Abstract
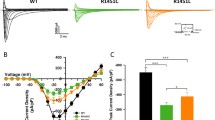
Three groups of mutations of the α subunit of the rat skeletal muscle sodium channel (rSkM1),homologous to mutations linked to human muscle hereditary diseases, have been studied byheterologous expression in frog oocytes: S798F, G1299E, G1299V, and G1299A, linked withpotassium-aggravated myotonia (PAM); T1306M, R1441C and R1441P, linked withparamyotonia congenita (PC); T698M and M1353V, linked with the hyperkalemic periodic paralysis(HyPP). Wild-type rSkM1 channels (WT) show two gating modes, M1 and M2, which differmainly in the process of inactivation. The naturally most representative mode M1 is tenfoldfaster and develops at ∼30 mV less depolarized potentials. A common feature ofmyopathy-linked mutants is an increase in the mode M2 probability, PM2, but phenotype-specific alterationsof voltage-dependence and kinetics of inactivation of both modes are also observed. Thecoexpression of the sodium channel β1 subunit, which has been studied for WT and for thefive best expressing mutants, generally caused a threefold reduction of PM2 without changingthe properties of the individual modes. This indicates that the mutations do not affect theα − β1 interaction and that the phenotypic changes in PM2 observed for the enhanced mode M2behavior of the sole α subunits, although largely depressed in the native tissue, are likely to bethe most important functional modification that causes the muscle hyperexcitability observed inall patients carrying the myotonic mutations. The interpretation of the more phenotype-specificchanges revealed by our study is not obvious, but it may offer clues for understanding the differentclinical manifestations of the diseases associated with the various mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Auld, V. J., Goldin, A. L., Krafte, D. S., Marshall, J., Dunn, J. M., Catteral, W. A., Lester, H. A., Davidson, N., and Dunn, R. J. (1988). Neuron 1, 449-61.
Barchi, R. L. (1995). Annu. Rev. Physiol. 57, 355-385.
Bulman, D. E. (1997). Human Mol. Genet. 6, 1679-1685.
Cannon, S. C. (1996a). Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 141-164.
Cannon, S. C. (1996b). TINS 19, 3-10.
Cannon, S. C., and Corey, D. P. (1993). J. Physiol. 466, 501-520.
Cannon, S. C., and Strittmatter, S. M. (1993). Neuron 10, 317-326.
Cannon, S. C., Brown, R. H., and Corey, D. P. (1991). Neuron 6, 619-626.
Cannon, S. C., Brown, R. H., and Corey, D. P. (1993a). Biophys. J. 65, 270-288.
Cannon, S. C., McClatchey, A. I., and Gusella, J. F. (1993b). Pflügers Arch. 423, 155-157.
Chahine, M., George, A. L., Zhou, M., Ji, S., Sun, W., Barchi, R. L., and Horn, R. (1994). Neuron 12, 281-94.
Chang, S. Y., Satin, J., and Fozzart, H. A. (1996). Biophys. J. 70, 2581-2592.
Cummins, T. R., and Sigworth, F. J. (1996). Biophys. J. 71, 227-236.
Cummins, T. R., Zhou, Y., Sigworth, F. J., Ukomadu, C., Stephan, M., Ptacek, L. J., and Agnew, W. S. (1993). Neuron 10, 667-678.
DeSilva, S. M., Kuncl, R. W., Griffin, J. W., Cornblath, D. R., and Chavoustie, S. (1990). Nerve Muscle 13, 21-26.
Featherstone, D. E., Fujimoto, E., and Ruben, P. C. (1998). J. Physiol. 406, 627-638.
Frenwick, E., Marty, A., and Neher, E. (1982). J. Physiol. 331, 599-635.
George, A. L. (1995). Kidney Intern. 48, 1180-1190.
Green, D. S., George, A. L., and Cannon, S. C. (1998). J. Physiol. 510, 685-694.
Hamill, O., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., and Sigworth, F. (1981). Pflügers. Arch. 391, 85-100.
Hayward, L. J., Brown, R. H., Jr., and Cannon, S. C. (1996). J. Gen. Physiol. 107, 559-576.
Hayward, L. J., Brown, R. H., Jr., and Cannon, S. C. (1997). Biophys. J. 72, 1204-1019.
Hille, B. (1992). Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
Hodgkin, A. L., and Huxley, A. F. (1952). J. Physiol. 117, 500-44.
Hoffman, E. P., Lehmann-Horn, F., and Rüdel, R. (1995). Cell 80, 681-686.
Ji, S., Sun, W., George, A. L., Jr., Horn, R., and Barchi, R. L. (1994). J. Gen. Physiol. 104, 625-643.
Ji, S., George, A. L., Horn, R., and Barchi, R. L. (1996). J. Gen. Physiol. 107, 183-194.
Kudel, T. A. (1985). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 488-492.
Lehmann-Horn, F., Iaizzo, P. A., Hatt, H., and Franke, C. H. (1991). Pflügers Arch. 418, 297-299.
Lerche, H., Heine, R., Pika, U., George, A., Mitrovic, N., Browatzki, M., Weiss, T., Rivet-Bastide, M., Franke, C., Lomonaco, M., Ricker, K., and Lehmann-Horn, F. (1993). J. Physiol. 470, 13-22.
Lerche, H., Mitrovic, N., Dubowitz, V., and Lehmann-Horn, F. (1996). Ann. Neurol. 39, 599-608.
Liman, E. R., Tytgat, J., and Hess, P. (1992). Neuron 9, 861-871.
Meves, H. (1984). In Current Topics in Membranes and Transport: The squid axon: Hodgkin-Huxley: Thirty Years After(Baker, P. eds.), Academic Press, New York, pp. 279-329.
Mitrovic, N., George, A. L. J., Heine, R., Wagner, S., Pika, S., Hartlaub, U., Zhou, M., and Lerche, H. (1994). J. Physiol. 478, 395-402.
Mitrovic, N., George, A. L., Lerche, H., Wager, S., Falke, C., and Lehmann-Horn, F. (1995). J. Physiol. 487, 107-114.
Moorman, J. R., Kirsch, G. E., VanDongen, A. M. J., Joho, R. H., and Brown, A. M. (1990). Neuron 4, 243-52.
Moran, O., Nizzari, M., and Conti, F. (1998a). In Neuronal Circuits and Networks: Modal Gating of Sodium Channels and Possible Physiological Implications on Hereditary Myopathies(Torre, V. and Nicolls, J., eds.), Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 3-19.
Moran, O., Melani, R., Nizzari, M., and Conti, F. (1998b). J. Bioenerg. Biomemb. 30, 579-588.
Moran, O., Nizzari, M., and Conti, F. (1998c). Biophys. Biochem. Res. Commun. 246, 792-796.
Patton, D. E., Isom, L. L., Catterall, W. A., and Goldin, A. L. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 17640-17655.
Richmond, J. E., Featherstone, D. E., and Ruben, P. C. (1997). J. Physiol. 499, 589-600.
Rudy, B. (1978). J. Physiol. 283, 1-21.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S., and Coulson, A. R. (1977). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5463-5467.
Shcherbatko, A., and Brehm, P. (1998). Biophys. J. 74, A394.
Stämpfli, R., and Hille, B. (1976). In Frog Neurobiology: Electrophysiology of the Peripheral Myelinated Nerve. (Llinás, R. and Precht, W., eds.), Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 1-32.
Stühmer, W. (1992). In Methods in Enzymology: Ion Channels: Electrophysiological Recording of Xenopus Oocytes(Rudy, B. and Iverson, L. E., eds.), Academic Press, New York pp. 319-339.
Sugimoto, M., Esaki, N., Tanaka, H., and Soda, K. (1989). Anal. Biochem. 179, 309-311.
Tahmoush, A. J., Schaller, K. L., Zhang, P., Hyslop, T., Heiman-Patterson, T., and Caldwell, J. H. (1994). Neuromusc. Disorders 4, 447-454.
Trimmer, J. S., Cooperman, S. S., Tomiko, S. A., Zhou, J., Crean, S. M., Boyle, M. B., Kallen, R. G., Sheng, Z., Barchi, R. L., Sigworth, F. J., Goodman, R. H., Agnew, W. S., and Mandel, G. (1989). Neuron 3, 33-49.
Ukomadu, C., Zhou, J., Sigworth, F. J., and W. S., Agnew (1992). Neuron 8, 663-676.
Wend, D. J., Starmer, C. F., and Grant, A. O. (1992). Amer. J. Physiol. 263, C1234-C1240.
Yang, N., Ji, S., Zhou, M., Patcek, L. J., Barchi, R. L., Horn, R., and George, A. L. J. (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 12785-12789.
Zhou, J., Potts, J. F., Trimmer, J. S., W. S., Agnew, and F. J., Sigworth (1991). Neuron 7, 775-785.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moran, O., Nizzari, M. & Conti, F. Myopathic Mutations Affect Differently the Inactivation of the Two Gating Modes of Sodium Channels. J Bioenerg Biomembr 31, 591–608 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005473129183
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005473129183