Summary
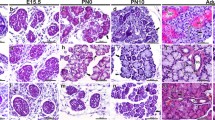
The submandibular glands of female mice and the sublingual and parotid glands of adult male and female mice have been examined by light microscopical immunocytochemistry for nerve growth factor (NGF). In female submandibular glands, staining for NGF was observed in granular convoluted tubule and striated duct cells. Sublingual glands of the mouse contained relatively few granular cells staining for NGF compared with submandibular glands. However, such granular cells appeared to be more numerous in male sublingual glands than in female glands. The remainder of the intralobular duct cells in both male and female sublingual glands exhibited apical subluminal staining for NGF as well as light basal plasmalemmal staining. Parotid glands in both male and female mice exhibited a similar pattern of staining for NGF in striated duct cells. However, the glands did not contain granular cells nor did they exhibit any pattern of staining which reflected a sexual dimorphism. Immunodot staining of salivary gland extracts confirmed the presence of immunoreactivity for NGF in all three of the major salivary glands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BARKA, T. (1980) Biologically active polypeptides in submandibular glands.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 836–59.
BERKMAN, M. D. & KRONMAN, J. H. (1970) A histochemical study of the effects of castration and testosterone administration on the major salivary glands of Swiss mice.Acta Anat. 76, 200–19.
BHOOLA, K. D., DOREY, G. & JONES, C. W. (1973) The influence of androgens on enzymes (chymotrypsin-and trypsin-like proteases, renin, kallikrein, and amylase) and on cellular structure of the mouse submaxillary gland.J. Physiol. 235, 503–22.
BOCCHINI, V. & ANGELETTI, P. U. (1969) The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30000-molecular weight protein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 64, 787–94.
BRADFORD, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–54.
CARAMIA, F. (1966) Ultrastructure of mouse submaxillary gland. I. Sexual differences; II. Effect of castration in the male.J. Ultrastruc. Res. 16, 505–23; 524–36.
CHRÉTIEN, M. (1977) Action of testosterone on the differentiation and secretory activity of a target organ: the submaxillary gland of the mouse.Int. Rev. Cytol. 50, 333–96.
CUTLER, L. S. (1980) The development and independent relationships between cytodifferentiation and morphogenesis in developing salivary gland secretory cells.Anat. Rec. 196, 341–7.
GOLDSTEIN, M. N. & BURDMAN, J. A. (1965) Studies of the nerve growth factor in submandibular glands of female mice treated with testosterone.Anat. Rec. 151, 199–208.
GRESIK, E. & BARKA, T. (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of epidermal growth factor in mouse submandibular glands.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 25, 1027–35.
GRESIK, E. W. & BARKA, T. (1983) Epidermal growth factor, renin, and protease A in hormonally responsive duct cells of the mouse sublingual gland.Anat. Rec. 205, 169–75.
GRESIK, E. W. & MACRAE, E. K. (1975) The postnatal development of the sexually dimorphic duct system and of amylase activity in the submandibular glands of mice.Cell Tissue Res. 157, 411–22.
GRESIK, E., MICHELAKIS, A., BARKA, T. & ROSS, T. (1978) Immunocytochemical localization of renin in the submandibular gland of the mouse.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 26, 855–61.
GRESIK, E. W, SCHENKEIN, I. & BARKA, T. (1981) Immunocytochemical investigations on the submandibular glands of developing and adult mice using a specific antiserum to protease. A.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 1411–17.
HAZEN-MARTIN, D. J. (1983) The effect of secretagogue stimulation on the granular tubule segment of the male mouse submandibular gland: an ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study.Anat. Rec. 205, 78–79A.
HAZEN-MARTIN, D. J. & SIMSON, J. A. V. (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of nerve growth factor: effects of fixation.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 32, 30–6.
HOFMANN, H.-D. & DRENCKHAHN, D. (1981) Distribution of nerve growth factor in the submandibular gland of the male and female mouse.Cell Tissue Res. 221, 77–83.
JACOBY, F. & LEESON, C. R. (1959) The post-natal development of the rat submaxillary gland.J. Anat. 93, 201–16.
JUNQUEIRA, C., FAJER, A., RABINOVITCH, M. & FRANK-ENTHAL, L. (1949) Biochemical and histochemical observations on the sexual dimorphism of mice submaxillary glands.J. Cell Comp. Physiol. 34, 129–58.
KOERKER, R. M. (1967) The effects of hypophysectomy on the digestive glands of the mouse.Am. J. Anat. 121, 571–600.
LACASSAGNE, A. (1940) Dimorphisme sexual de la glande sous maxillaire chez la souris.C. R. Soc. Biol., Paris 133, 180–81.
LANGUNOFF, D., BENDITT, E. P. & WATTS, R. M. (1962) Histochemical study of esterases homospecific with trypsin.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 672–3.
LAWSON, K. A. (1972) The role of mesenchyme in the morphogenesis and functional differentiation of rat salivary epithelium.J. Embryol. Exp. Morph. 27, 497–513.
LEVI-MONTALCINI, R. (1964) The nerve growth factor.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 118, 149–70.
MASON, T. E., PHIFER, R. F., SPICER, S. S., SWALLOW, R. A. & DRESKIN, R. B. (1969) An immunoglobulinenzyme bridge method for localizing tissue antigens.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 563–9.
OGER, J., ARNASON, B. G. W., PANTAZIS, N., LEHRICH, J. & YOUNG, M. (1974) Synthesis of nerve growth factor by L and 3T3 cells in culture.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 1554–8.
SCHWAB, M. E., STOCKEL, K. & THOENEN, H. (1976) Immunocytochemical localization of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the submandibular gland of adult mice by light and electron microscopy.Cell Tissue Res. 169, 289–99.
SIMSON, J. A. V., HAZEN, D., SPICER, S. S., MURPHY, R. A. & YOUNG, M. (1978) Secretagogue-mediated discharge of nerve growth factor from granular tubules of male mouse submandibular glands: An immunocytochemical study.Anat. Rec. 192, 375–88.
SIMSON, J. A. V., SPICER, S. S., CHAO, J., GRIMM, L. & MARGOLIUS, H. S. (1979) Kallikrein localization in rodent salivary glands and kidney with the immunoglobulin-enzyme bridge technique.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 1567–76.
SIMSON, J. A. V., FENTERS, R. & CHAO, J. (1983) Electron microscopic immunostaining of kallikrein in rat submandibular glands.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 301–6.
VREUGDENHIL, A. P., DELANGE, G. L., NIEUW AMERONGEN, A. V. & ROUKEMA, P. A. (1980) Morphological changes in the salivary glands upon stimulation by receptor-selective agonists. III. Sublingual glands of the mouse.J. Biol. Buccale 8, 87–98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hazen-Martin, D.J., Landreth, G. & Simson, J.A.V. Immunocytochemical localization of nerve growth factor in mouse salivary glands. Histochem J 19, 210–216 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01680631
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01680631