Summary
Phenotypic and genotypic correlation coefficients as well as path analysis were computed to evaluate the genetic association between six agronomic traits and rice grain yield and also among the traits in a representative sample of F7 lines in the tall Peta × semi-dwarf I-geo-tze cross maintained as an unselected bulk from F3 through F5. Data were taken on grain yield, duration from seeding to heading, panicle number, ratio of panicles to tillers, angle of the flag leaf, angle of the leaf below the flag leaf, and plant height on the two parents and 139 F7 lines. The F7 lines were divided into three groups based on plant height: tall, intermediate, and short (semi-dwarf).
Differences in grain yield were highly significant among lines in the tall and short groups, and significant among the intermediate lines. Significant to highly significant differences among lines were obtained in each of the height groups for all of the agronomic traits except for the ratio of panicles to tillers in the intermediate and tall groups.
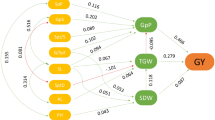
Path analysis showed that among the semi-dwarf progenies, erect flag leaf angle made the largest positive contribution to grain yield, followed by high panicle number and early maturity. Among the intermediates, the erectness of the leaf below the flag contributed most to high yield and was closely followed by earliness in maturity. For the tall lines, erect leaves below the flag leaf and high panicle number contributed positively to yield, whereas tallness and late maturity had a negative effect.
Phenotypic and genotypic correlation coefficients indicated that low grain yield was closely associated with tall stature, drooping leaves, and low panicle number in the tall lines. In the intermediate lines, low grain yield was associated with late maturity and drooping leaves. Among the semi-dwarf lines, high grain yield was correlated with erect flag leaves and a high ratio of panicles to tillers. When the lines in different height groups were combined, highly significant phenotypic correlations were obtained between high yield levels and erect leaves, a short plant stature, early maturity, or a high panicle number. Erect flag leaves and high yield levels were associated at a significant level. The genotypic correlation coefficients of the above paired traits were identical in sign and generally greater in value than the corresponding phenotypic correlation coefficients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous, 1964. Annual Report International Rice Research Institute. Los Baños, Philippines, p. 32–36.
Anonymous Institute. Los Baños, Philippines, p. 67–68.
Anonymous, 1968. 60th Annual Progress Report. Rice Experiment Station, Crowley, Louisiana State University Agricultural Experiment Station, Louisiana, p. 13–14.
Beachell, H. M., 1966. The development of rice varietal types for the tropics. Indian J. Genet. Pl. Breeding 26A: 200–205.
Beachell, H. M. &Jennings, P. R., 1965. Need for modification of plant type. The Mineral Nutrition of the Rice Plant. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p. 29–35.
Bollich, C. N., Adair, C. R., Webb, B. D. &Scott, J. E., 1969. Performance of new Asian rice varieties in the United States. Rice J. 72(4): 9, 12–13.
Chang, T. T., 1964. Varietal differences in lodging resistance. Int. Rice Commn. Newslett. 13(4): 1–11.
Chang, T. T., 1967a. Varietal characteristics, lodging and grain development. Int. Rice Commn. Newslett. Special Symposium Issue, p. 54–61.
Chang, T. T., 1967b. The genetic basis of wide adaptability and yielding ability of rice varieties in the tropics. Int. Rice Commn. Newslett. 16(4): 4–12.
Chang, T. T., Morishima, H., Huang, C. S., Tagumpay, O. &Tateno, K., 1965. Genetic analysis of plant height, maturity and other quantitative traits in the cross of Peta x I-geo-tze. J. Agr. Assoc. China 51 (N.S.): 1–8.
De Datta, S. K., Tauro, A. C. &Balaoing, S. N., 1968. Effect of plant type and nitrogen level on the growth characteristics and grain yield of indica rice in the tropics. Agron. J. 60: 643–647.
Dewey, D. R. &Lu, K. H., 1959. A correlation and path-coefficient analysis of components of crested wheatgrass seed production. Agron. J. 51: 515–518.
Guevarra, A. B. &Chang, T. T., 1965. Internode elongation in rice varieties of reduced plant stature. Philippine Agr. 49: 23–42.
Jennings, P. R. &Beachell, H. M., 1965. Breeding rice for nitrogen responsiveness. The Mineral Nutrition of the Rice Plant. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p. 449–455.
Jennings, P. R. &Herrera, R. M., 1968. Studies on competition in rice. II. Competition in segregating populations. Evolution 22: 332–336.
Jennings, P. R. &Sornchai, S., 1964. The influence of lodging on rice yields. Int. Rice Commn. Newslett. 13(3): 10–21.
Li, C. C., 1955. Population Genetics. Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 366.
Morishima, H., Oka, H. I. &Chang, T. T., 1967. Analysis of genetic variations in plant type of rice. 1. Estimation of indices showing plant types and their correlations with yielding capacity in a segregating population. Jap. J. Breeding 17: 73–84.
Sastry, N. S., Balakrishna Rao, M. J. &Rawlo, S., 1967. The relationship between grain yield and associated characters in some short stature and high yielding rice varieties. Int. Rice Commn. Newslett. 16(4): 20–42.
Tanaka, A., 1965. Plant characters related to nitrogen response in rice. The Mineral Nutrition of the Rice Plant. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p. 419–435.
Tanaka, A., Kawano, K. andYamaguchi, J., 1966. Photosynthesis, respiration, and plant type of the tropical rice plant. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Tech. Bull. 7: 1–46.
Tanaka, A., Navasero, S. A., Garcia, C. V., Parao, P. T. &Ramirez, E., 1964. Growth habit of the rice plant in the tropics and its effect on nitrogen response. Int. Rice Res. Inst. Tech. Bull. 3: 1–80.
Tsunoda, S., 1965. Leaf characters and nitrogen response. The Mineral Nutrition of the Rice Plant. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p. 401–418.
Vergara, B. S., Lilis, R. &Tanaka, A., 1965. Studies of the internode elongation of the rice plant. I. Relationships between growth duration and internode elongation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 11(6): 26–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mail address: P. O. Box 583, Manila, Philippines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, T.T., Tagumpay, O. Genotypic association between grain yield and six agronomic traits in a cross between rice varieties of contrasting plant type. Euphytica 19, 356–363 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01904214
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01904214