Abstract
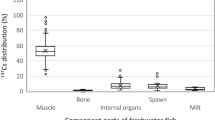
Samples of fish and sediments collected from waters within 10 km of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant were analysed for radiocaesium and other atmospherically transported pollutants (lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg)) were measured in fish tissues. For comparison, fish muscle was also sampled from a less-contaminated area of the Kiev Reservoir and from a hatchery in Kiev. In sediments, 137Cs was the major gamma-emitting isotope, with concentrations of over 100 Bq g−1 in canals adjacent to the reactor and in ponds that were downwind during the accident. The radiocaesium distributions appeared non-normal, were very patchy and could vary by over 100% in samples collected metres to tens of metres apart. Fish muscle radiocaesium from ponds within 10 km of the power plant was in the range of 6–192 Bq g−1. The fish muscle radiocaesium concentrations were highest in ponds from the downwind sites and were correlated with the sediment radiocaesium concentrations. The lead and mercury concentrations in fish were relatively low (medians <0.8 μg Hg per g dry mass and <150 ng Pb per g dry mass), suggesting little contamination from lead applied to the burning reactor after the accident. The radiocaesium levels in fish in areas close to the reactor continue to be high enough to cause health concerns to humans that might utilize these resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borovoi, A.A. and Sich, A.R. (1995) The Chernobyl accident revisited, part II: the state of the nuclear fuel located within the Chernobyl sarcophagus. Nucl. Safety 36, 1–32.
Brisbin, I.L., Beyers, R.J., Dapson, R.W., Geiger, R.A., Gentry, J.B., Gibbons, J.W., Smith, M.H. and Woods, S.K. (1974) Patterns of radiocesium in the sediments of a stream channel contaminated by production reactor effluents. Health Phys. 27, 19–27.
Currie, L.E. (1968) Limits for qualitative detection and quantitative determination. Anal. Chem. 40, 586–93.
Dallas, C.E., Jagoe, C.H., Fisher, S.K., Holloman, K.A., Chesser, R.K., Smith, M.H. and Lomakin, M.D. (1995) Evaluation of genotoxicity in wild organisms due to the Chernobyl nuclear disaster. Ecol. Indust. Regions 1, 44–54.
Dallas, C.E., Lingenfelser, S.F., Lingenfelser, J.T., Holloman, K., Jagoe, C.H., Kind, R.K. and Smith, M.H. (1998) Flow cytometric analysis of erythrocyte and leukocyte DNA in fish from Chernobyl-contaminated ponds in the Ukraine. Ecotoxicology 7, in press.
Davison, W., Hilton, J., Hamilton-Taylor, J., Kelly, M., Livens, F., Rigg, E., Carrick, T.R. and Singleton, D.L. (1993) The transport of Chernobyl-derived radiocaesium through two freshwater lakes in Cumbria, UK. J. Environ. Radioact. 19, 125–153.
Evans, D.W., Alberts, J.J. and Clark, R.A. (1983) Reversible ionexchange fixation of cesium-137 leading to mobilization from reservoir sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47, 1041–9.
Feshbach and Friendly (1992) Ecocide in the Soviet Union. New York: Basic Books.
Fleishman, D.G., Nikiforov, V.A., Saulus, A.A. and Komov, V.T. (1994) 137Cs in fish in some lakes and rivers of the Bryansk region and north-west Russia in 1990–1992. J. Environ. Radioact. 24, 145–58.
Haines, T.A., Komov, V.T. and Jagoe, C.H. (1992) Lake acidity and mercury content of fish in Darwin National Reserve, Russia. Environ. Pollut. 78, 107–12.
Haines, T.A., Komov, V.T., Matey, V.E. and Jagoe, C.H. (1996) Perch mercury content is related to acidity and color of 26 Russian lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 823–8.
Hakanson, L., Nilsson, A. and Andersson, T. (1988) Mercury in fish in Swedish lakes. Environ. Pollut. 49, 145–62.
Hakanson, L., Andersson, T. and Nilsson, A. (1990) Mercury in fish in Swedish lakes-linkages to domestic and European sources of emissions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 50, 171–91.
International Atomic Energy Agency (1991) The International Chernobyl Project. Surface Contamination Maps. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency.
International Commission on Radiological Protection (1990) Agedependent Doses to Members of the Public from Intake of Radionuclides. New York: Pergamon.
Jagoe, C.H., Chesser, R.K., Smith, M.H., Lomakin, M.D., Lingenfelser, S.K. and Dallas, C.E. (1997) Levels of cesium, mercury and lead in fish, and cesium in pond sediments in an inhabited region of the Ukraine near Chernobyl. Environ. Pollut. 98, 223–232.
Kolehmainen, S.E. (1972) The balances of 137Cs stable cesium and potassium of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus Raf.) and other fish in White Oak Lake. Health Phys. 23, 301–15.
Kolehmainen, S.E., Hasanen, E. and Miettinen, J.K. (1966) 137Cs levels in fish of different limnological types of lakes in Finland during 1963. Health Phys. 12, 917–22.
Koulikov, A.O. and Ryabov, I.N. (1992) Specific radiocesium activity in freshwater fish and the size effect. Sci. Total Environ. 112, 125–42.
Kryshev, I.I. (1992) Radioecological Consequences of the Chernobyl Accident. Moscow: Nuclear Society International.
Lingenfelser, S.K., Dallas, C.E., Jagoe, C.H., Chesser, R.K., Smith, M.H. and Lomakin, M.D. (1997) Variation in blood cell DNA in Carassius carassius from ponds near Chernobyl, Ukraine. Ecotoxicology 6, 187–203.
Lomenick, T.F. and Gardiner, D.A. (1965) The occurrence and retention of radionuclides in the sediments of White Oak Lake. Health Phys. 11, 567–77.
Medvedev, Z.A. (1990) The Legacy of Chernobyl. New York: W.W. Norton and Co.
Medvedev, Z.A. (1994) Chernobyl; eight years after. Trends Ecol. Evol. 9, 369–71.
Meuleman, C., Leermakers, M. and Baeyens, W. (1995) Mercury speciation in Lake Baikal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 80, 539–51.
Mourad, R. and Snell, V. (1987) Source term and radiological consequences of the Chernobyl accident. Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 54, 226–8.
Pinder, J.E. and Smith, M.H. (1975) Frequency distributions of radiocesium concentrations in soils and biota. In F.G. Howell, J.B. Gentry and M.H. Smith (eds) Mineral cycling in southeastern ecosystems, pp. 107–25. Washington, DC: Technical Information Center, Energy Research and Development Administration.
Powers, D.A., Kress, T.S. and Jankowski, M.W. (1987) Chernobyl source term. Nucl. Safety 28, 10–28.
Preston, A., Jeffries, D.F. and Dutton, J.W.R. (1967) The concentrations of caesium-137 and strontium-90 in the British Isles between 1961 and 1966: the variables determining the concentrations and their use in radiological assessments. Water Res. 1, 475–96.
Sarkka, J., Jamsa, A. and Lukko, A. (1995) Chernobyl-derived radiocesium in fish as dependent on water quality and lake morphometry. J. Fish Biol. 46, 227–40.
Schmitt, C.J., Dwyer, F.J. and Finger, S.E. (1984) Bioavailability of Pb and Zn from mine tailings as indicated by erythrocyte ä-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-D) activity in suckers (Pisces: Catostomidae). Can. J. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 41, 1030–40.
Sich, A.R. (1994) Chernobyl accident management actions: implications for source term estimates. Nucl. Safety 35, 1–24.
Sorensen, E.M.B. (1991) Metal Poisoning in Fish. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Sugg, D.W., Bickham, J.W., Brooks, J., Lomakin, M.D., Jagoe, C.H., Dallas, C.E., Smith, M.H., Baker, R.J. and Chesser, R.K. (1996) DNA damage and radiocesium in channel catfish from Chernobyl. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 1057–63.
Sun, L.C., Clinton, J.H., Kaplan, E. and Meinhold, C.B. (1997) 137Cs exposure in the Marshallese populations: an assessment based on whole body counting measurements (1989–1994). Health Phys. 73, 86–99.
Tarasov, V.I. and Vikharev, V.D. (1994) Statistical analysis of radioactive contamination levels in settlements of the Chernobyl middle zone. Health Phys. 66, 444–9.
Van Hassel, J.H., Ney, J.J. and Garling, D.L. (1980) Heavy metals in a stream ecosystem at sites near highways. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 109, 636–43.
World Health Organization (1972) Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and of the Contaminants Mercury, Lead and Cadmium. Geneva: Joint UN Food and Agriculture Organization and the World Health Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagoe, C.H., Dallas, C.E., Chesser, R.K. et al. Contamination Near Chernobyl: radiocaesium, Lead and Mercury in Fish and Sediment Radiocaesium from Waters Within the 10 km Zone. Ecotoxicology 7, 201–209 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008934710904
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008934710904