients by bivalve larvae (Mytilus edulis) and marine bacteria. Mar. Biol. 75, 241–247 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406008
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406008